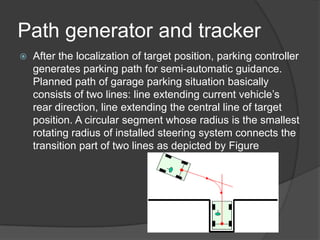
The document discusses an intelligent parking assist system (IPAS) that uses cameras, sensors, and computer processors to help drivers steer into parking spaces with little input. It describes how early versions had difficulty detecting objects but were improved over time. The IPAS helps with parallel parking and reverse parking by visualizing the parking path and maneuver on a dashboard display screen for the driver to follow.