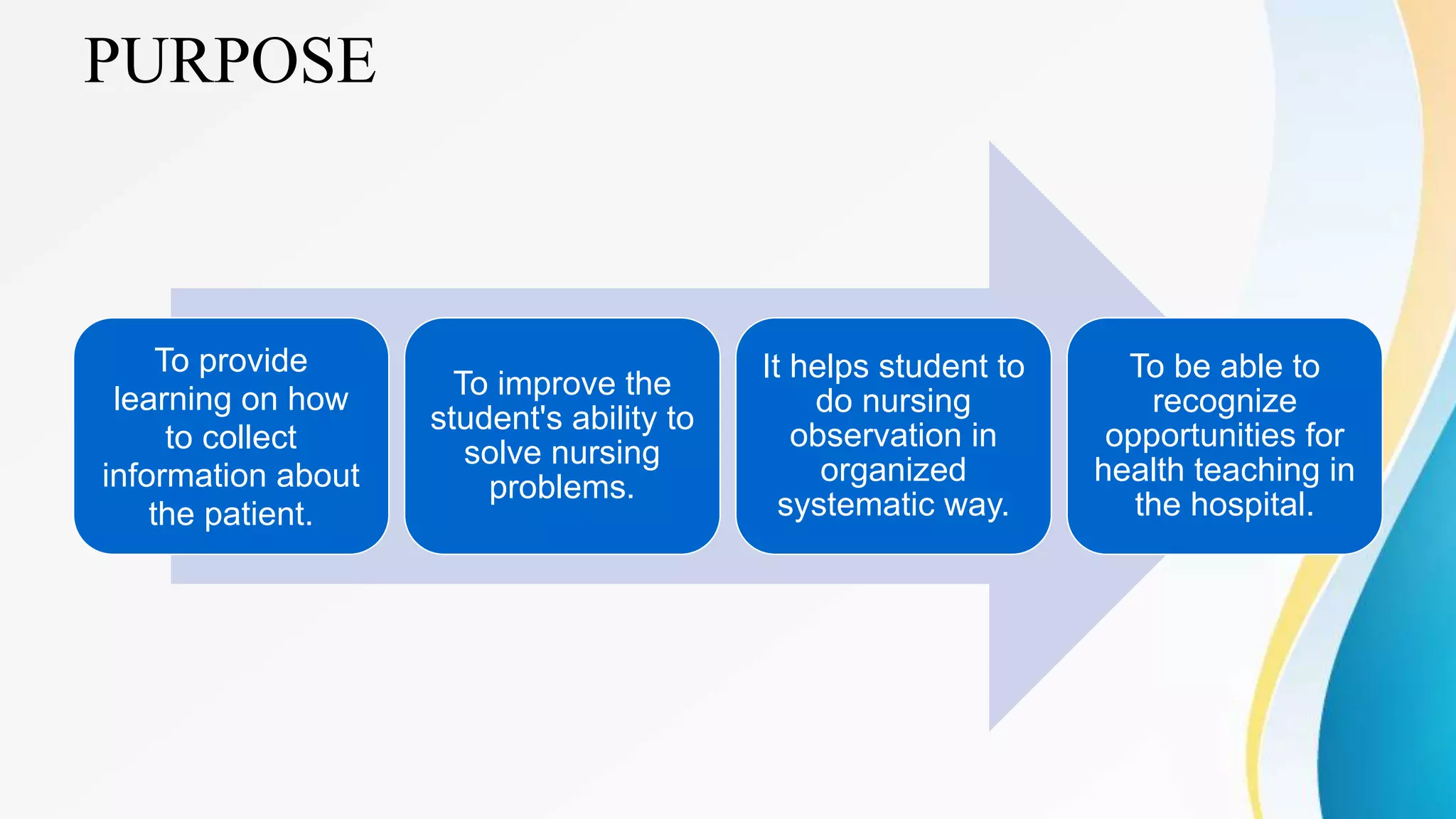
