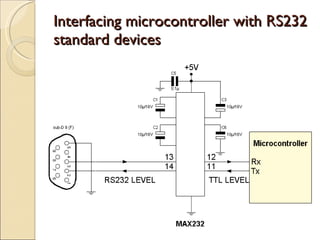
The document discusses interfacing RS232 with microcontrollers. RS232 uses asynchronous communication and the UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) to interface with microcontrollers like the ATmel 89C51. The MAX232 IC is used as a driver to interface RS232 with other devices. Baud rates for communication are set using special function registers in the microcontroller that control the serial port. The baud rate can be doubled by setting the SMOD bit in the PCON register. Data is transmitted by storing it in the serial buffer and cleared the transmit interrupt flag, and received by reading the serial buffer when the receive interrupt flag is set. Functions make it easier to send and receive multiple characters of data through the