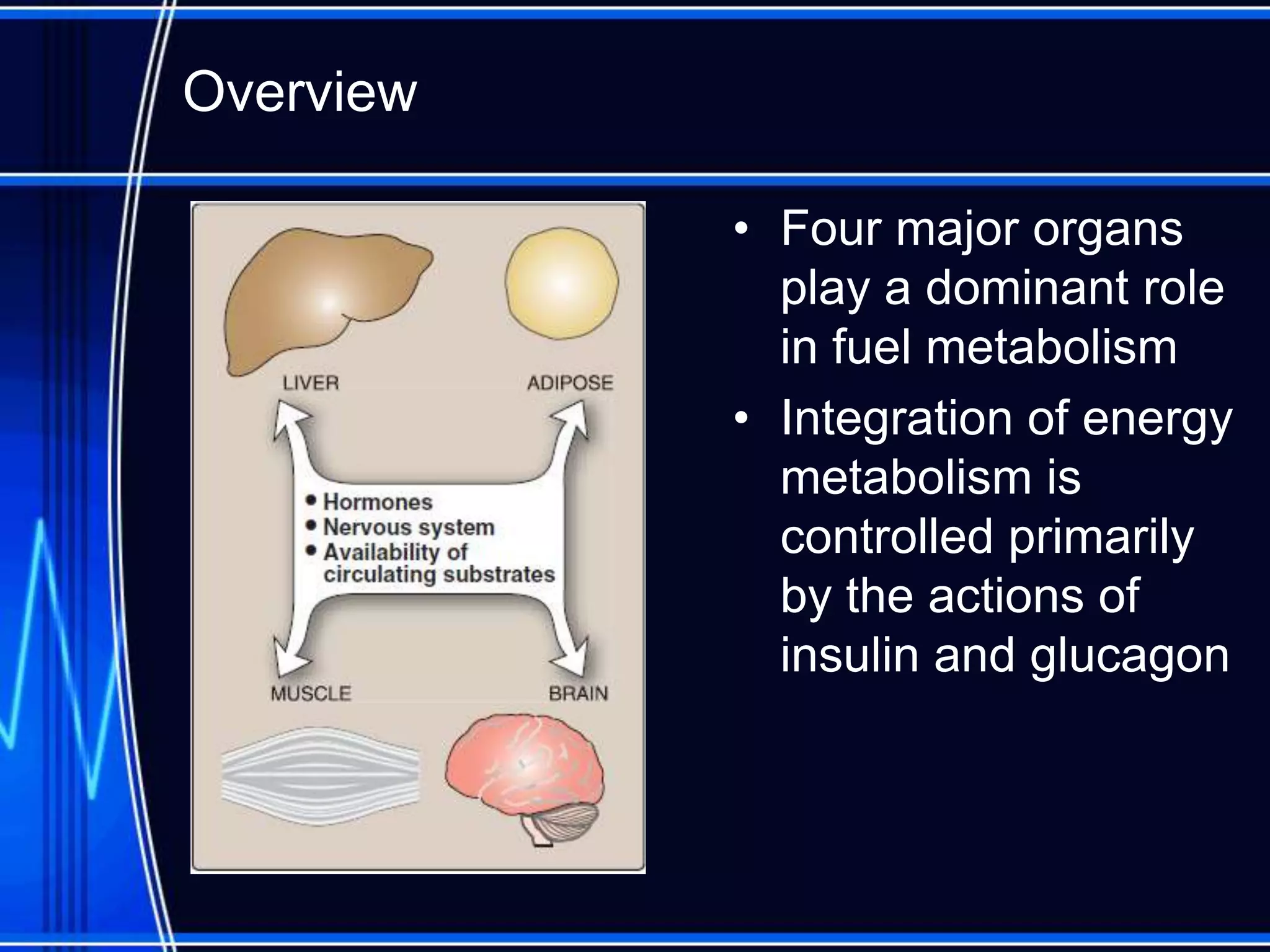
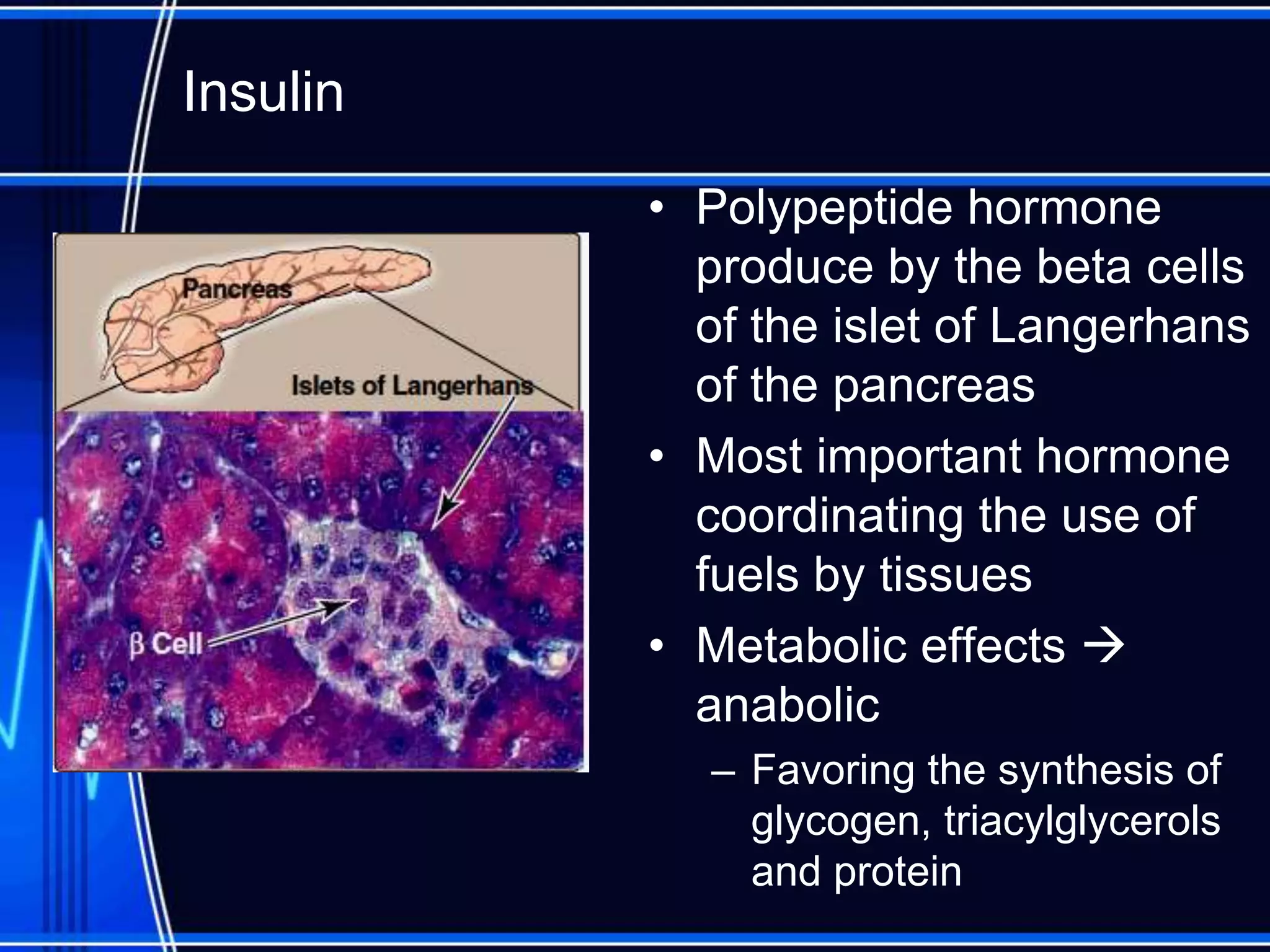
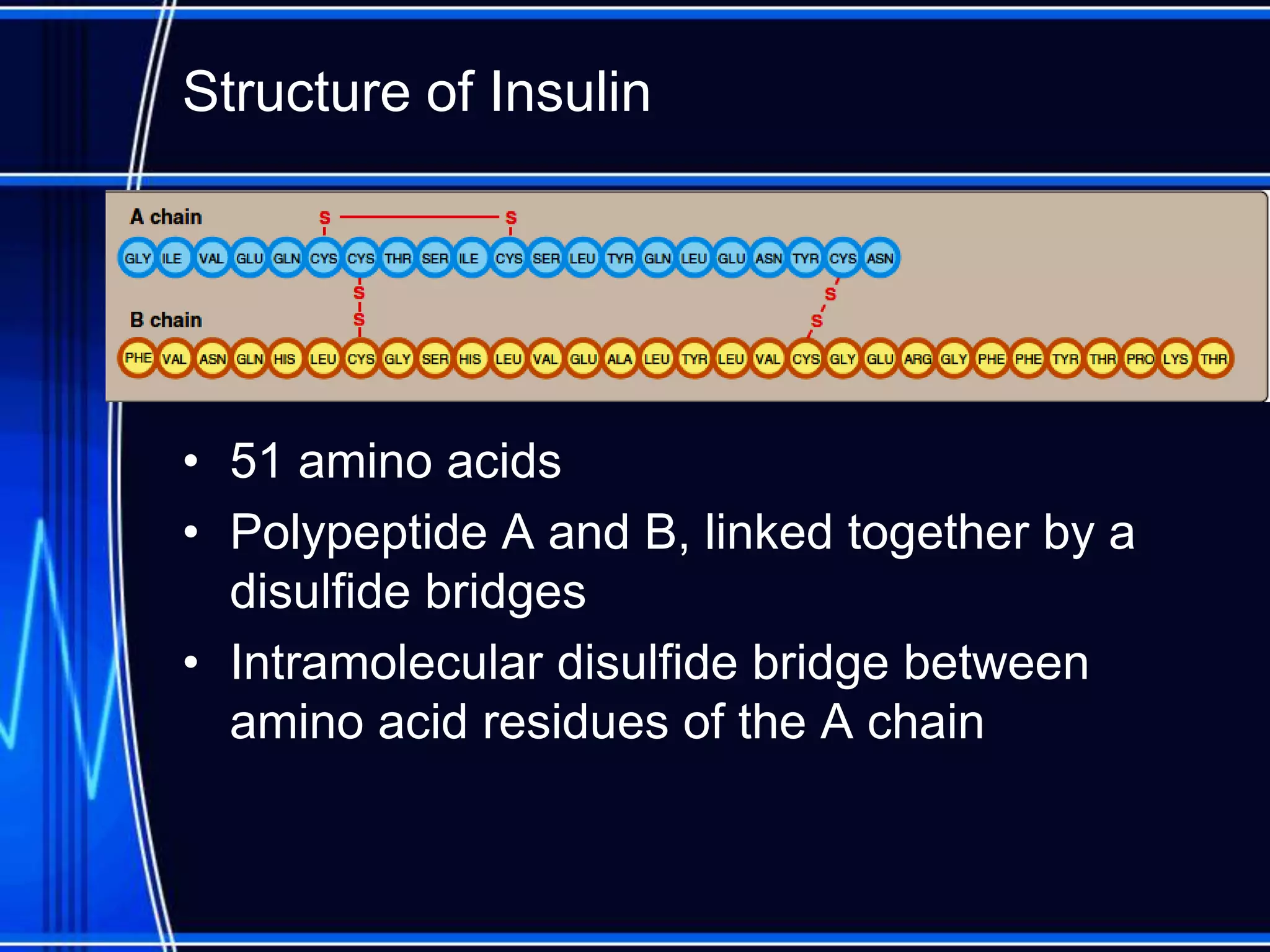
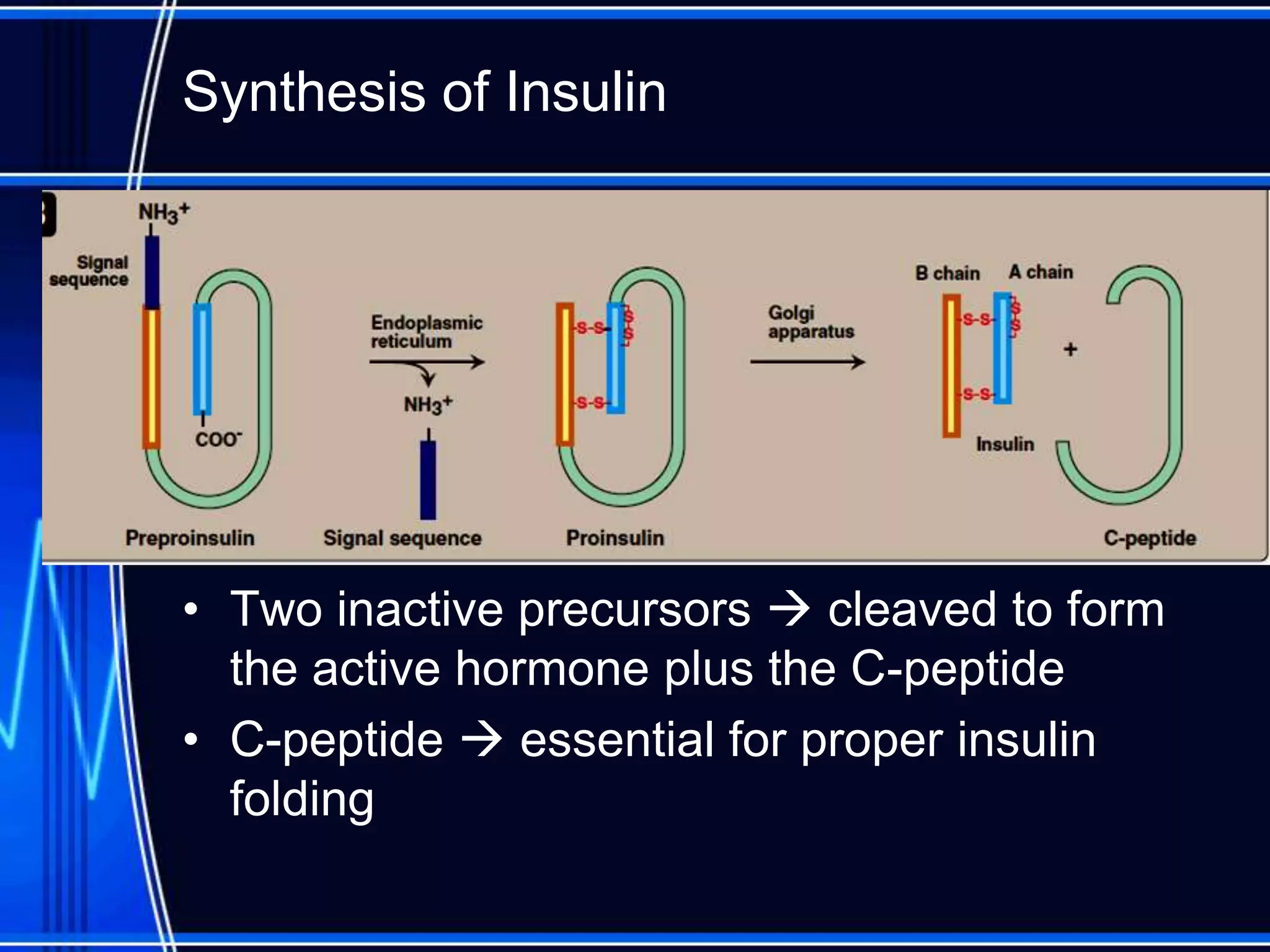
