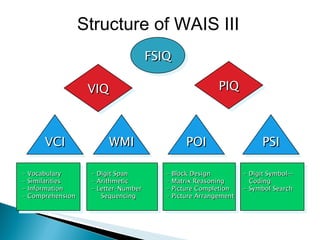
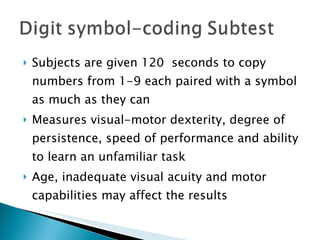
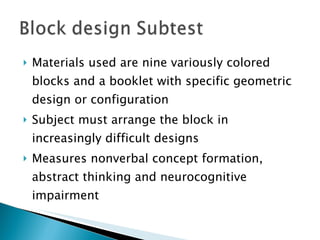
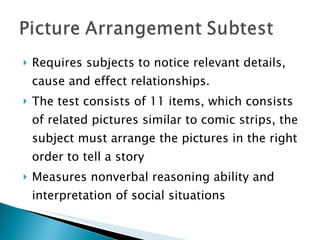
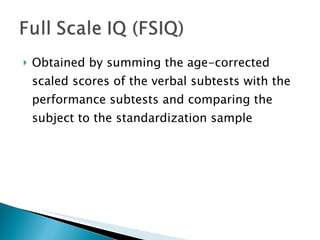
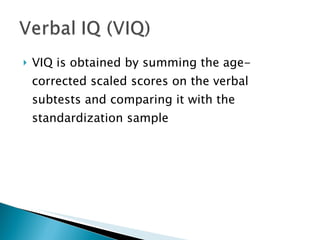
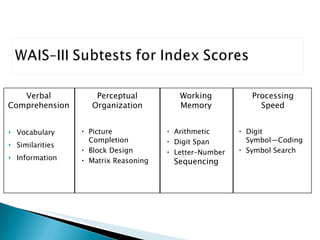
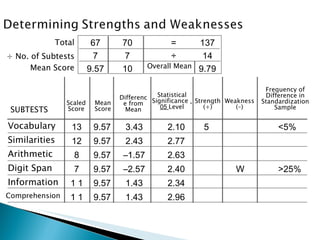
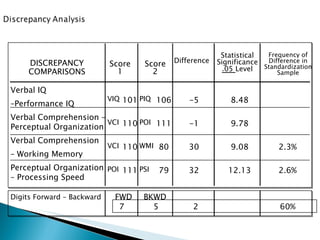
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale Third Edition (WAIS-III) is an individually administered intelligence test for adults and older adolescents. It was created by David Wechsler to address some limitations of Alfred Binet's original intelligence test, including that Binet's test was focused more on language and verbal skills, used mental age norms that did not apply to adults, and its emphasis on speed handicapped older adults. The WAIS-III addresses these issues through improved content, stimulus materials, and de-emphasis on speed. It provides Verbal, Performance, and Full Scale IQ scores as well as index scores in Verbal Comprehension, Perceptual Organization, Working Memory, and Processing Speed. The WAIS-III