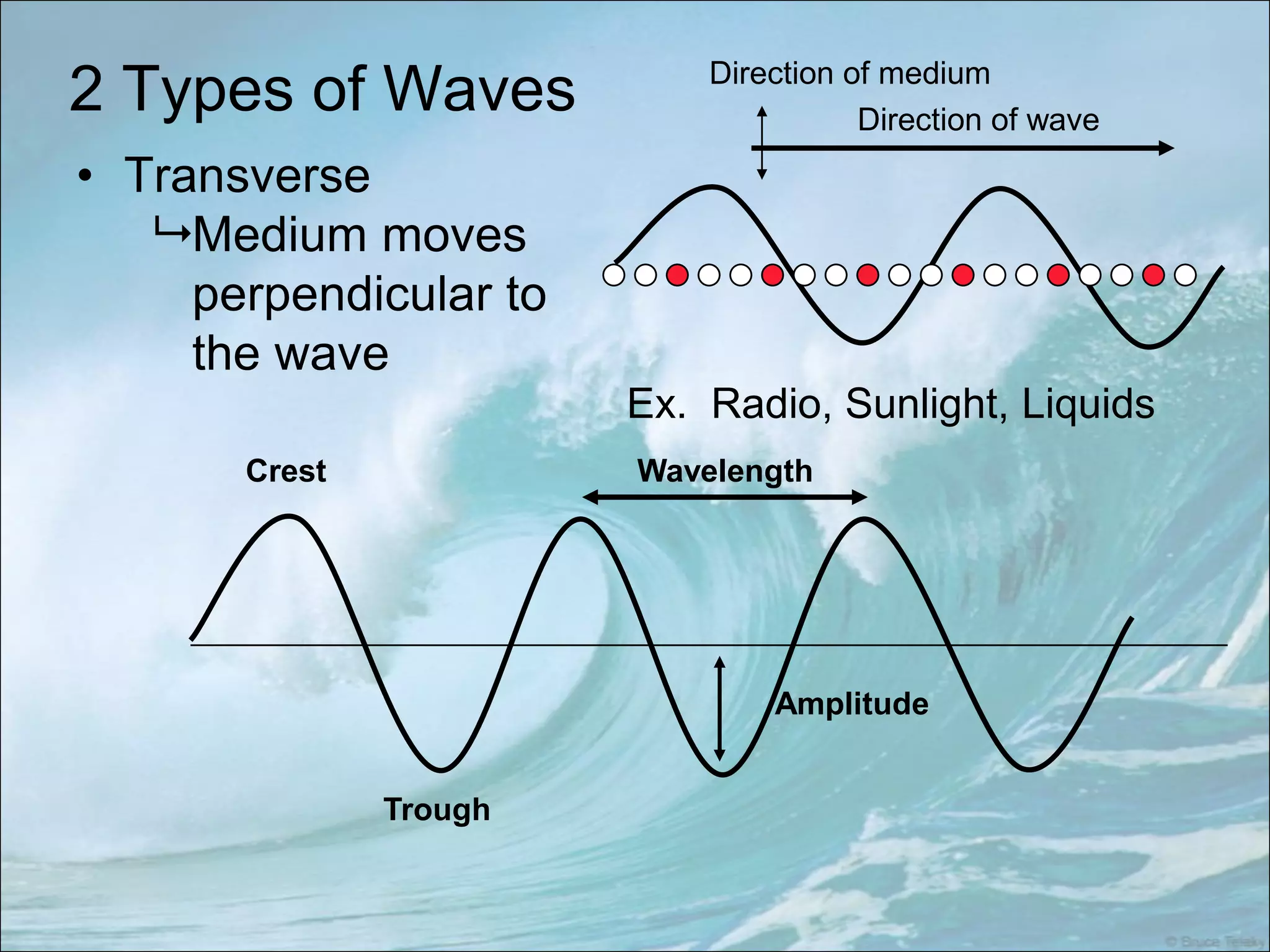
This document summarizes key concepts about wave properties. It defines waves as a movement of energy through space and time that requires a medium to travel through. It describes the characteristics of frequency, period, speed, wavelength, and how they are related. It differentiates between transverse and longitudinal waves, and provides examples of each. It also explains several phenomena waves can undergo, including interference, reflection, refraction, diffraction, polarization, and standing waves.