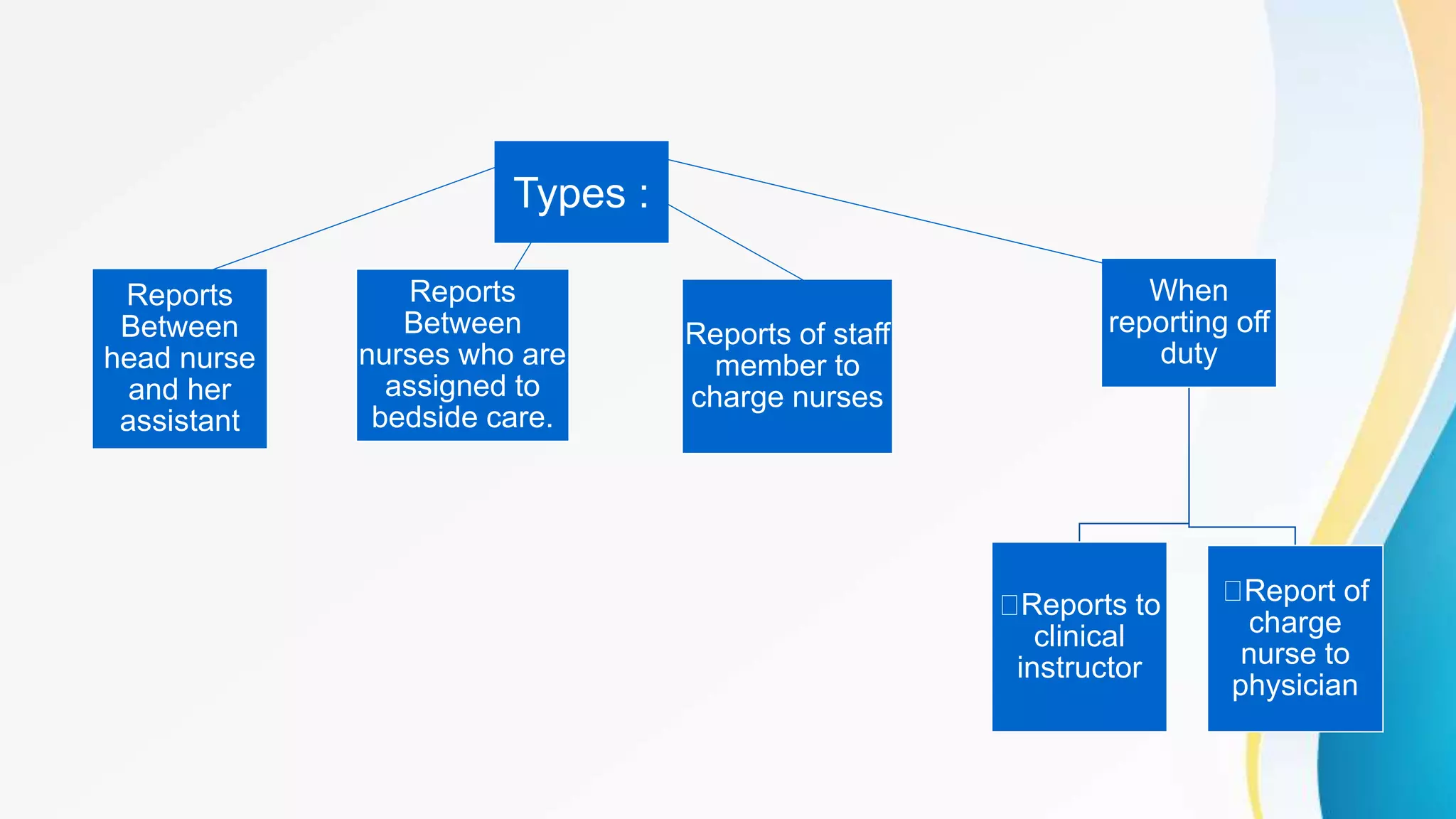