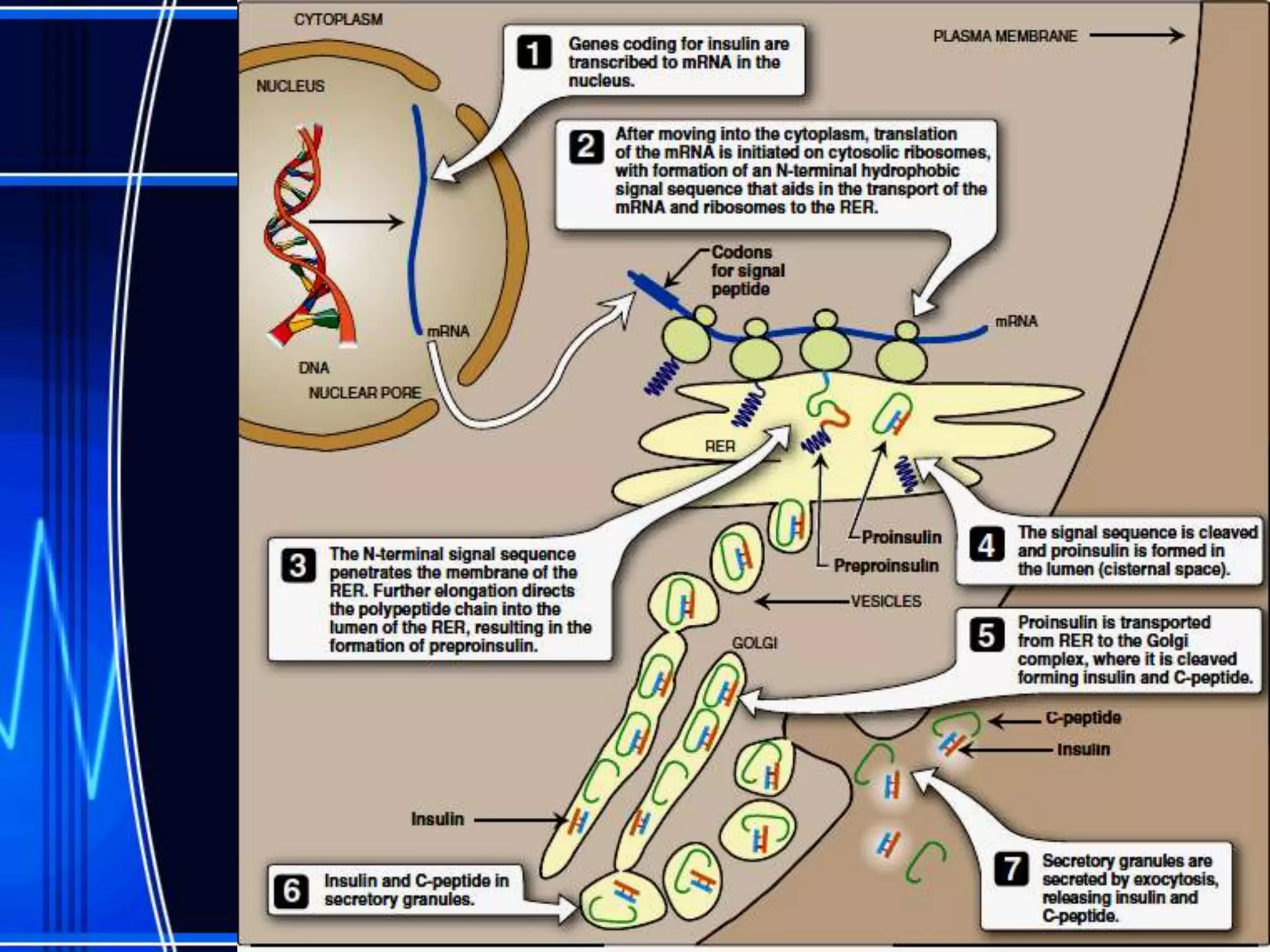
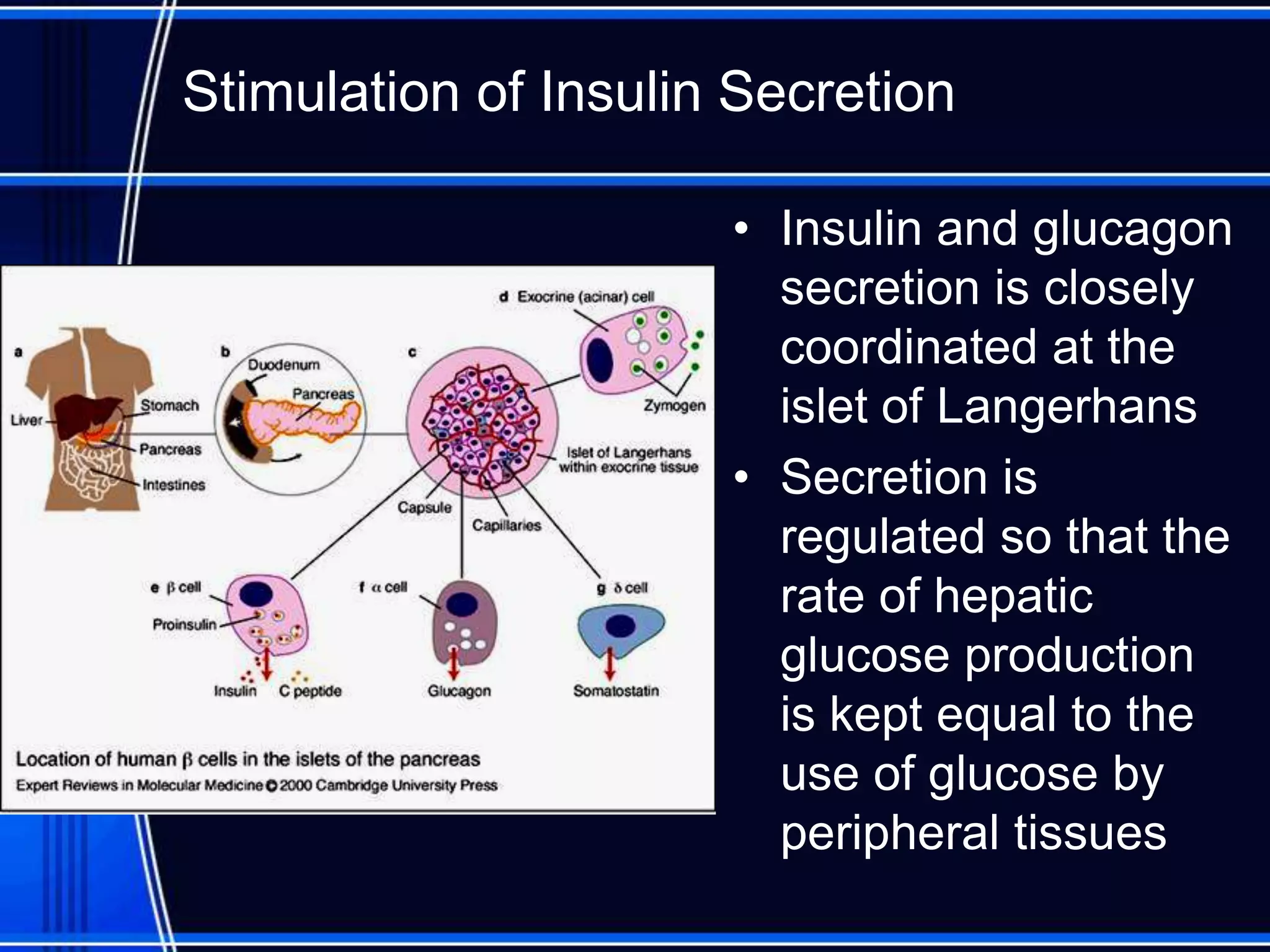
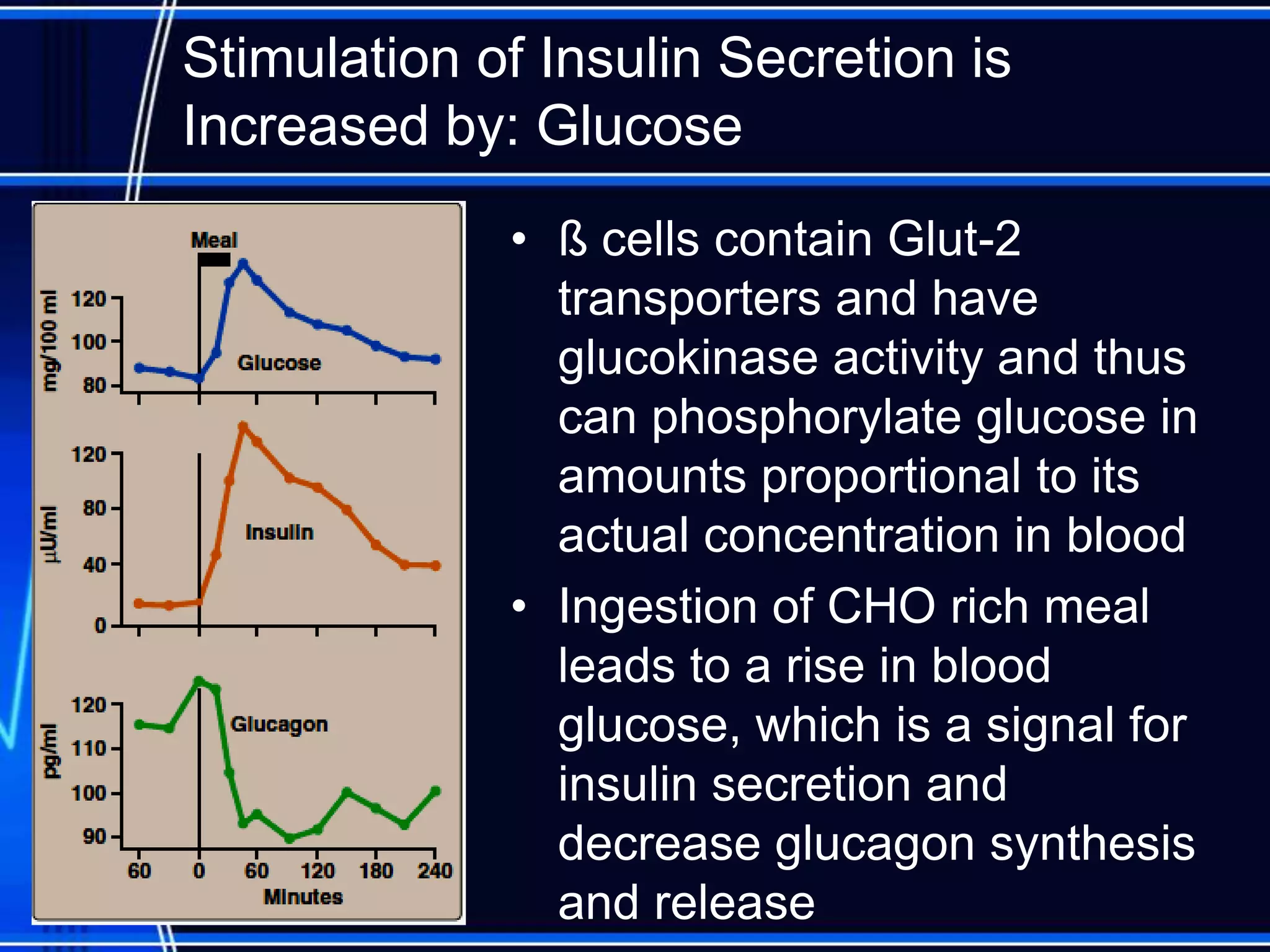
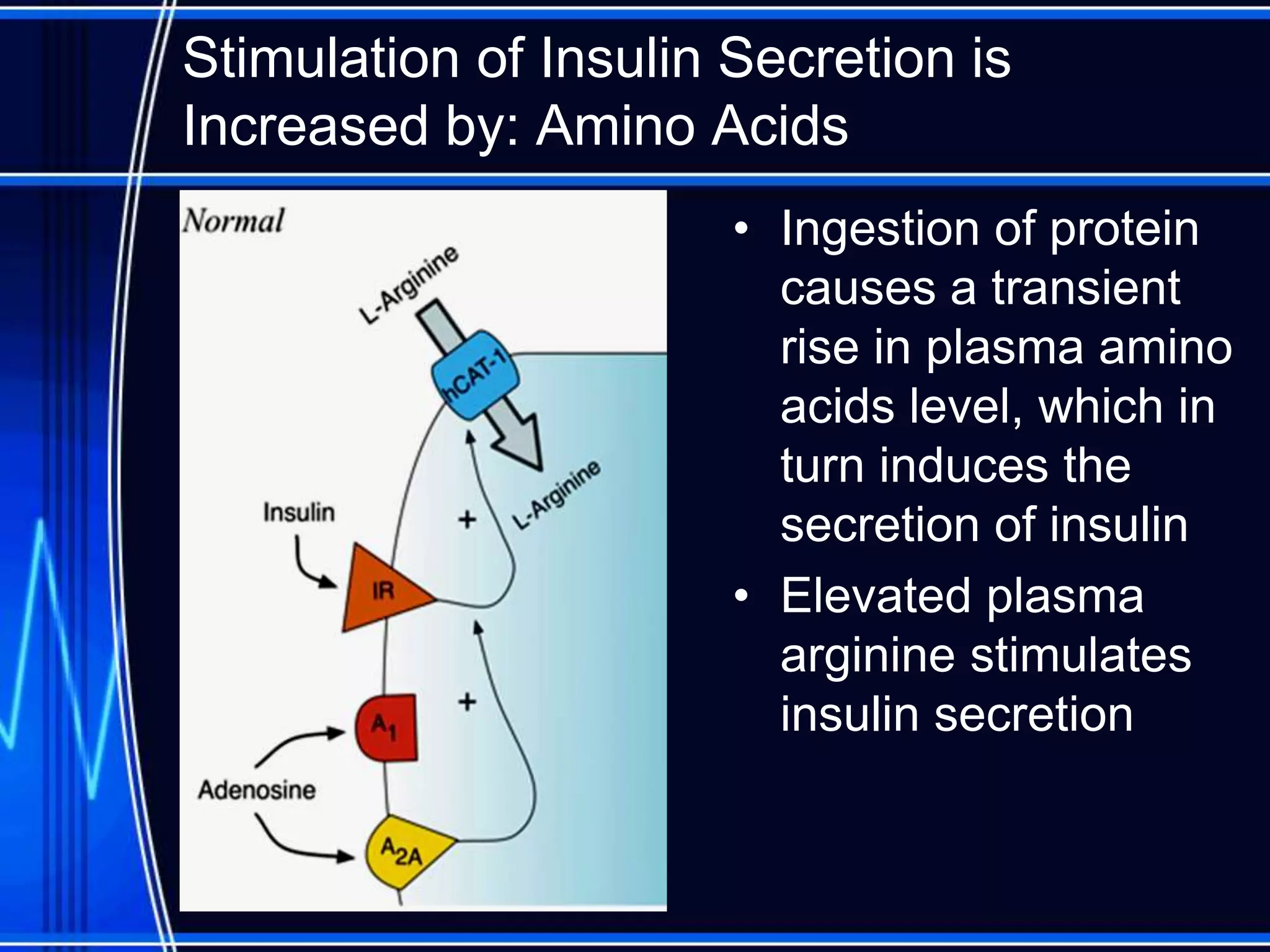
