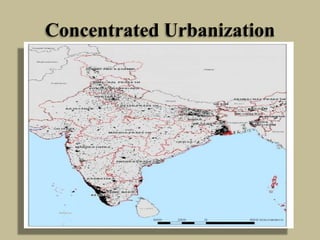
This document discusses integrated rural and urban development in India. It covers the policy background of prioritizing rural development, principal rural-urban interactions like villagers using urban facilities and working in nearby cities/towns. It also discusses factors driving increased interactions like transportation improvements and technology advances. Recommendations include expanding infrastructure, telecommunications, and education/skills programs to better integrate development across rural and urban areas.