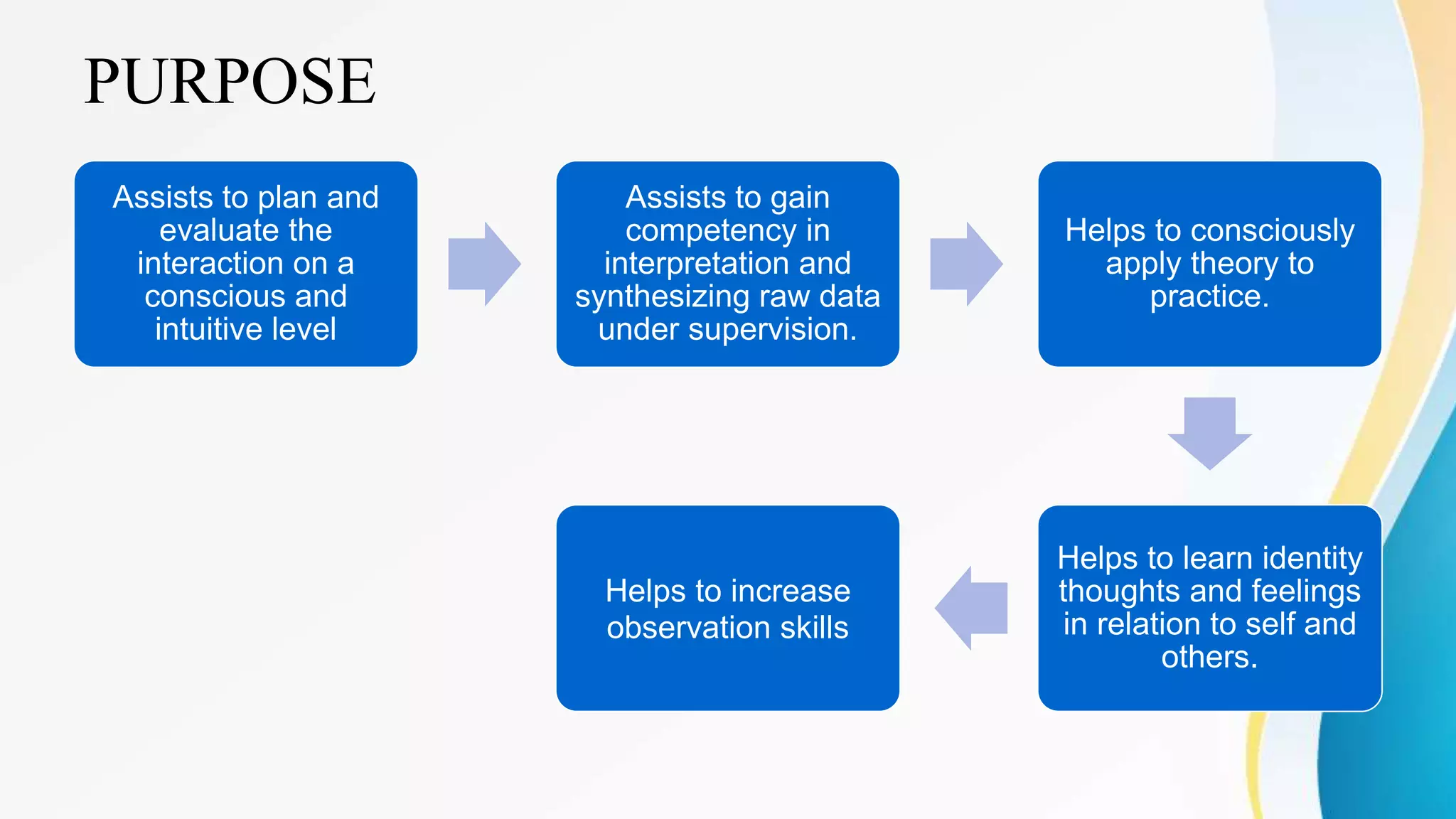
