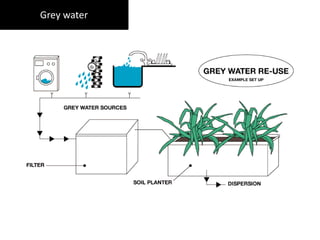
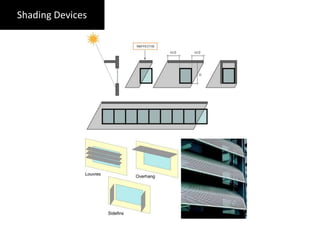
The document discusses the relationship between people and the natural environment, highlighting different perspectives on how humans interact with nature. It defines sustainable architecture as an approach aimed at minimizing environmental impact through efficient design and materials, and outlines its benefits in terms of environmental protection, economic savings, and community health. The text also mentions renewable energy technologies that complement sustainable architectural practices.