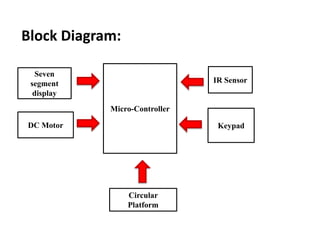
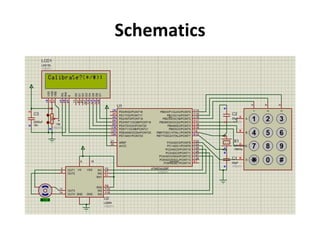
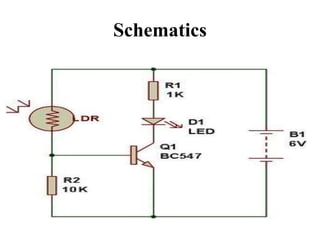
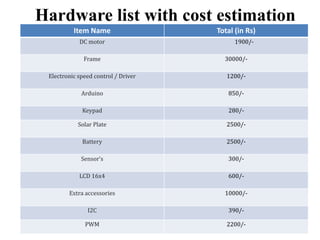
The document discusses the design and functionality of an automated solar vertical car parking system using an 8051 microcontroller to enhance parking efficiency and reduce environmental impact. It addresses common issues in robotic parking systems, particularly those arising from poor planning, and outlines the system's operational mechanics, safety precautions, and cost estimations for hardware and software. Ultimately, the project aims to improve parking convenience and safety in urban environments.