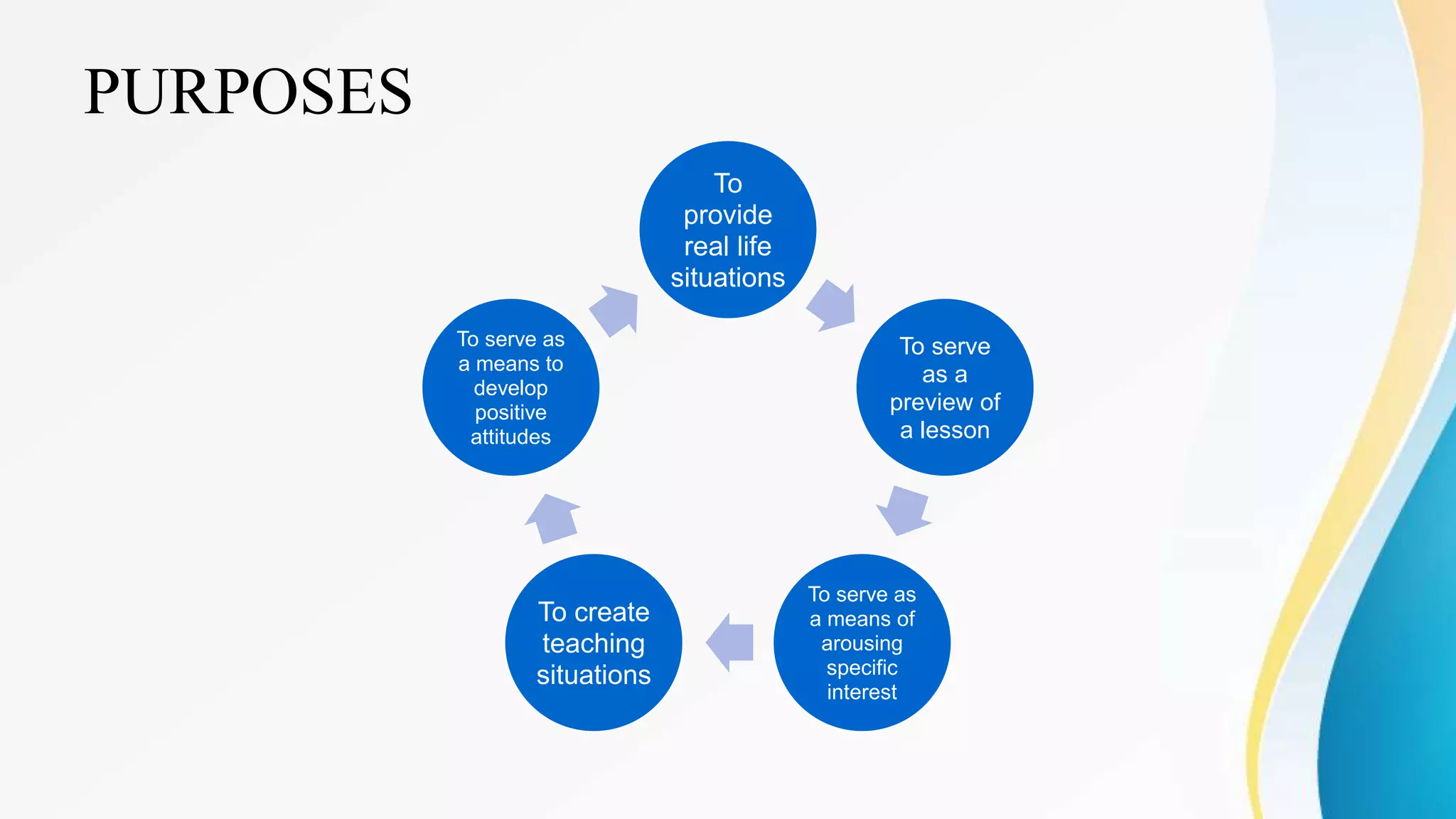
