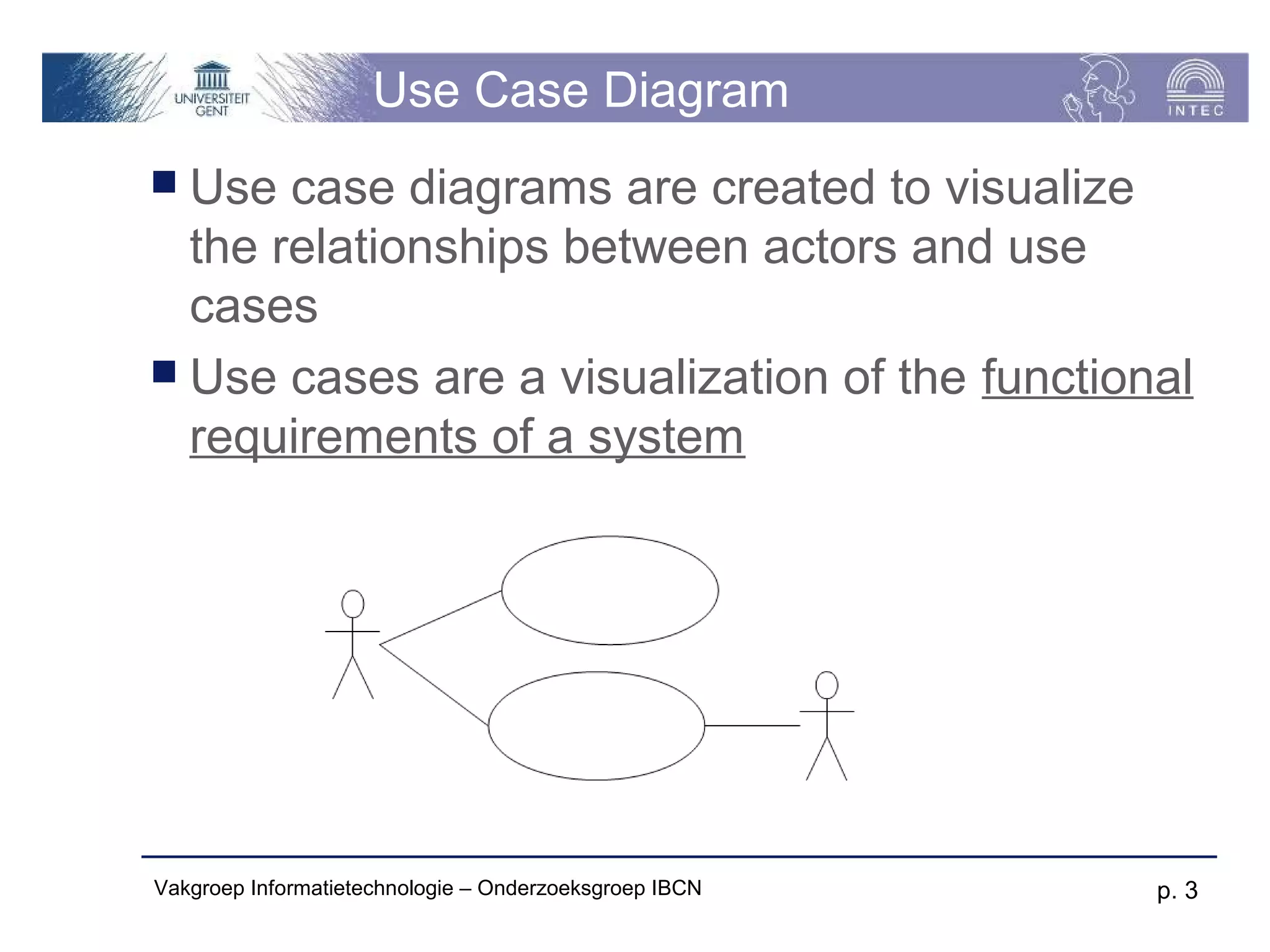
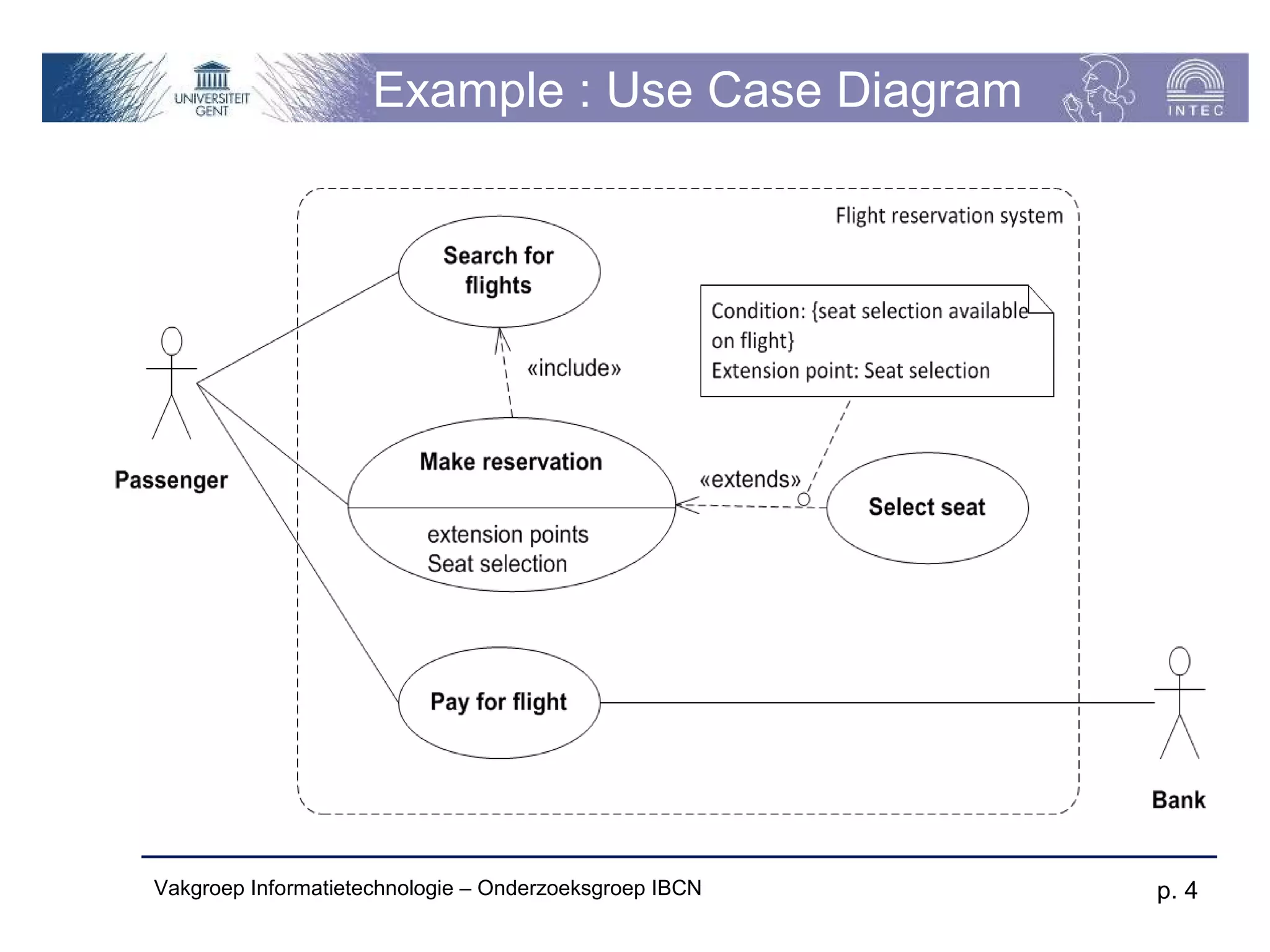
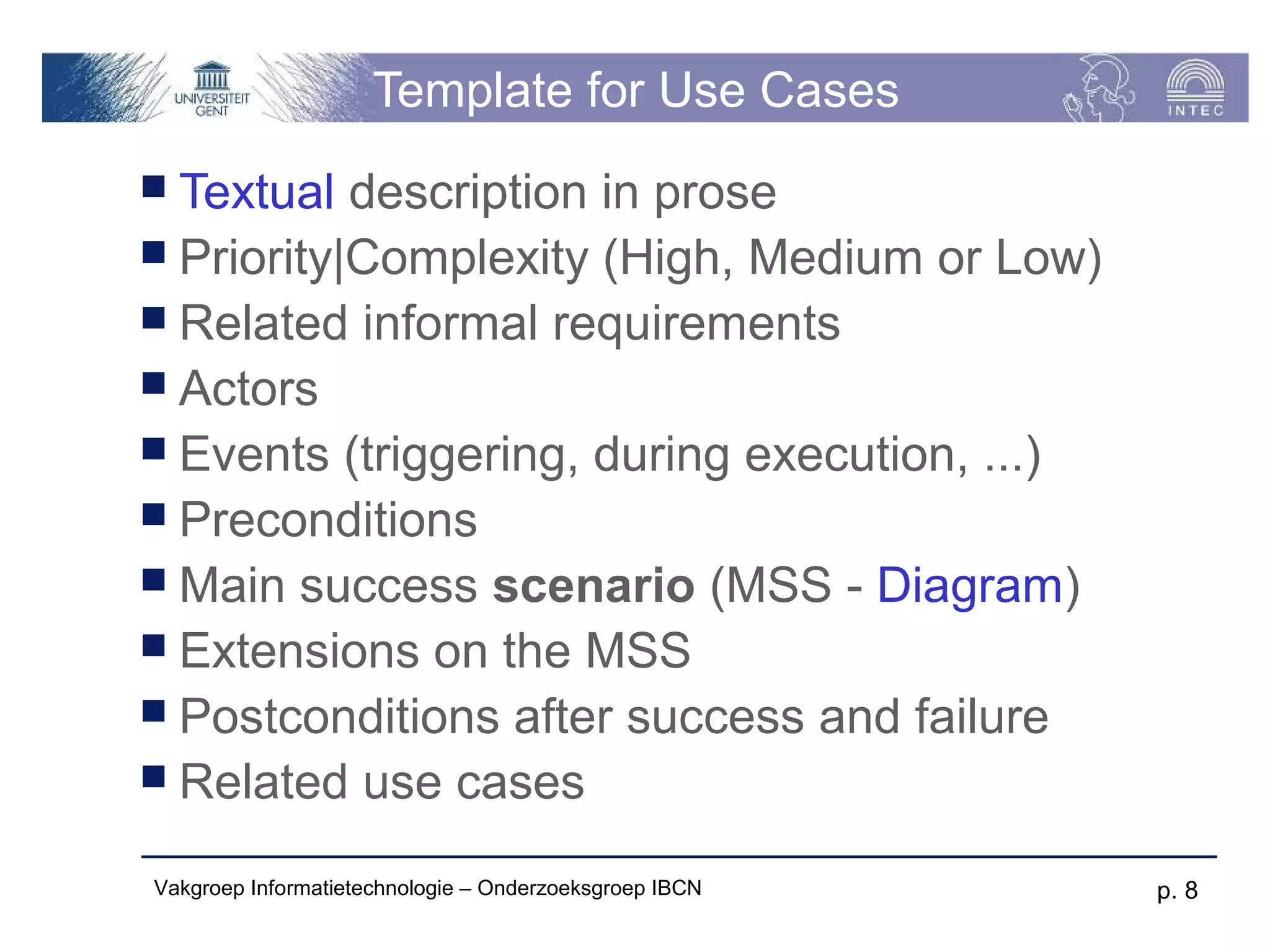
