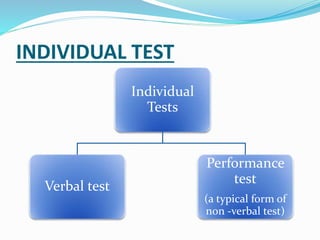
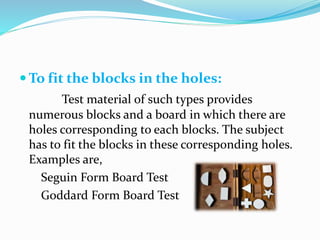
This document discusses modern intelligence tests, which are categorized into individual and group tests, highlighting key examples such as the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Test and the Wechsler Bellevue Intelligence Scale. It details the characteristics and structures of these tests, including various verbal and non-verbal components used to assess cognitive abilities across different age groups. Additionally, the document outlines the methods of calculating IQ and the significance of both crystallized and fluid abilities in intelligence measurement.