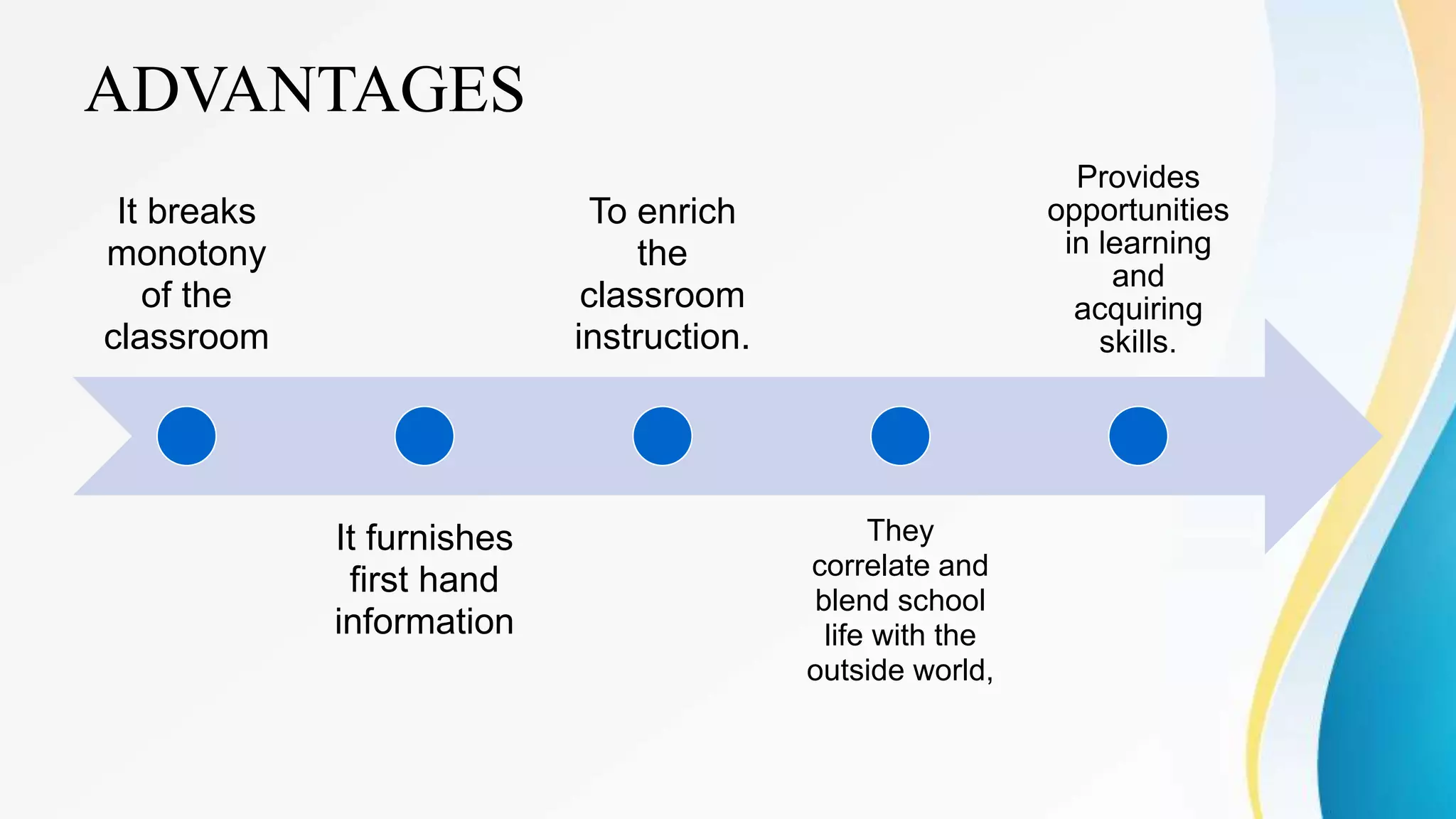