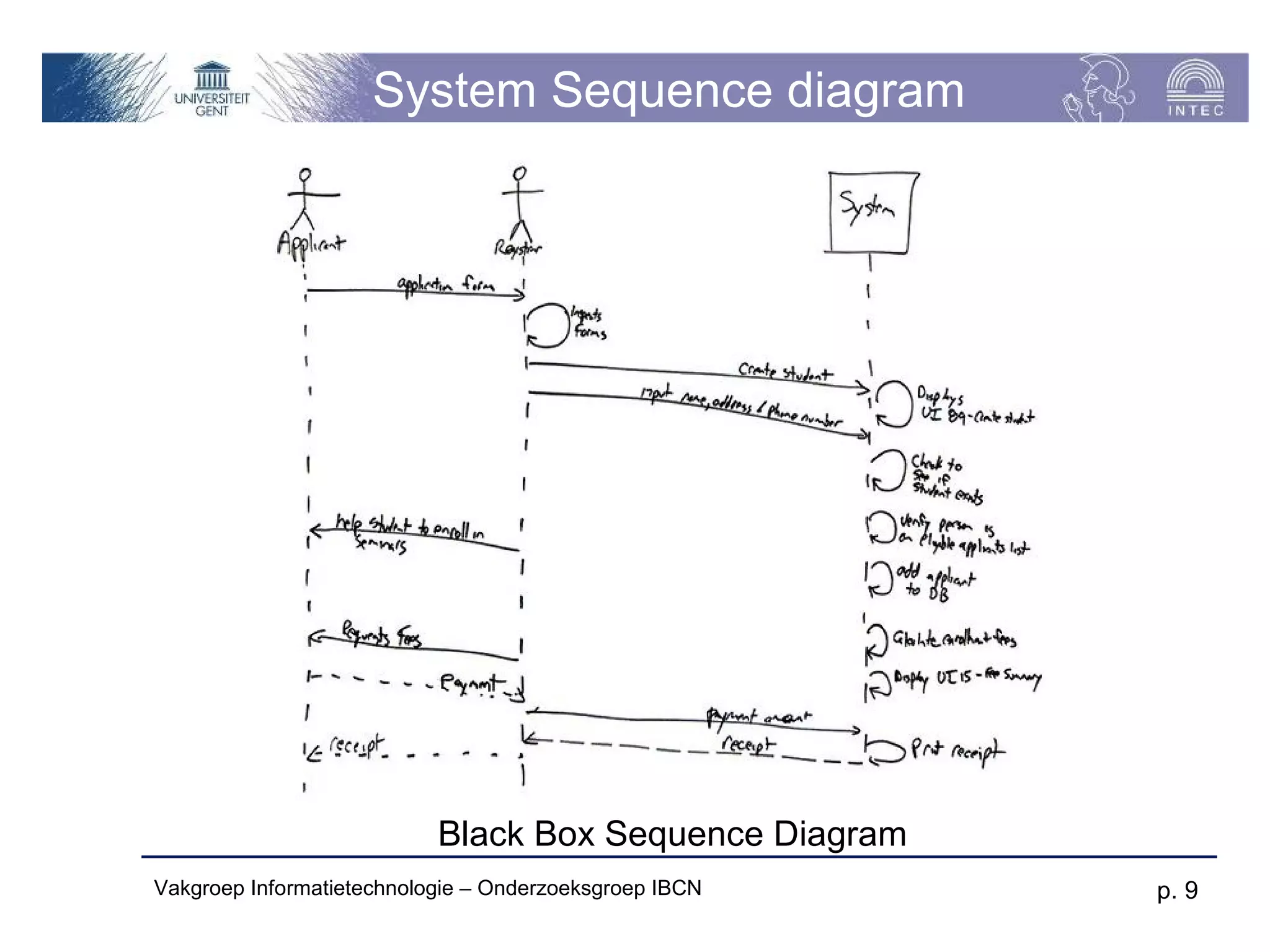
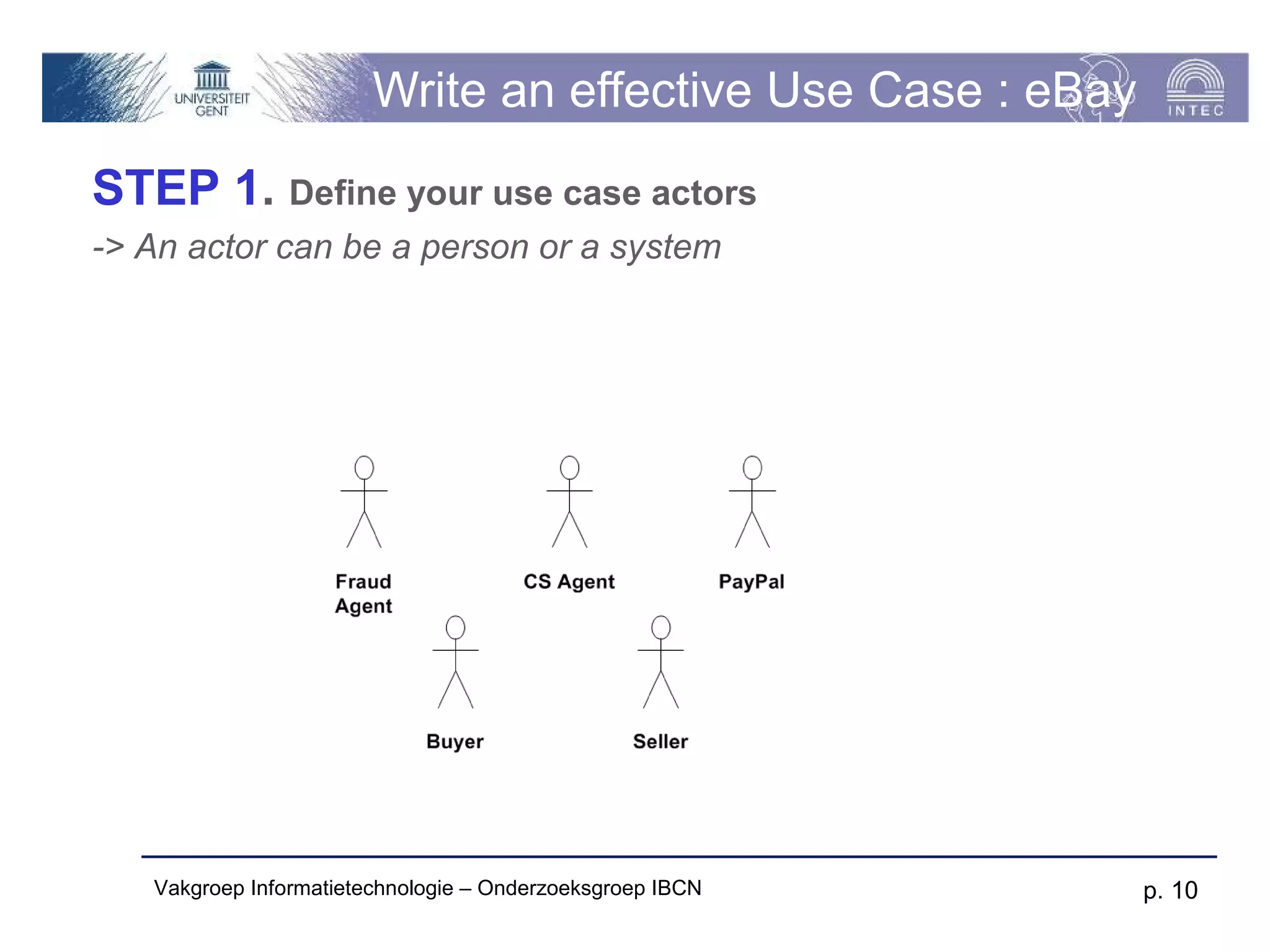
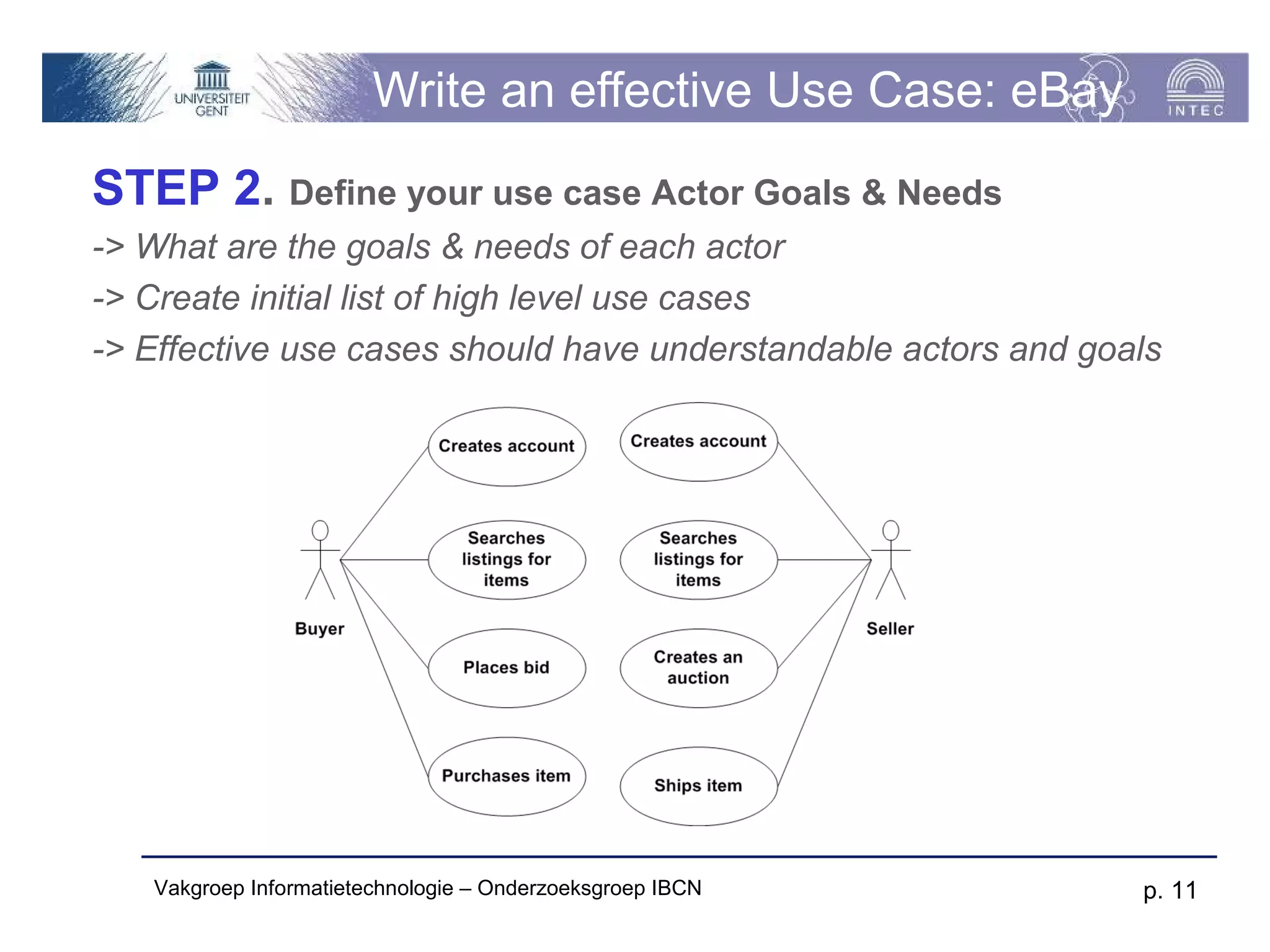
