Embed presentation
Downloaded 54 times


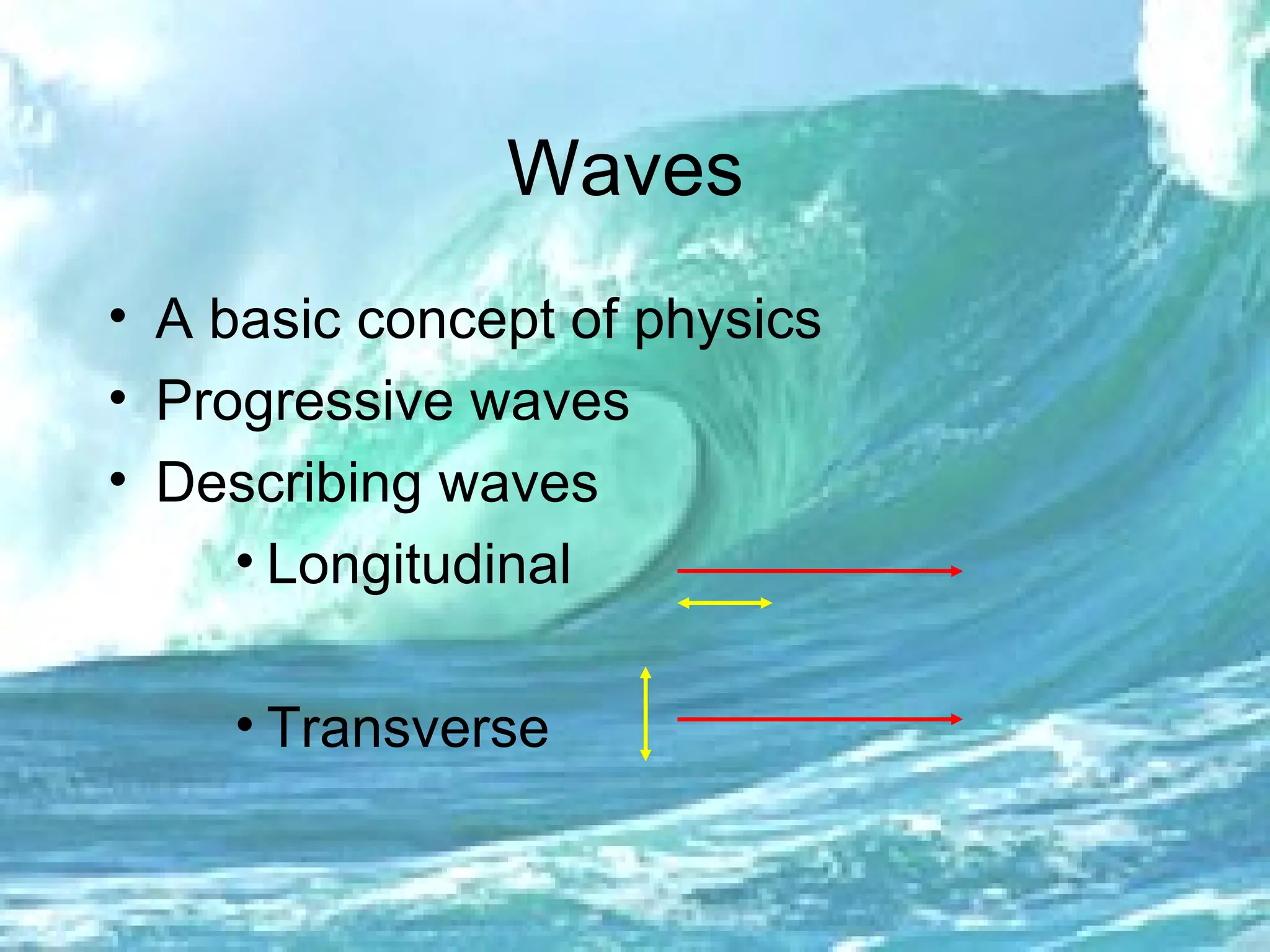
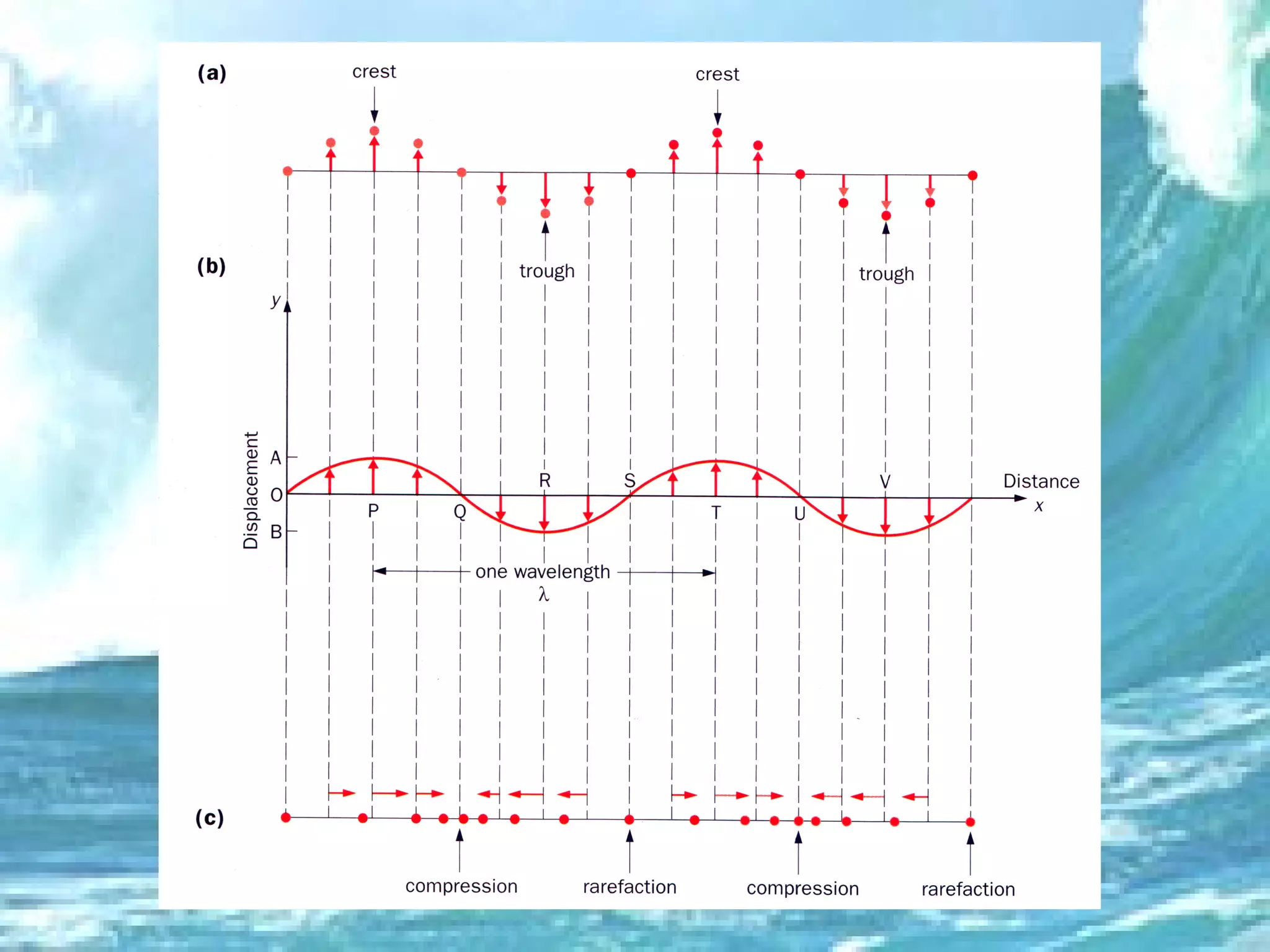

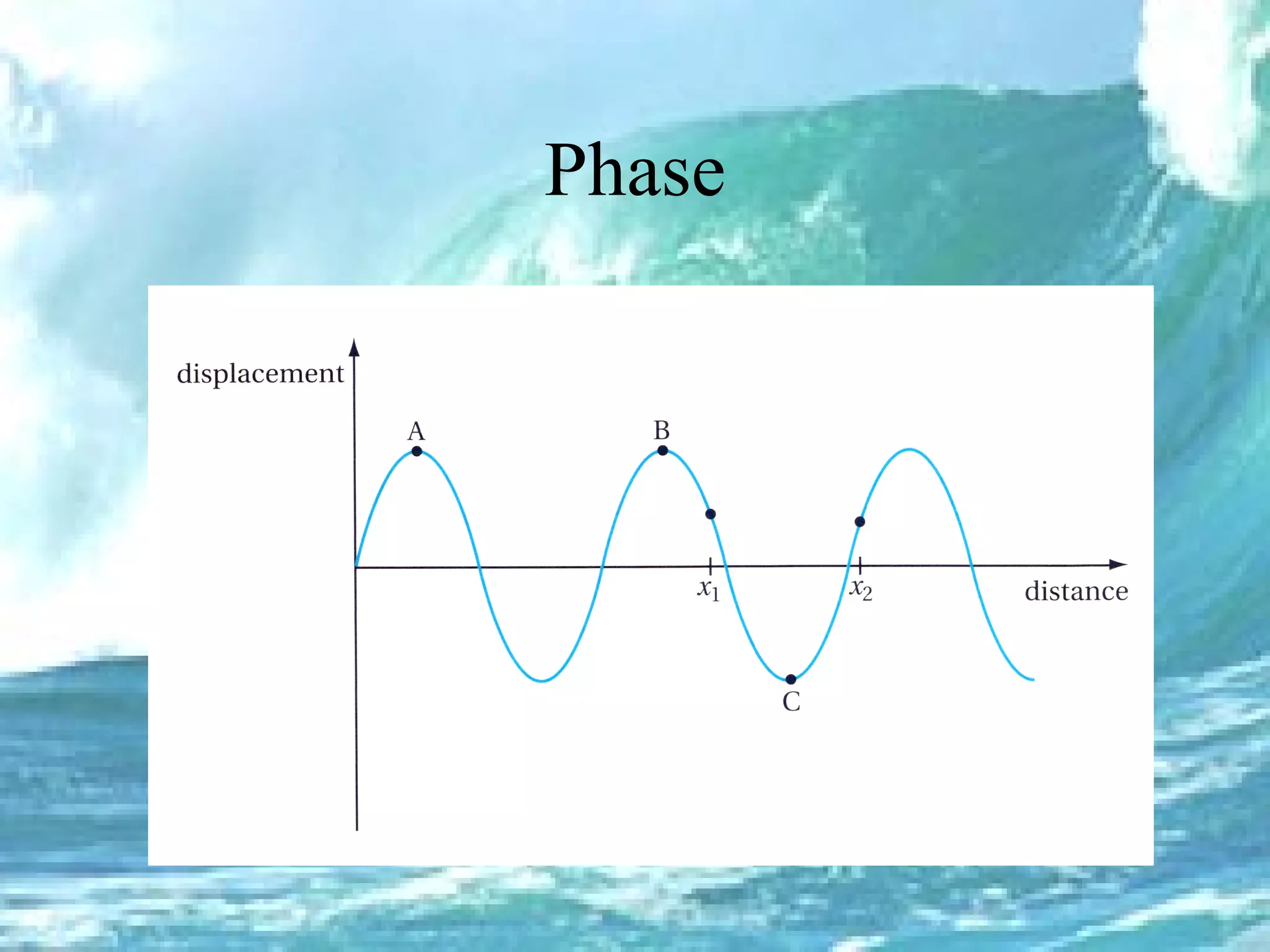

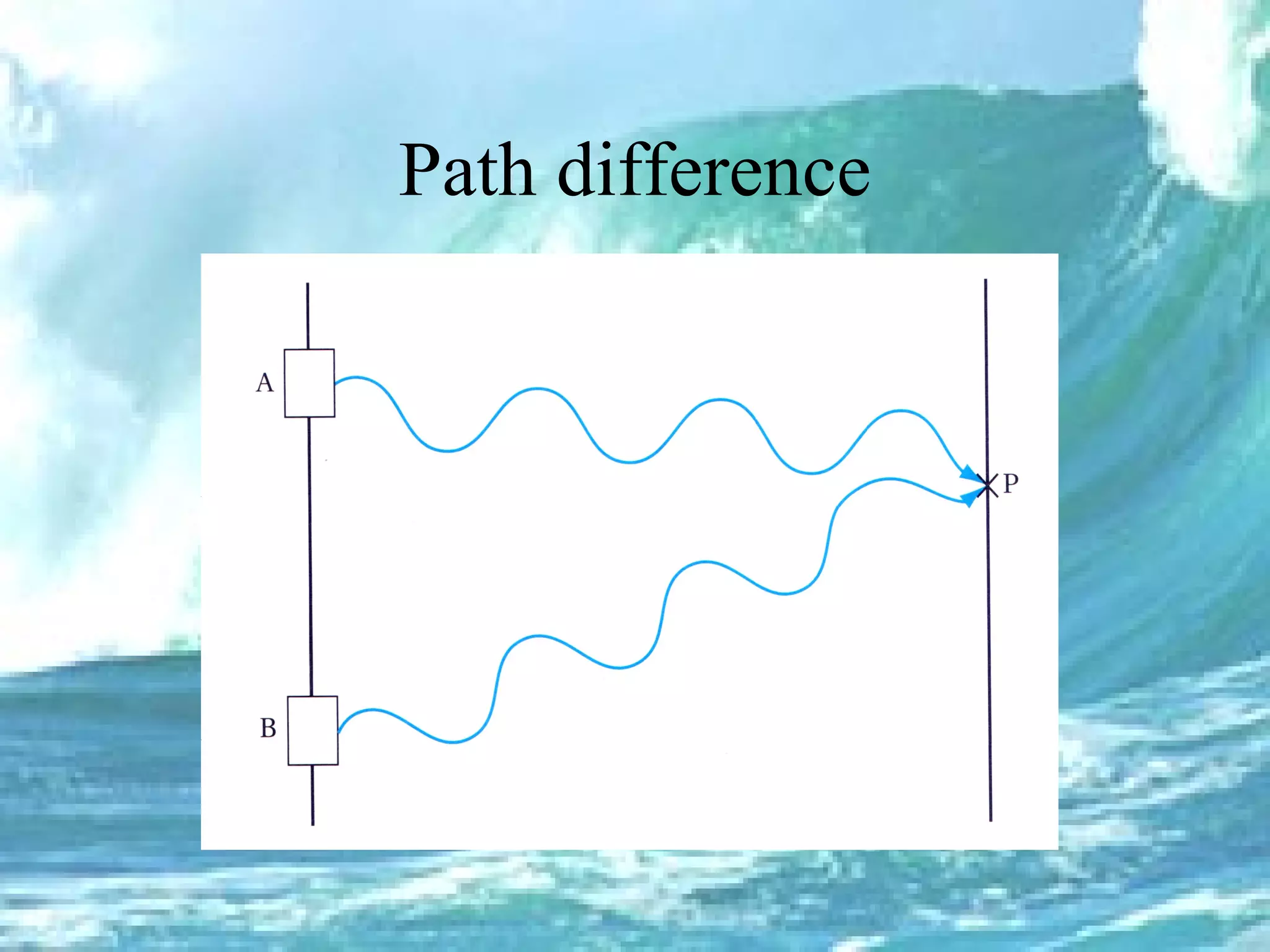


1. The document discusses progressive waves, which are waves that transfer energy and information through a medium from one point to another. 2. It defines key wave properties such as amplitude, wavelength, frequency, phase, and path difference which are used to describe and analyze wave behavior. 3. Graphs and equations are presented that show the relationships between wavelength, frequency, wave speed, phase difference, and path difference which determine whether waves will constructively or destructively interfere when they meet.









