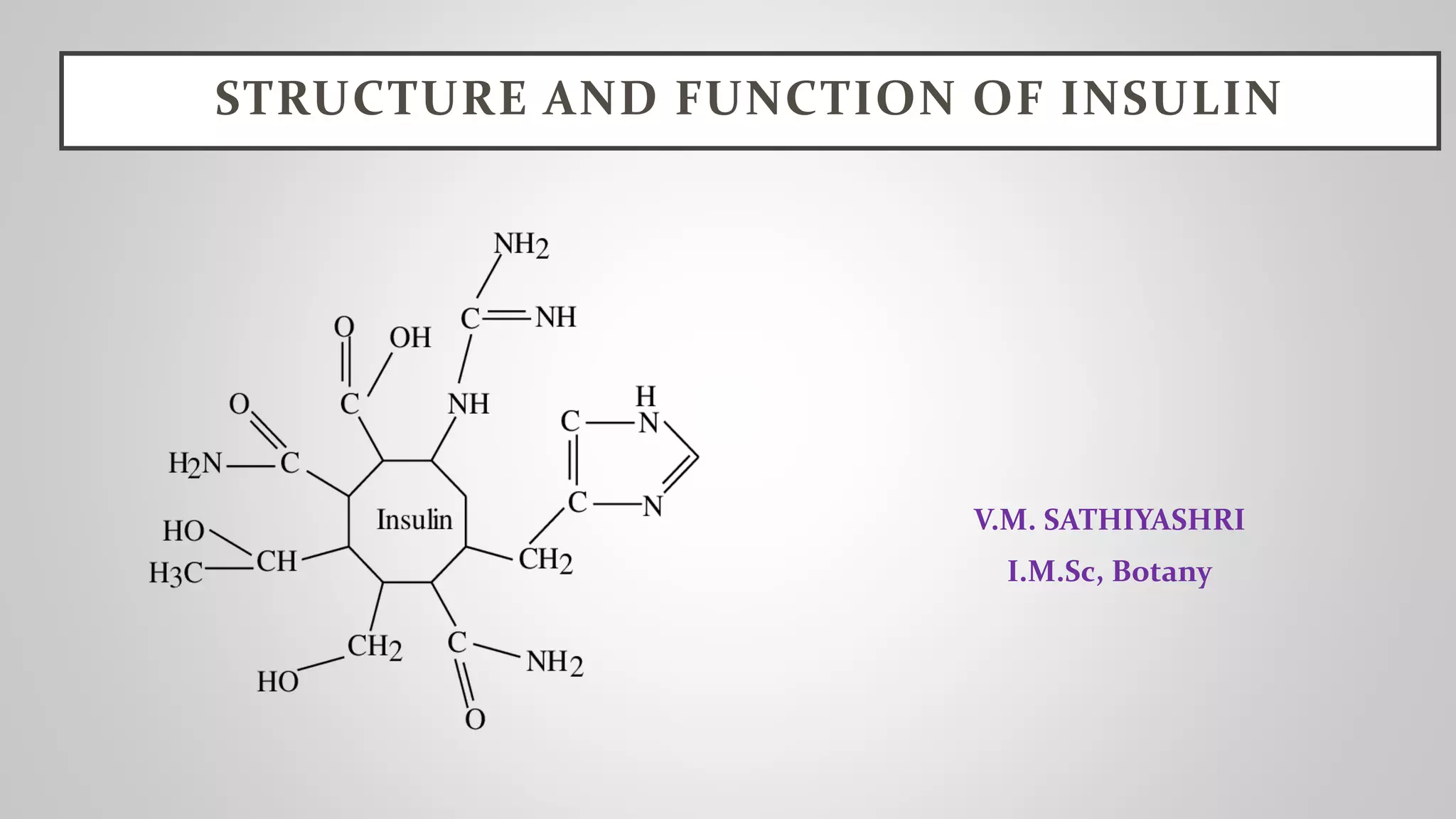
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone composed of 51 amino acids that is produced in the beta cells of the pancreas. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins by promoting the absorption of glucose from the bloodstream into fat, liver, and muscle cells. Insulin acts by binding to insulin receptors on cells and stimulating the movement of glucose transporters to cell membranes to bring glucose inside, where it is used for energy or stored as glycogen or fat. Without sufficient insulin production or action, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to the condition of diabetes mellitus.