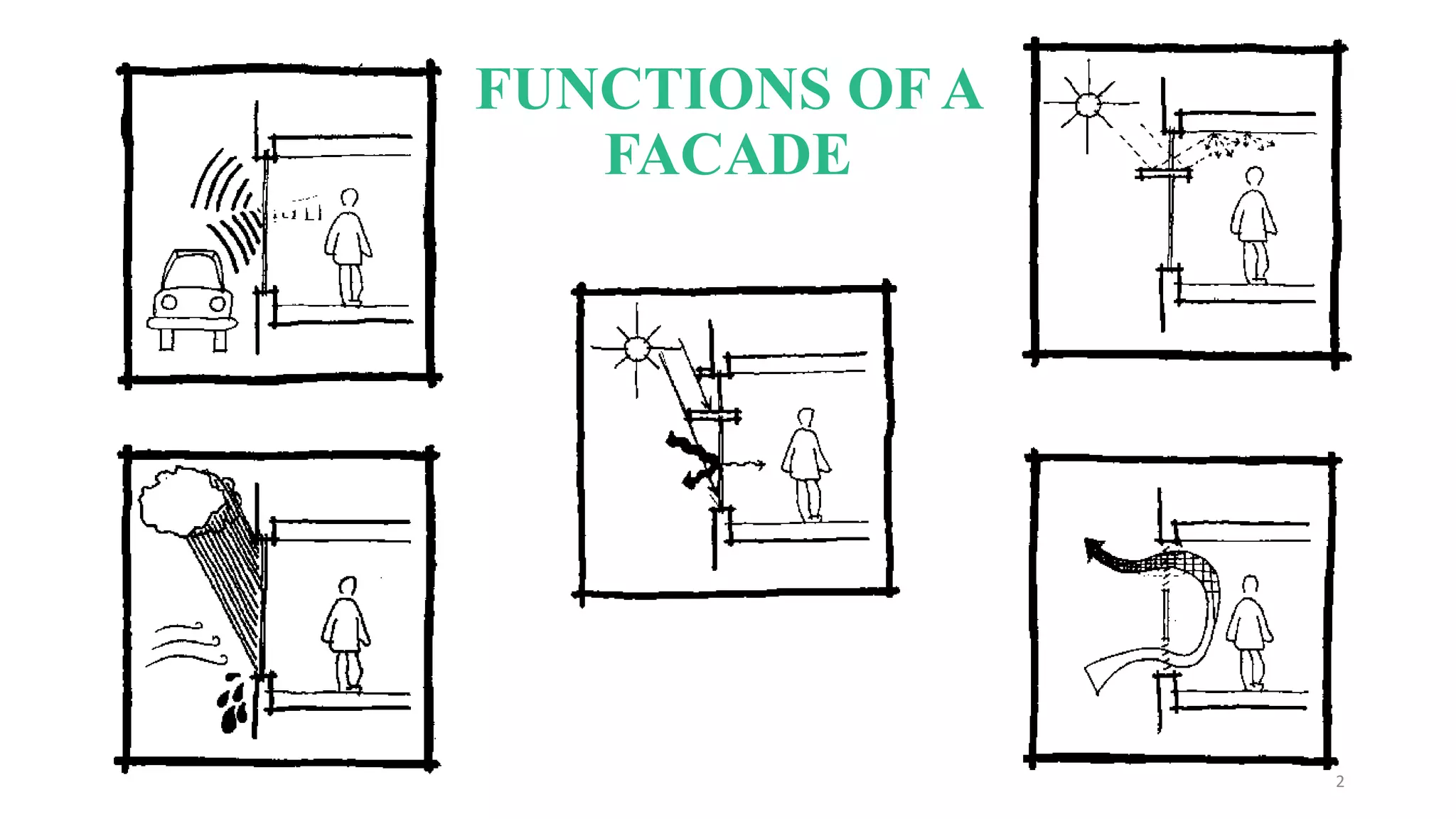
Intelligent buildings feature adaptive façades that respond to changing climatic conditions, enhancing occupant comfort and reducing energy consumption. With projections of significant growth in India's building sector, energy efficiency is increasingly crucial, prompting the need for better adoption of national energy conservation codes. These intelligent designs aim to integrate dynamic capabilities that adjust to environmental stimuli and occupant behavior for optimal performance.