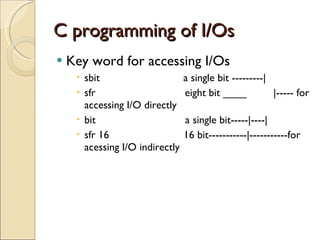
The document discusses digital I/O programming on microcontrollers, including how to access different ports, avoid issues with ports 0 and 3, and use keywords like sbit, sfr, and bit to directly access I/O ports and registers to set inputs and outputs as well as create software delays for applications like displaying a Fibonacci series using LEDs.