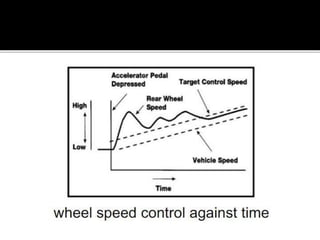
Traction control systems help vehicles maintain motion on slippery surfaces by regulating wheel spin. They can manage traction through torque reduction methods like adjusting fuel/ignition or using the brakes. Traction control is beneficial for accelerating in low-grip conditions as it prevents wheel slip and allows for better use of available traction compared to without traction control. It improves vehicle control and handling on low traction surfaces.