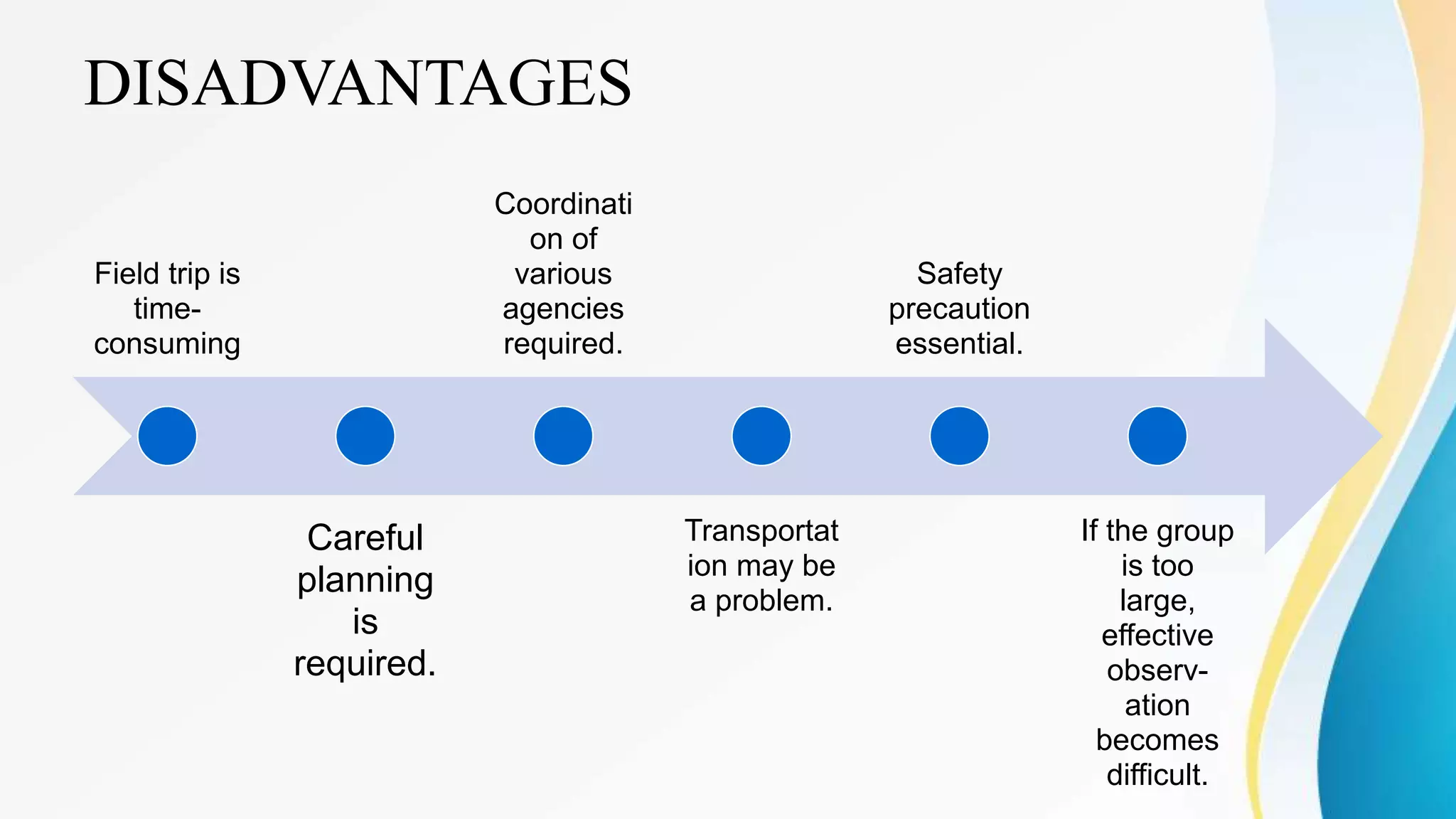
