This document discusses voltage testing and partial discharge measurement techniques for power cable accessories. It provides:
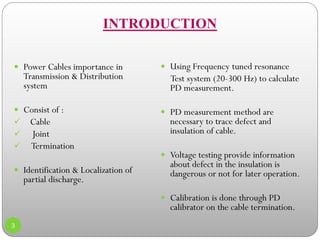
1) An overview of the objective to compare cable testing best practices and determine cable defects using partial discharge methods.
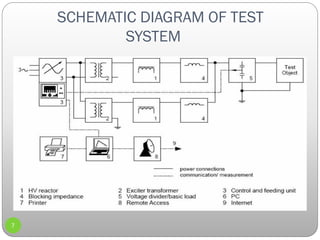
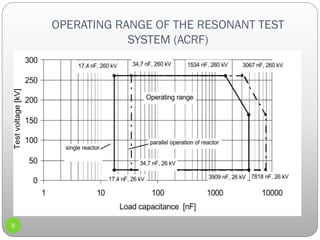
2) A description of an ACRF test system used, including its components like an HV reactor, control unit, and voltage divider.
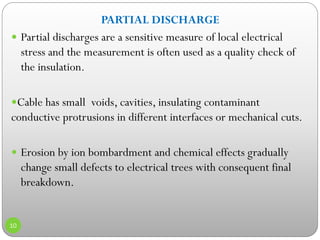
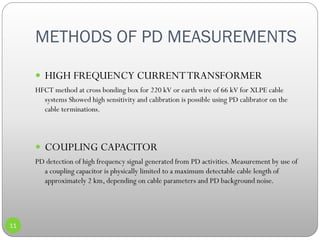
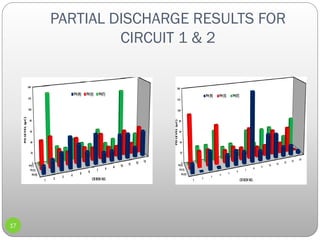
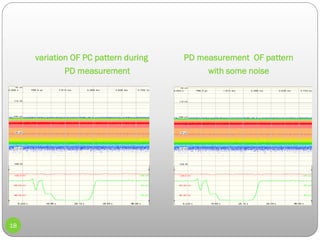
3) Details on partial discharge measurement methods like using high frequency current transformers and coupling capacitors to detect discharges in cables.
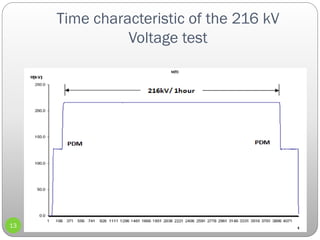
4) The conclusion that resonant testing between 20-300Hz along with partial discharge detection reduces risks from cable systems after installation by locating faults.