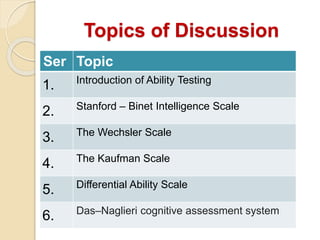
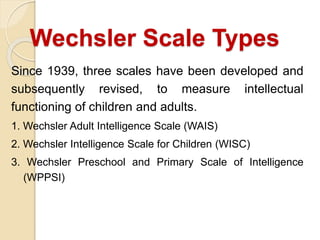
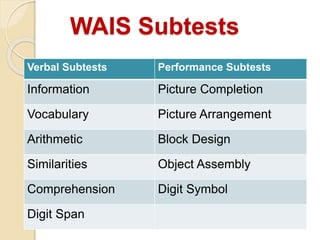
Ability tests are standardized methods used to assess individuals' performance on work-related tasks. The document discusses various types of ability tests including psychomotor tests, multiple ability tests, and cognitive ability tests. It provides details on specific tests like the Stanford-Binet, Wechsler scales, Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test, and Differential Ability Scales. These tests measure abilities such as intelligence, reasoning, memory, processing speed, and visual skills. Ability tests are used to assess individuals' potential and strengths/weaknesses for educational or employment purposes.