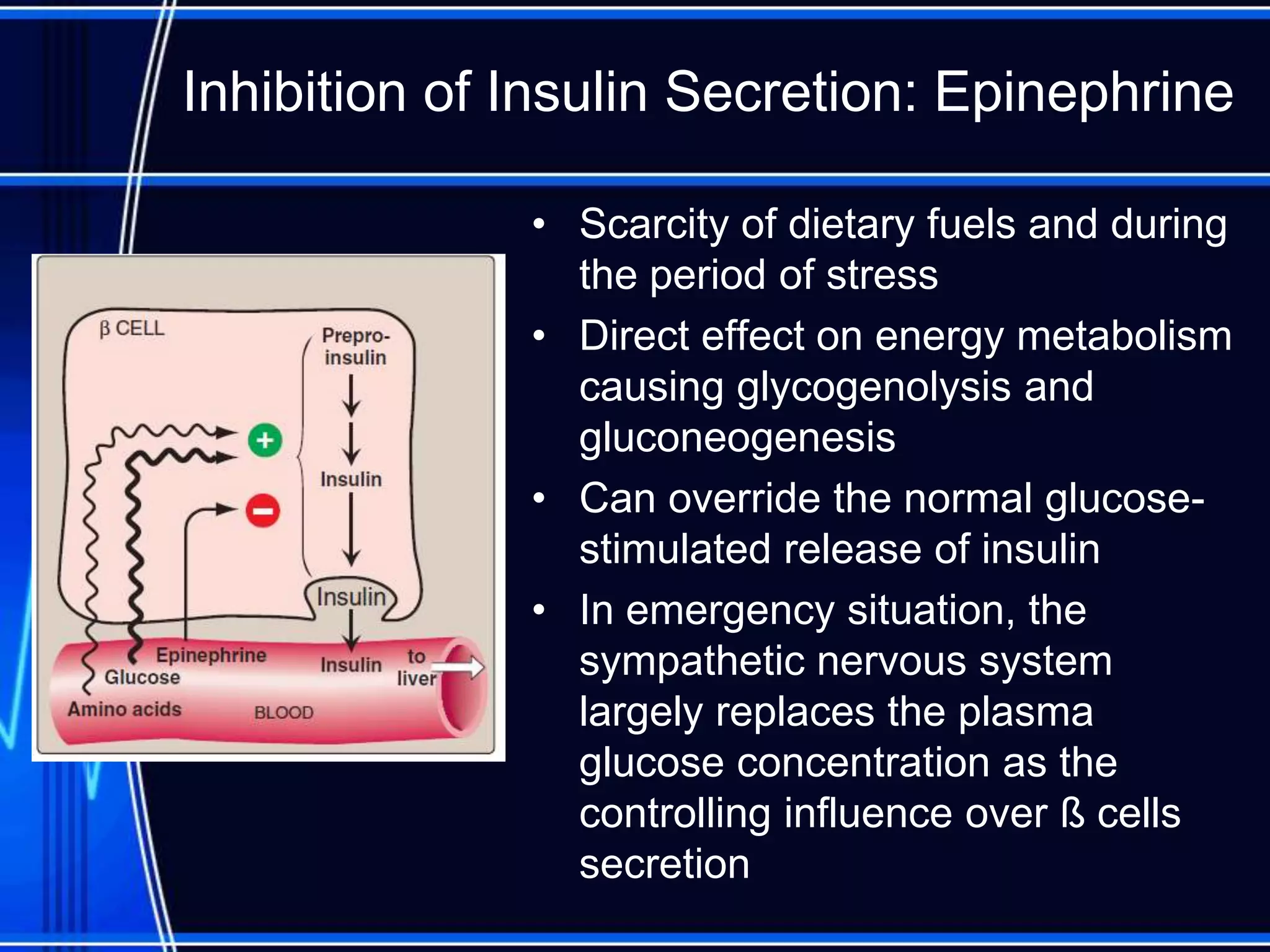
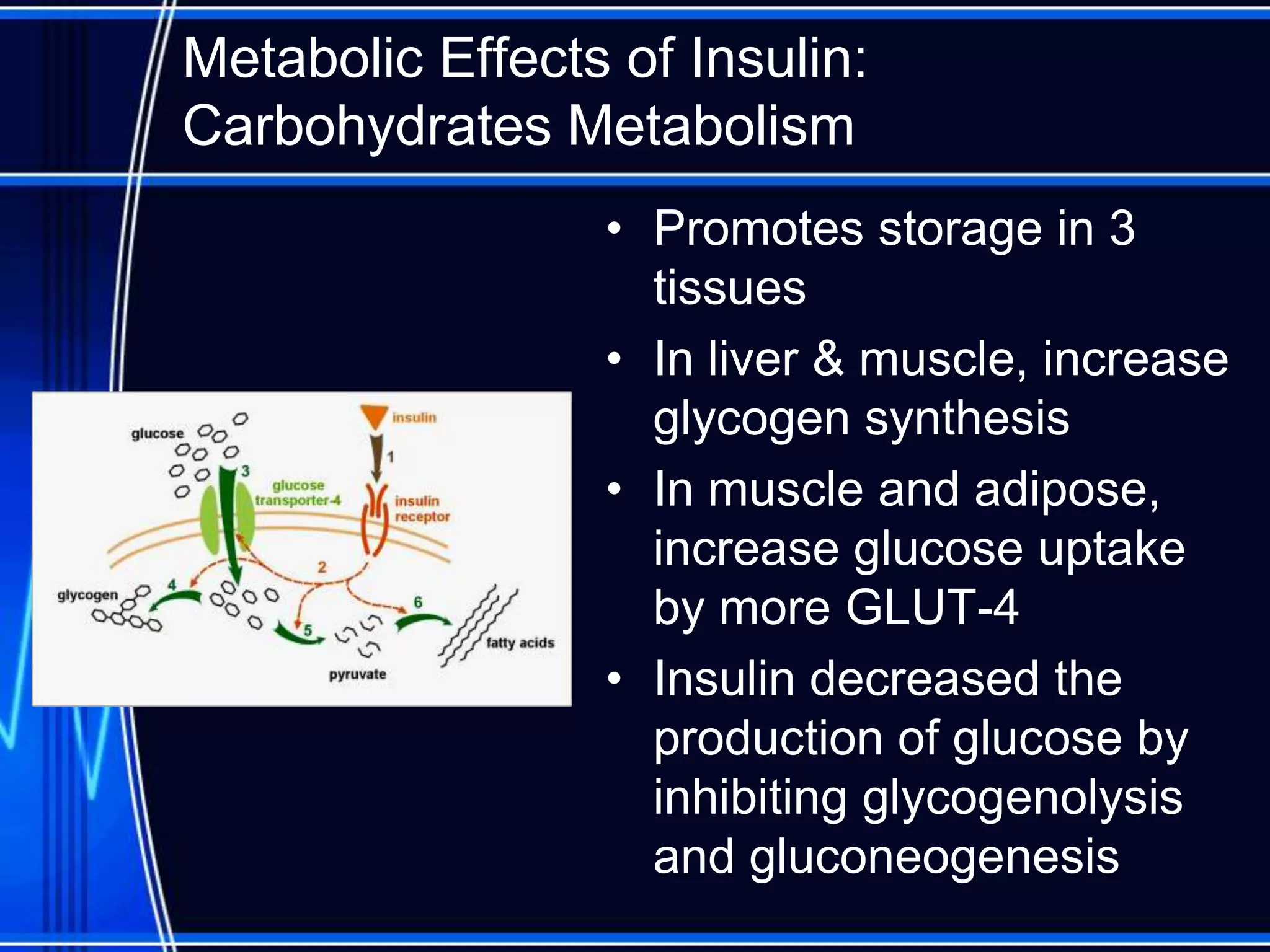
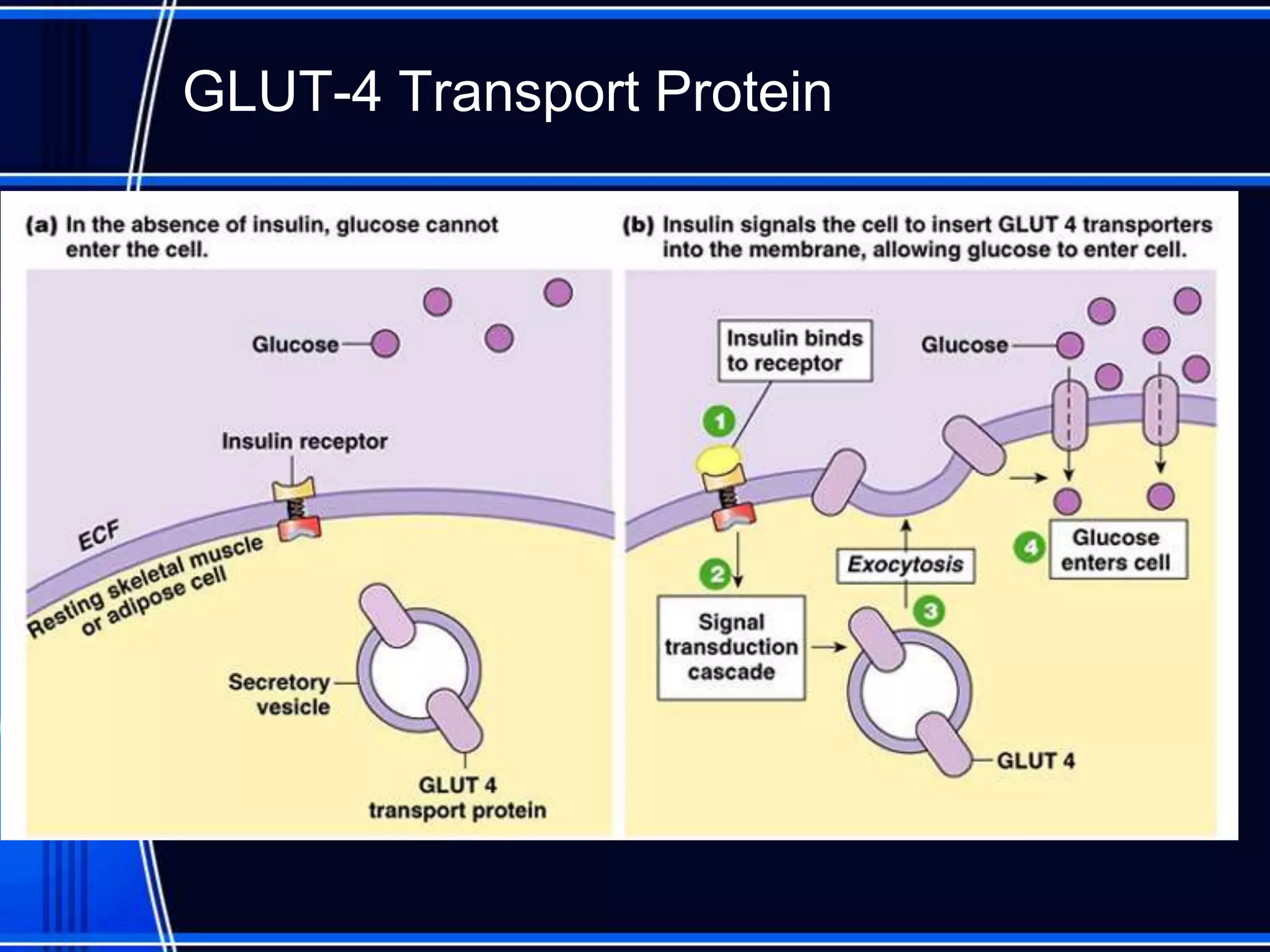
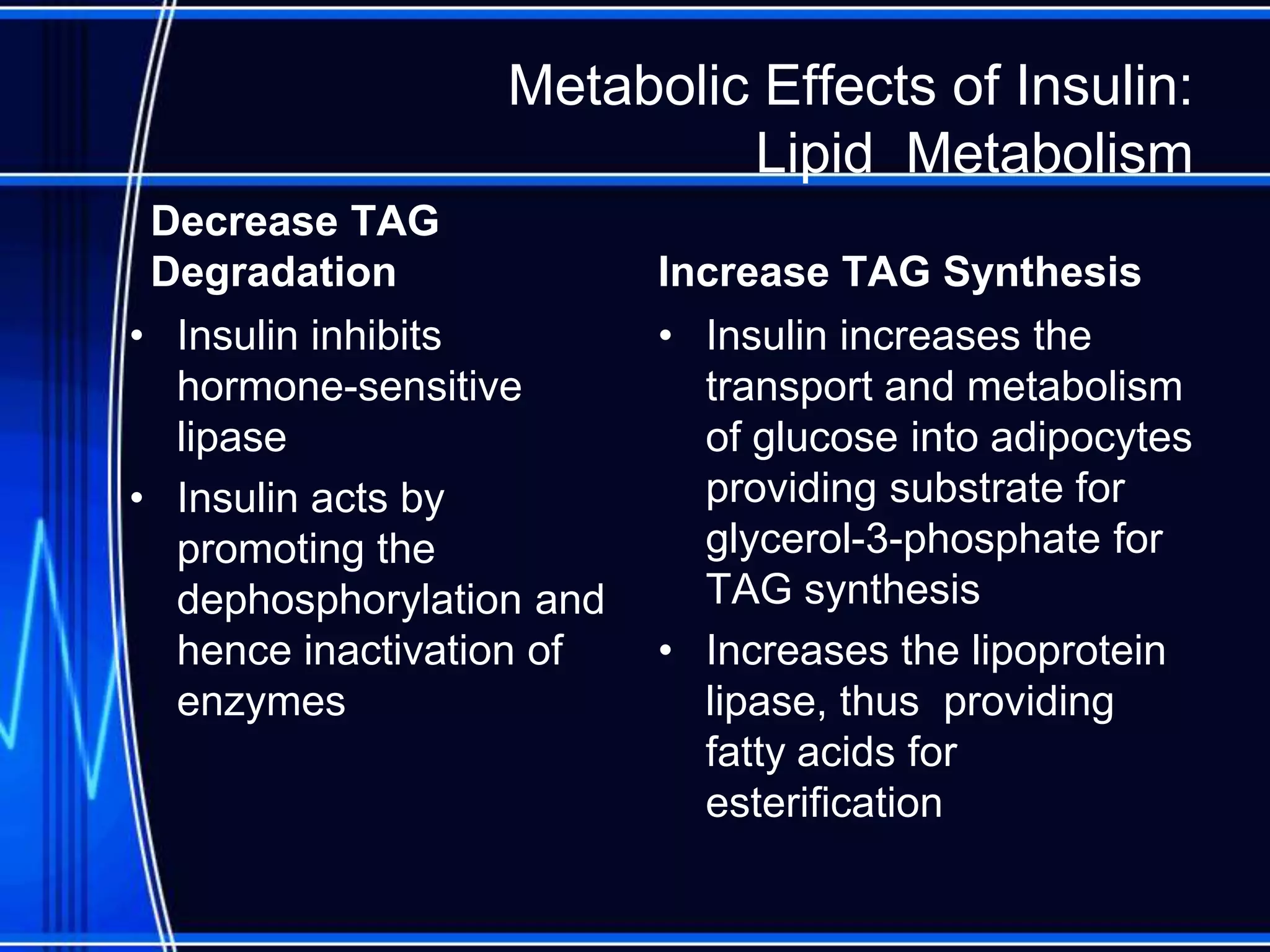
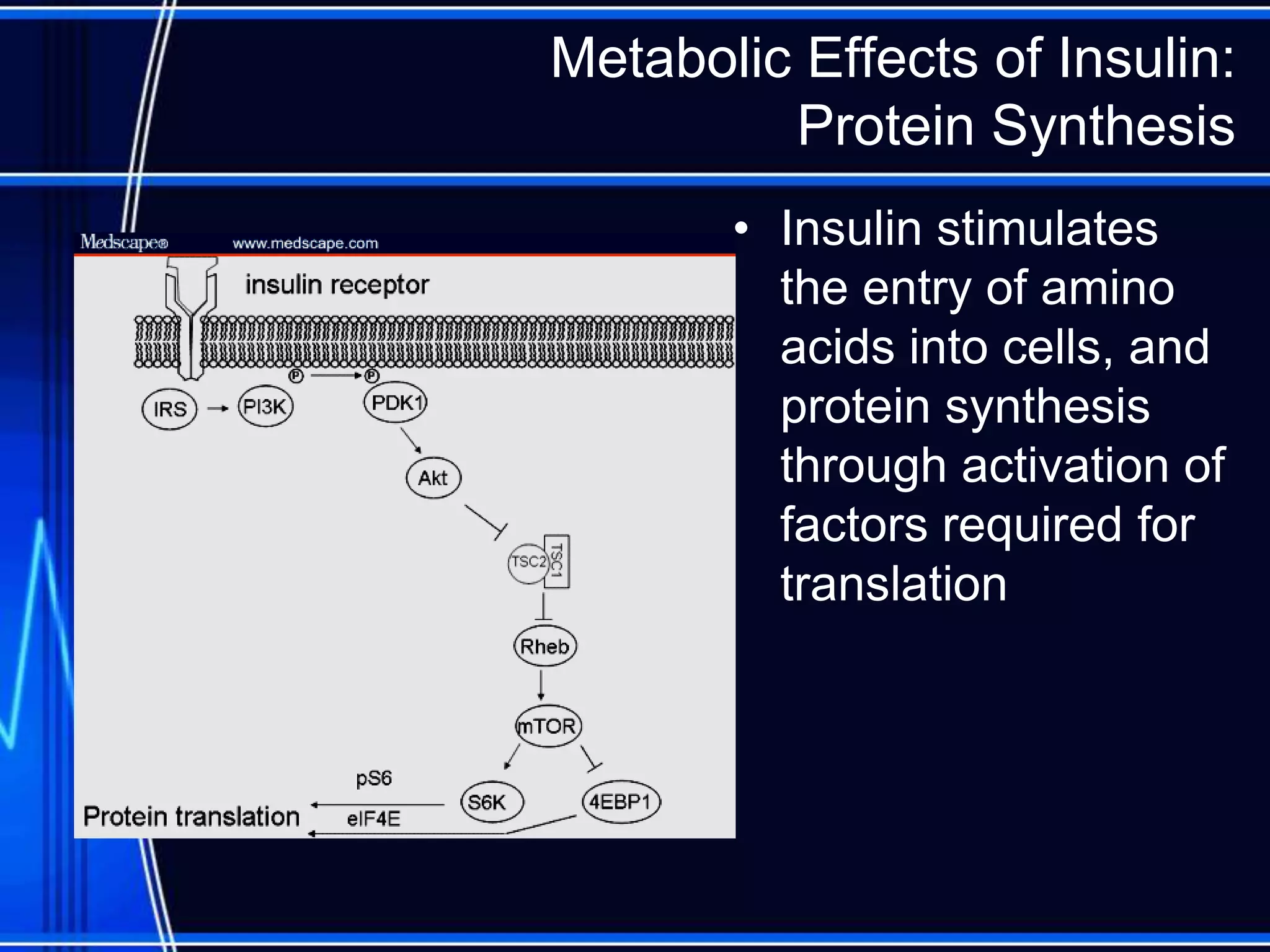