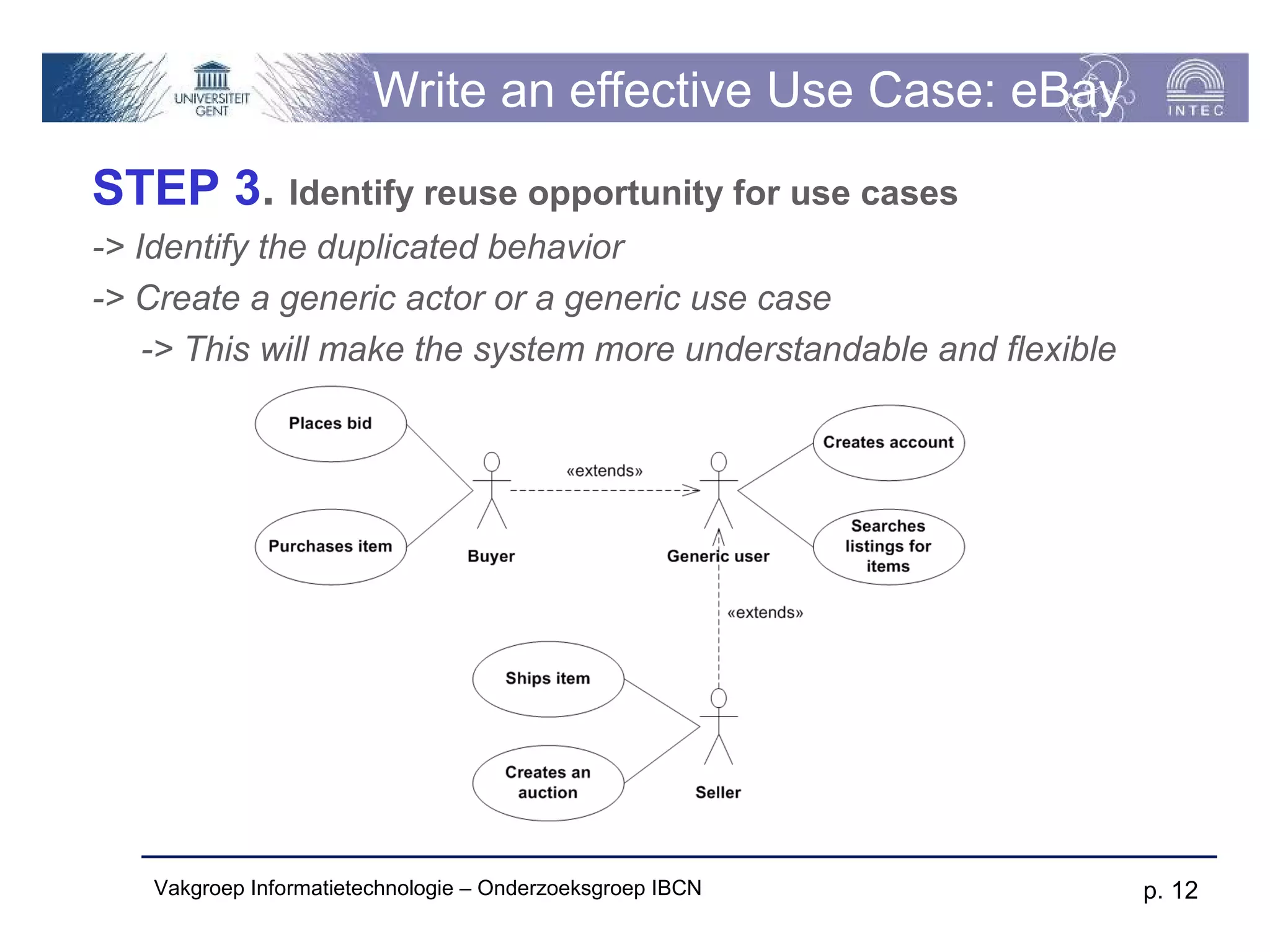
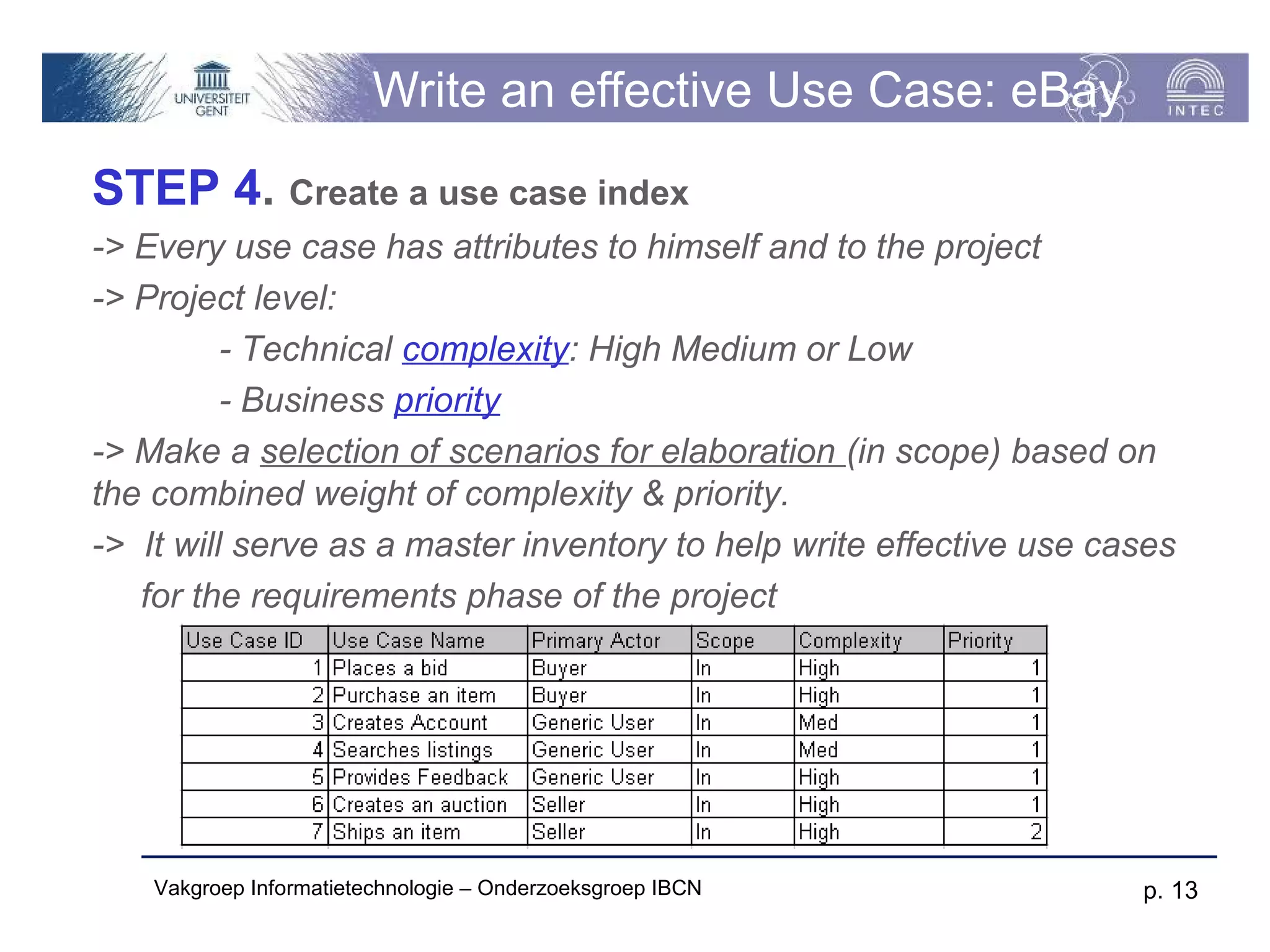
