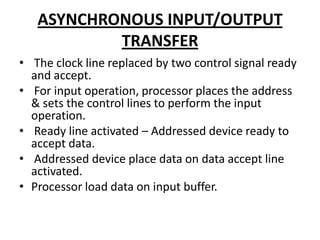
There are two types of data transfer schemes: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous uses a common clock signal where the processor addresses a device at t0, the device places data on the bus at t1, and the processor reads the data at t2. Asynchronous replaces the clock with ready and accept control signals, where the ready signal indicates the device is ready to accept data and the accept signal confirms the data was received.