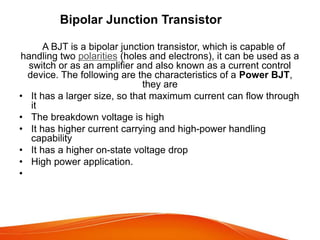
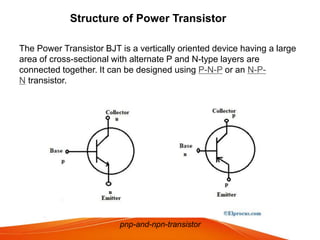
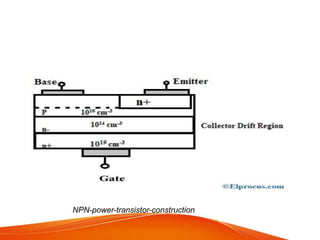
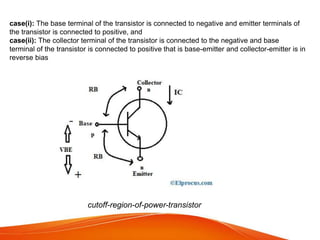
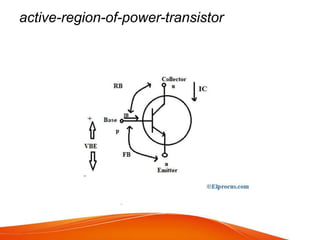
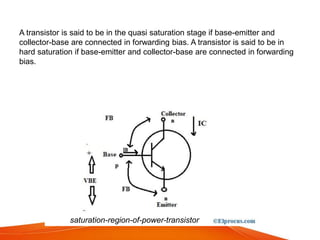
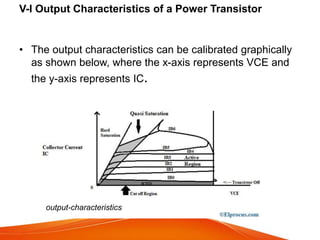
A power transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device designed to control high current and voltages. There are four main types: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), static induction transistors (SITs), and insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs). A power BJT is a bipolar junction transistor capable of handling large currents and voltages. It operates in four regions - cut-off, active, quasi saturation, and hard saturation - depending on the bias voltages applied. Power transistors are used in applications like switch-mode power supplies, relays, and power amplifiers.