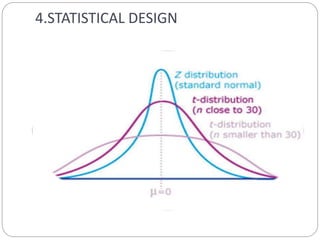
This document provides information about A.THANGAMANI RAMALINGAM, including his contact details and areas of expertise. It then outlines the structure and key aspects of methodology in research, including research design, sample design, observational design, and statistical design. Finally, it discusses common signs of dubious data and misuses of statistics.