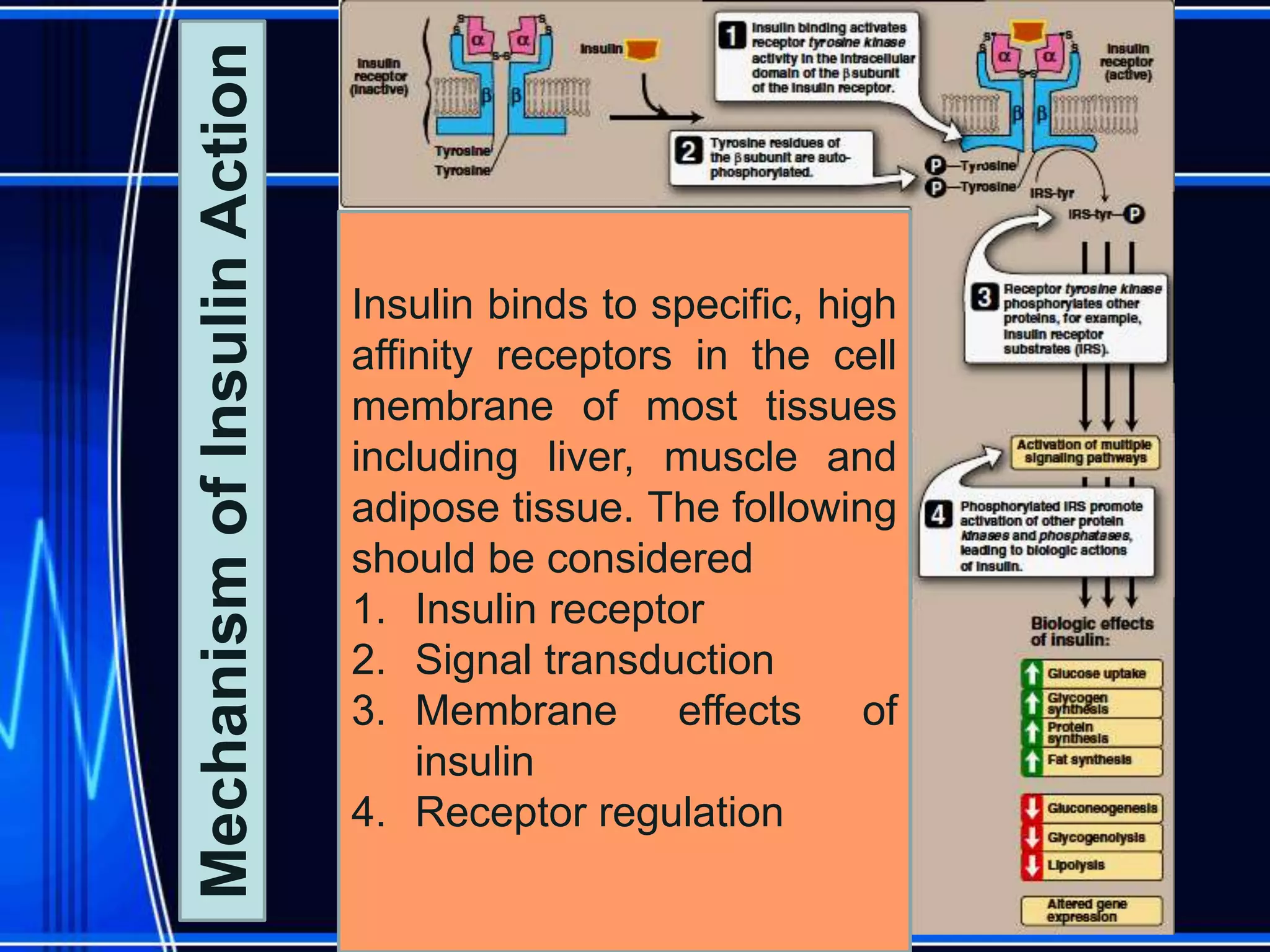
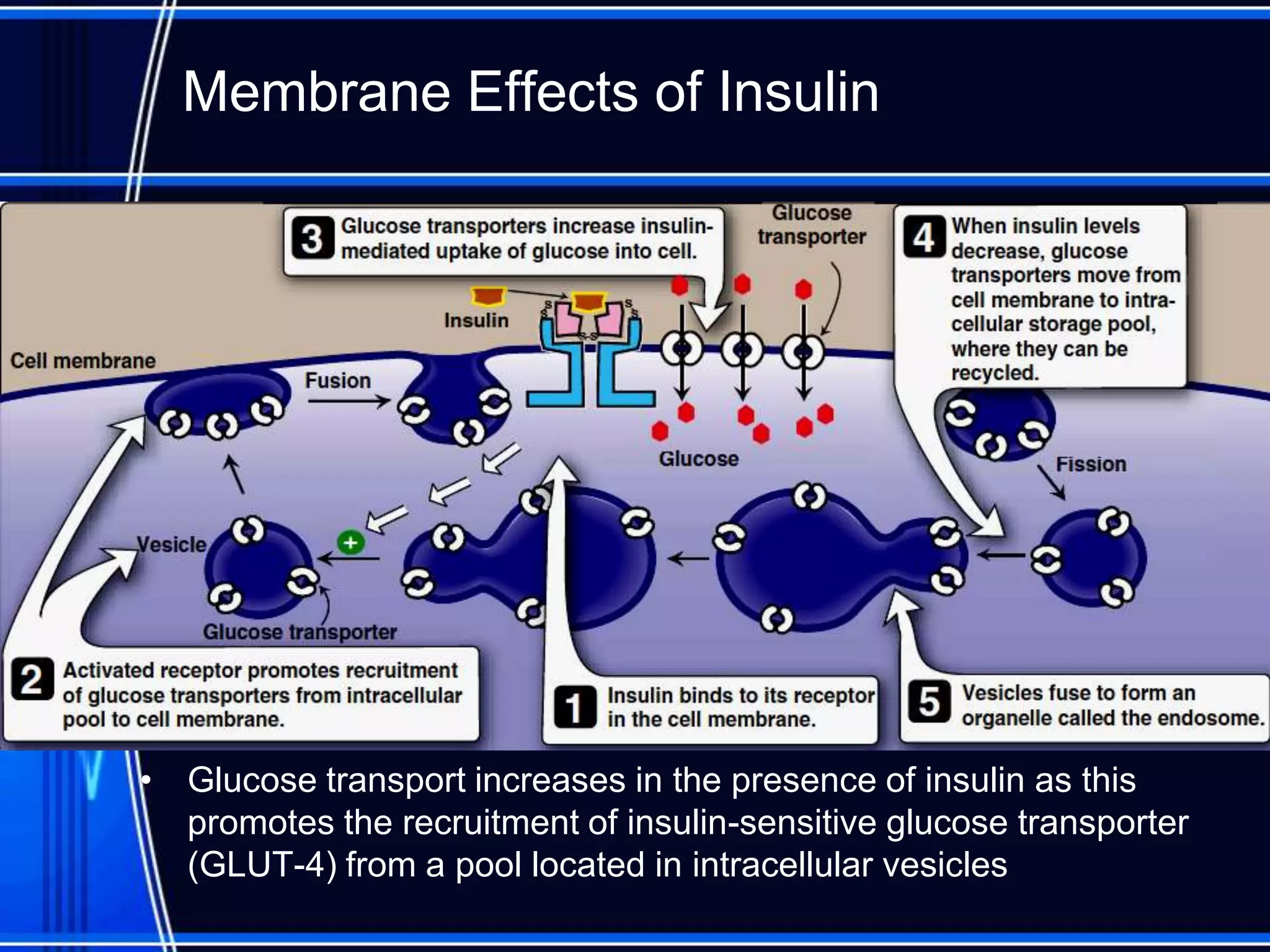
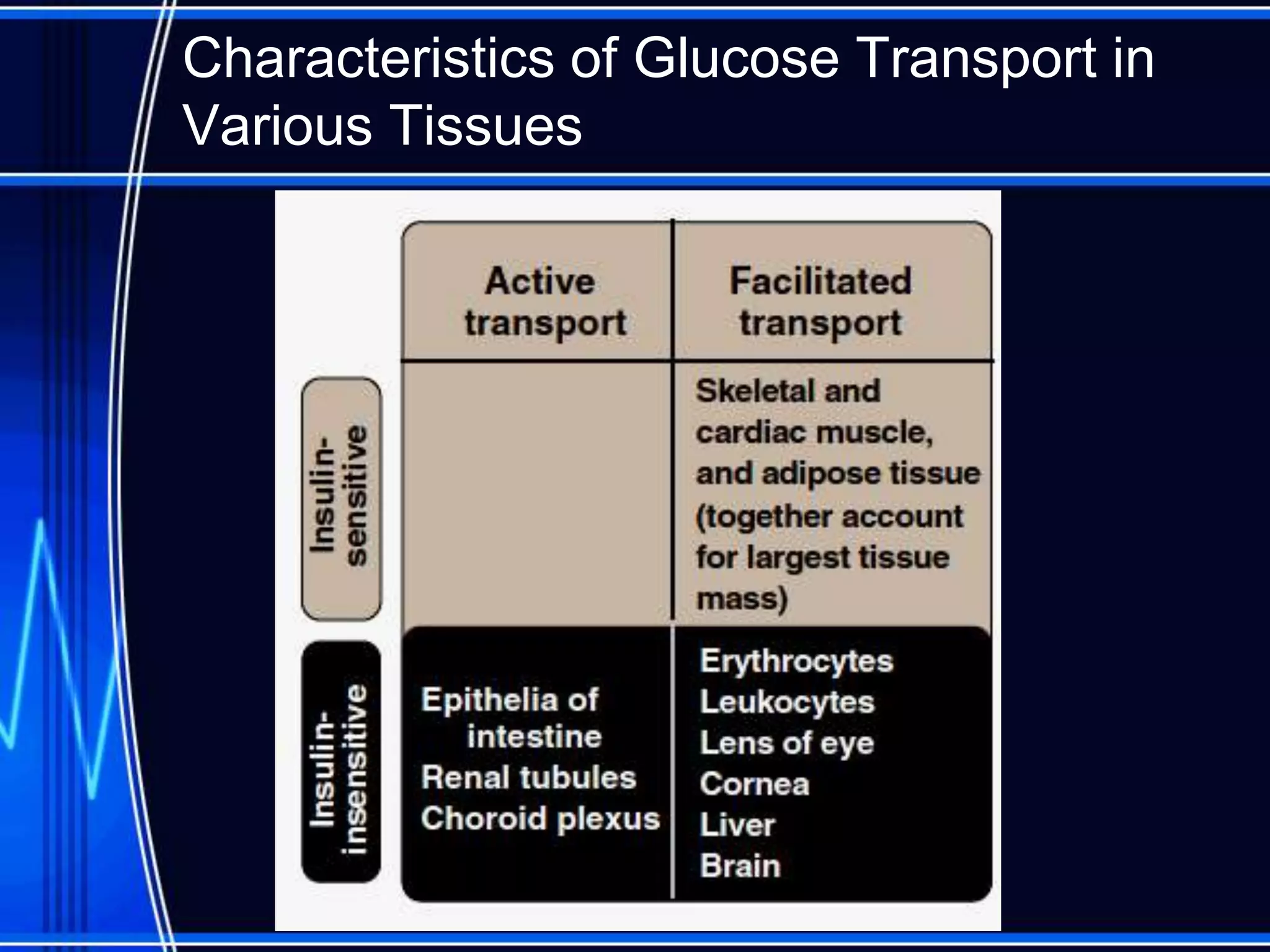
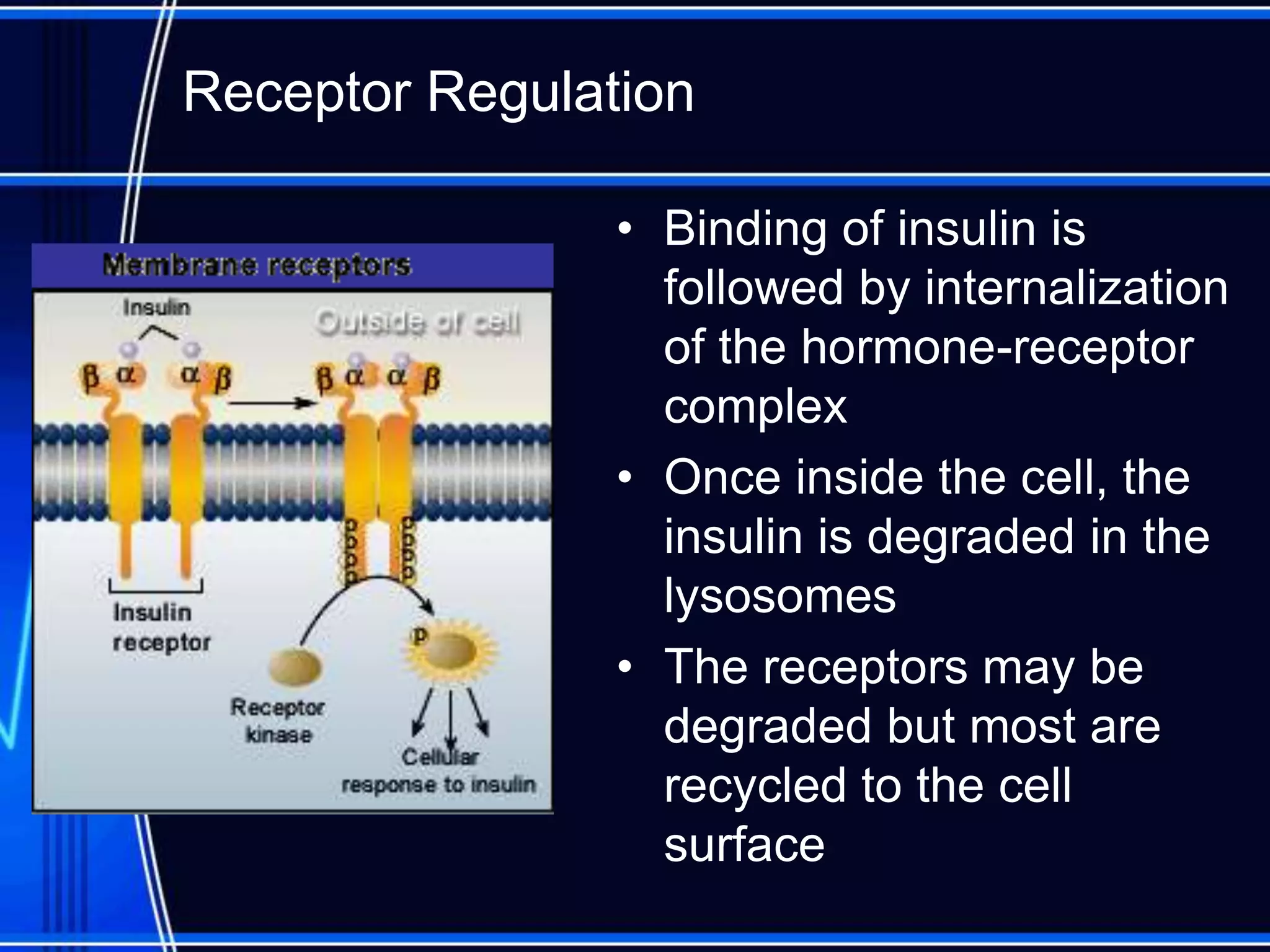
