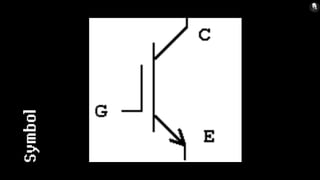
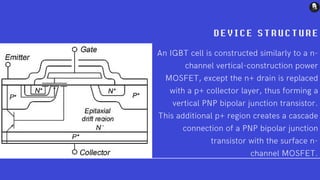
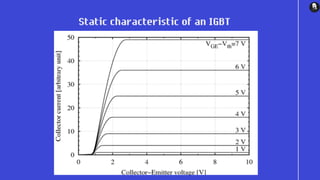
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal semiconductor device that combines high efficiency and fast switching. It consists of alternating P-N-P-N layers controlled by a metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) gate structure, without regenerative action. The IGBT structure is similar to a thyristor with an isolated MOS gate that completely suppresses the thyristor action. IGBTs are used in switching power supplies for applications requiring high power, such as variable frequency drives, electric vehicles, and air conditioners. The IGBT combines the simple gate drive of MOSFETs with the high-current and low-saturation-voltage capabilities of bipolar transistors.