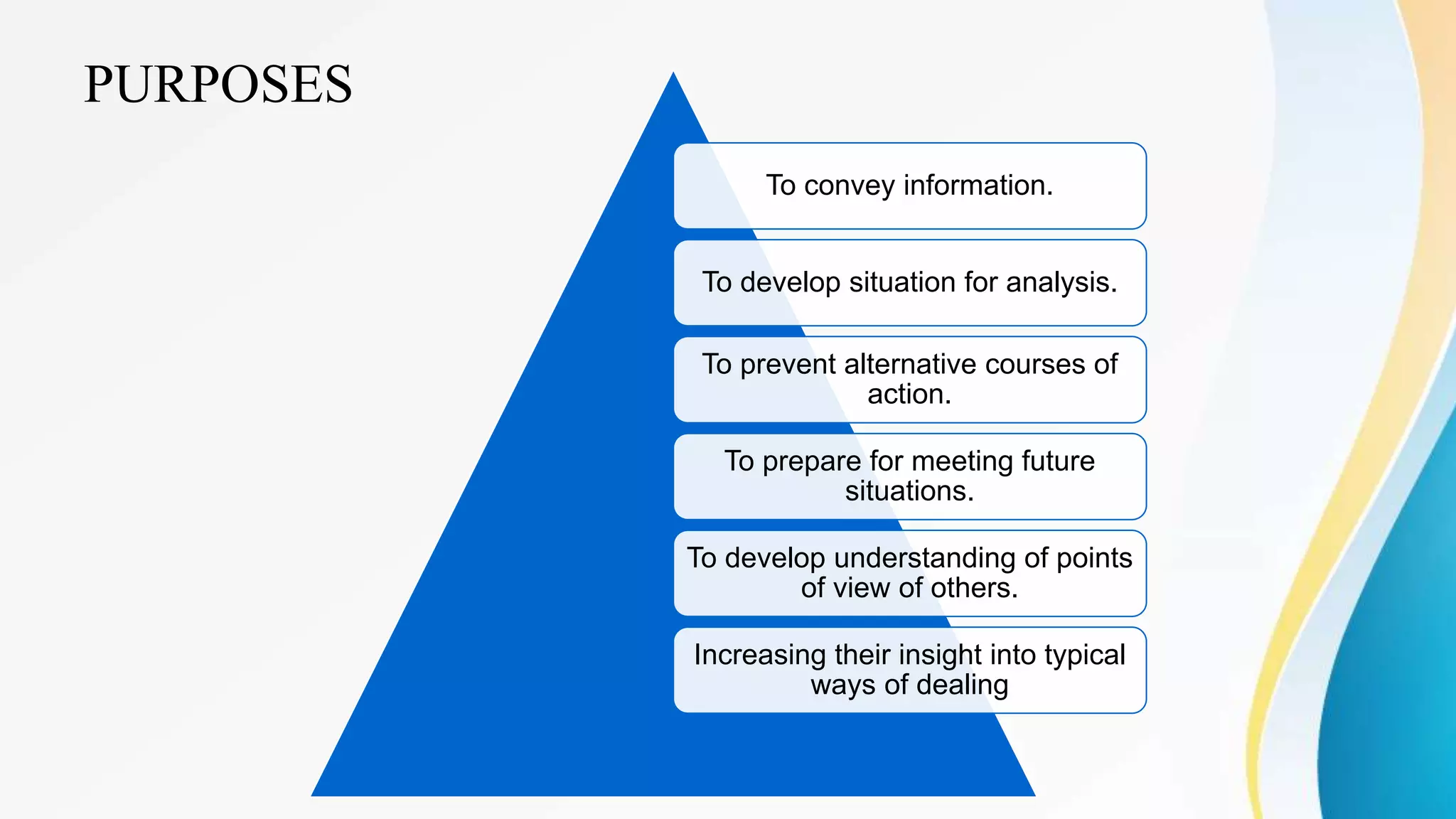
