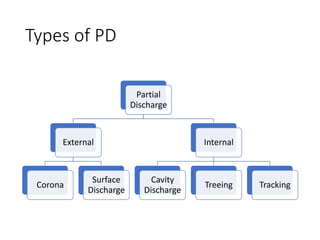
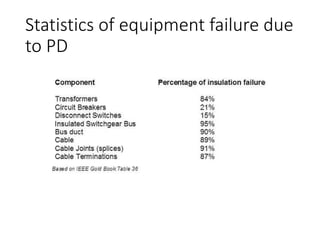
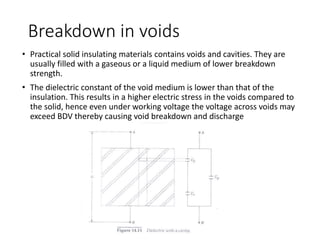
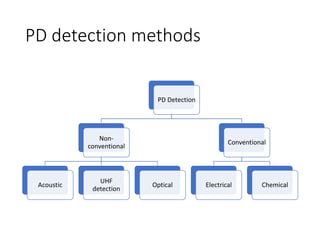
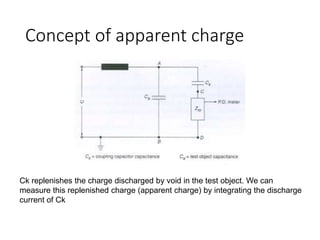
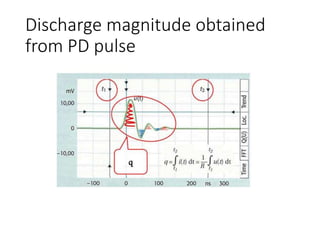
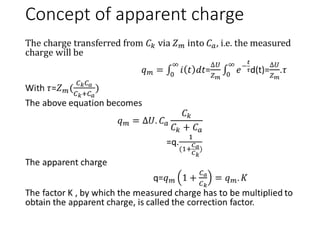
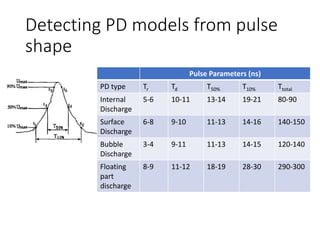
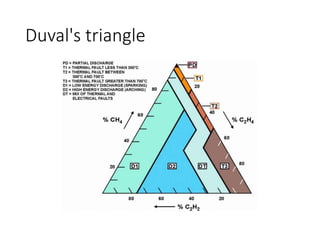
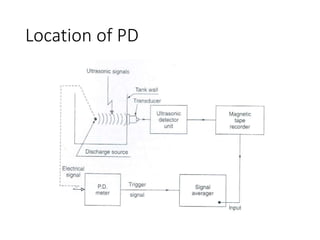
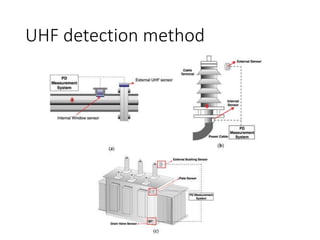
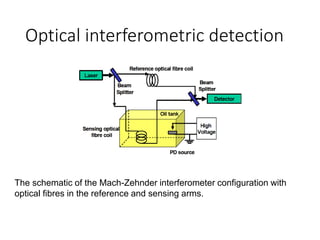
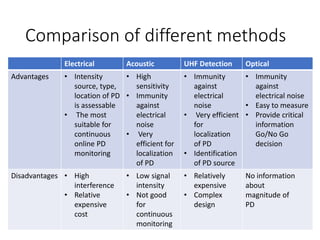
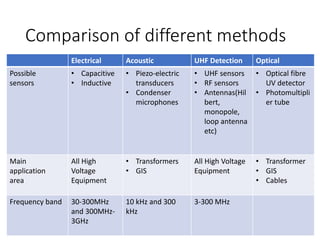
The document discusses various aspects of partial discharge (PD) testing, including definitions, types, and detection methods. It defines PD as localized electrical discharges that only partially bridge insulation between conductors. Four main types are discussed: corona, surface, cavity, and treeing discharges. Detection methods covered include electrical, acoustic, UHF, optical, and chemical (DGA) techniques. The electrical method measures apparent charge, while acoustic localization and UHF detection have advantages of immunity to electromagnetic noise. Optical detection relies on light emission during discharges. A comparison table outlines advantages and disadvantages of each detection method.