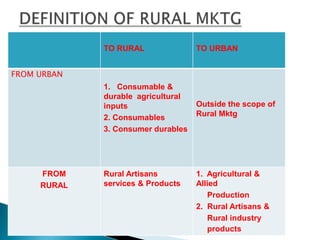
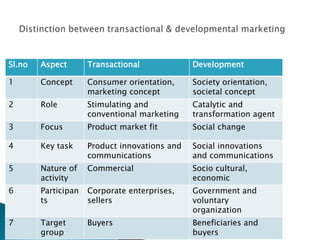
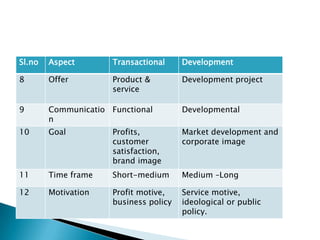
This document provides an overview of rural marketing in India. It discusses how rural markets have evolved over time from primarily marketing agricultural produce to now including household consumables and durables. Rural markets present both opportunities and challenges for marketers. Some key points made in the document include:
- Rural markets now outpace urban markets in growth and present a significant business potential.
- However, rural markets also have problems like vastness, low incomes, and inadequate infrastructure that make them difficult to operate in.
- Marketers have found innovative solutions like using local sales agents and partnering with retailers to better reach rural customers.