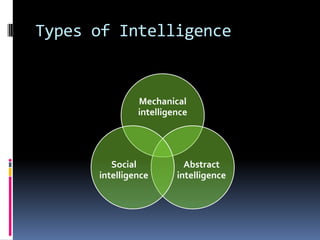
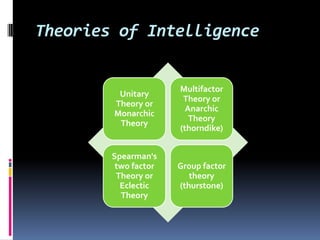
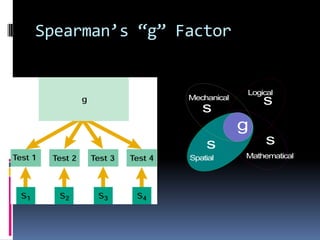
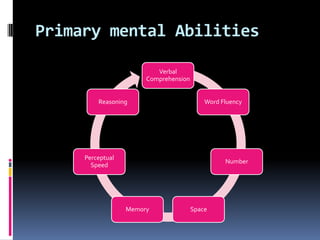
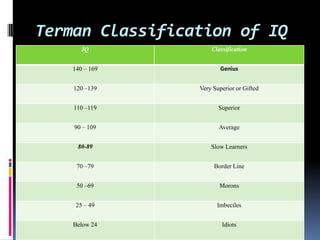
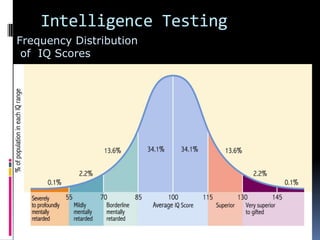
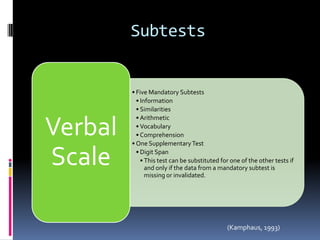
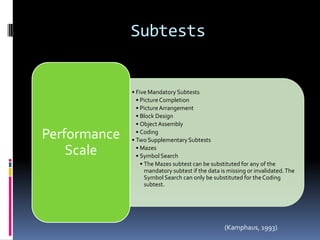
Intelligence is defined as the ability to think rationally, act purposefully, and effectively deal with the environment. There are different types and theories of intelligence. Intelligence tests aim to measure intelligence through individual or group tests that assess verbal, non-verbal, or performance abilities. Famous intelligence tests include the Stanford-Binet, Wechsler scales, and Raven's matrices. The Wechsler scales separately measure verbal and performance IQ through subtests, and the Stanford-Binet was influential in establishing the intelligence quotient score.