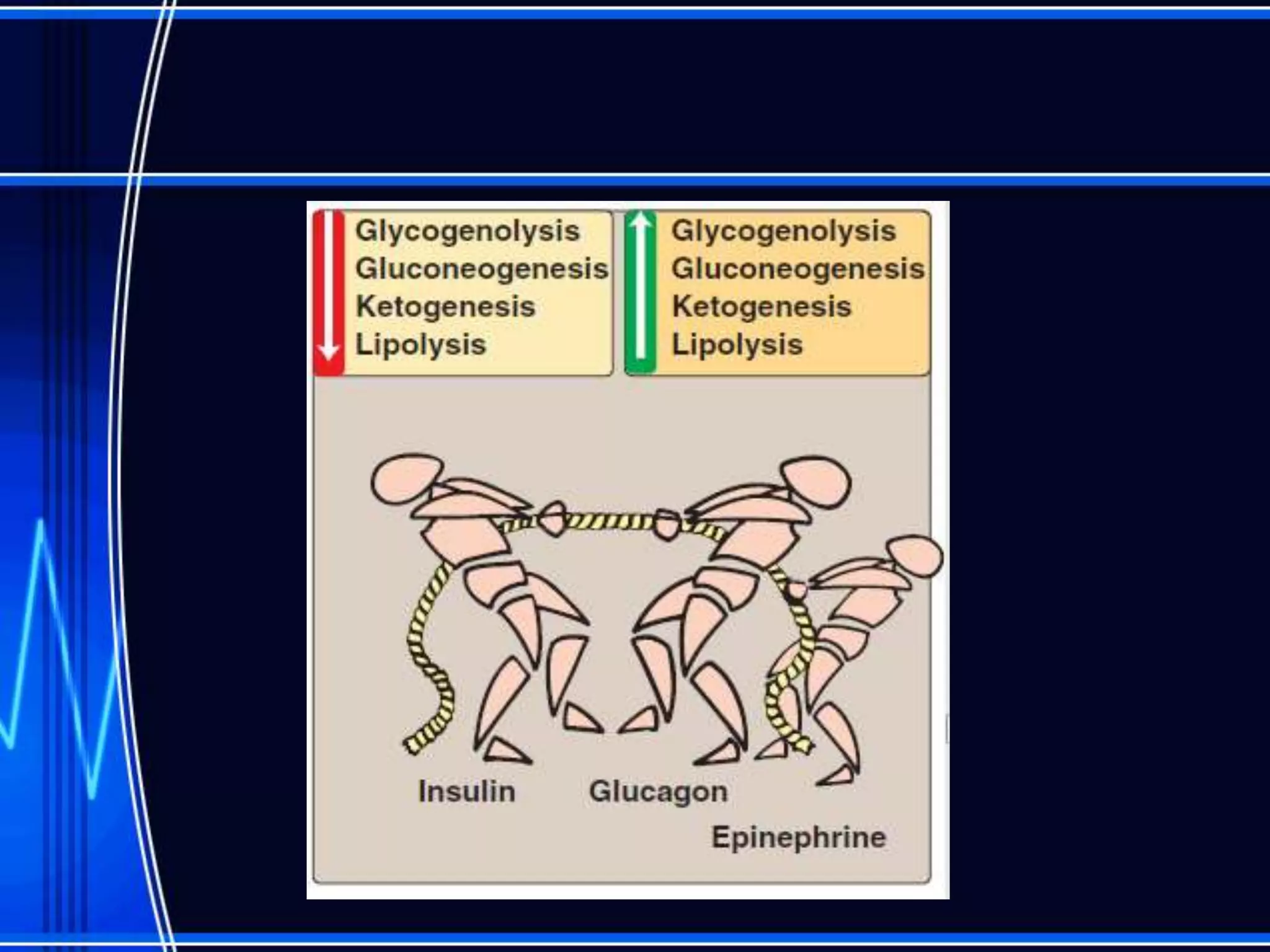
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates glucose metabolism and favors the storage and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in cells. It binds to insulin receptors on cells, triggering a signaling cascade that increases the translocation of GLUT-4 glucose transporters to cell membranes. This allows glucose uptake into cells, where it is used or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscle or converted to triglycerides for storage in adipose tissue. Insulin also inhibits the breakdown of glycogen, triglycerides, and proteins, favoring their synthesis and storage over degradation.