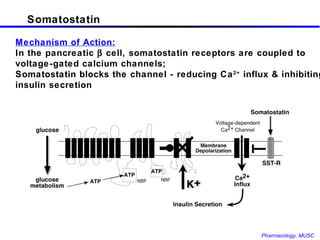
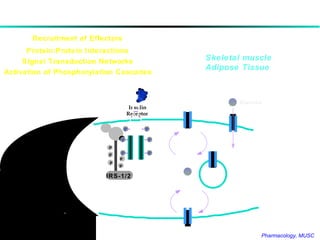
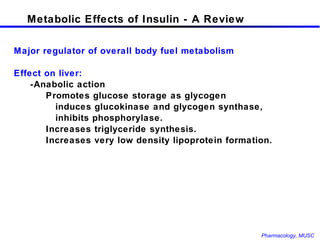
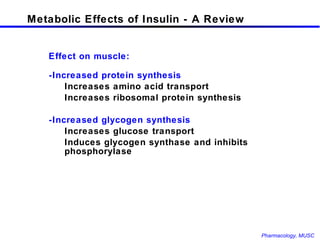
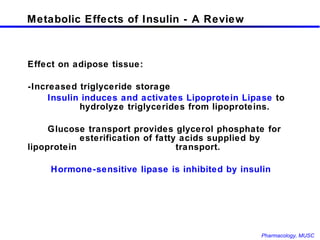
The document discusses insulin, its synthesis and secretion, mechanisms of action, and effects on metabolism. It also covers oral hypoglycemic agents and their mechanisms. Insulin is synthesized in the pancreas as proinsulin and processed into insulin and C-peptide. Insulin regulates glucose and lipid metabolism through effects on liver, muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin resistance and deficiency lead to hyperglycemia and other metabolic abnormalities.




















































![RESULTS: Intensive vs. Conventional Therapies [glucose] HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin ) Intensive ~150 mg/dl 7% Conventional ~225 mg/dl 9% Retinopathy Microalbuminuria Albuminuria Neuropathy 1° cohort 76% 39% 54% 60% Conclusion : Intensive insulin therapy delayed onset and slowed progression of retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy in Type 1 diabetes. Side Effects • 3X increase in severe hypoglycemic events • Significant increase in cost of supervision associated with intensive treatment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insulinandoral3167/85/Insulin-and-Oral-63-320.jpg)