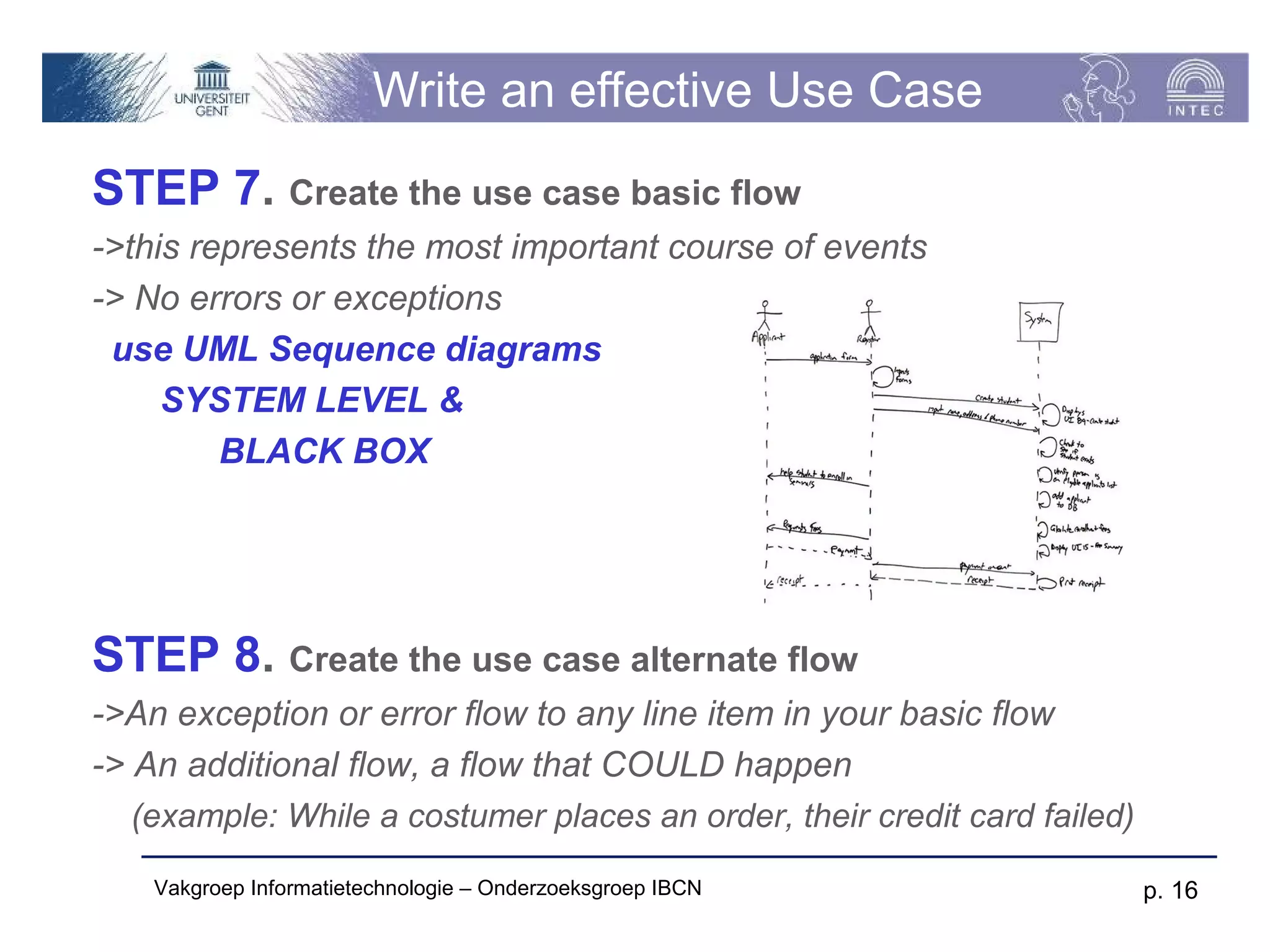
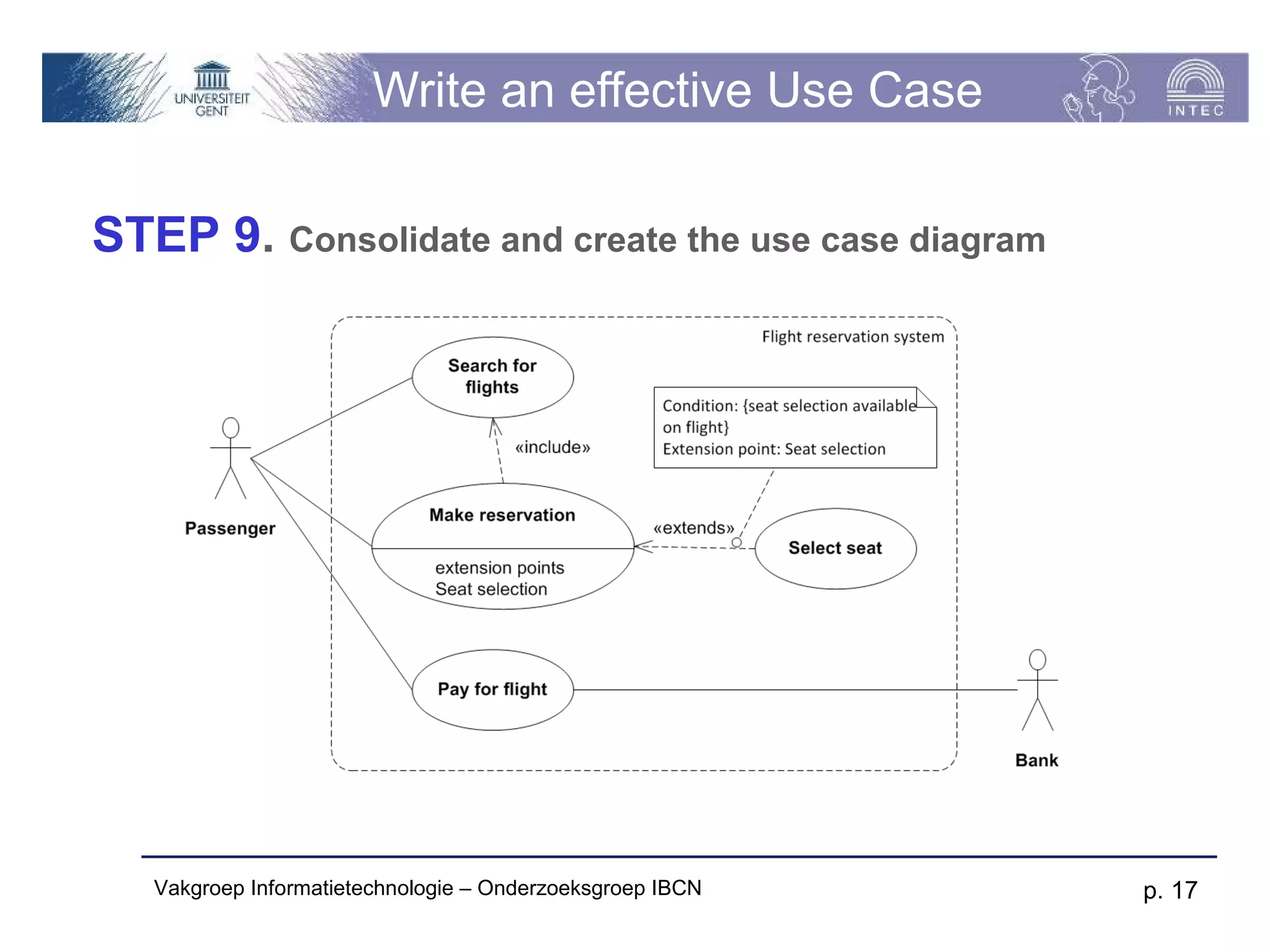
The document discusses use cases and scenarios in software engineering. It defines use cases as narratives that describe how users will interact with a system. Use case diagrams visualize relationships between actors and use cases. The document provides examples of use case diagrams and describes how to document use cases, including typical elements like actors, flows, and alternate flows. It provides guidance on writing effective use cases, such as defining goals and needs for each actor.