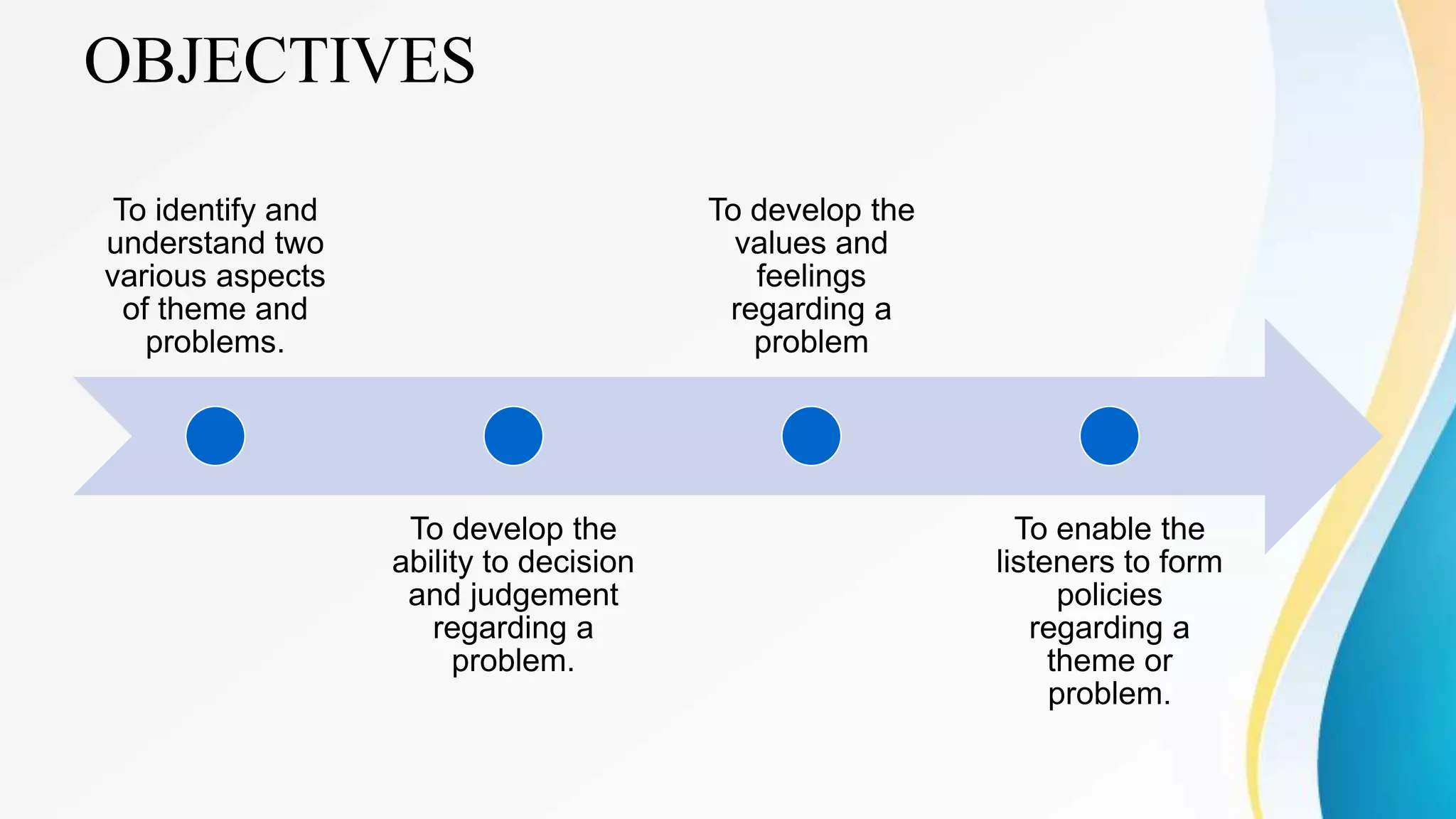
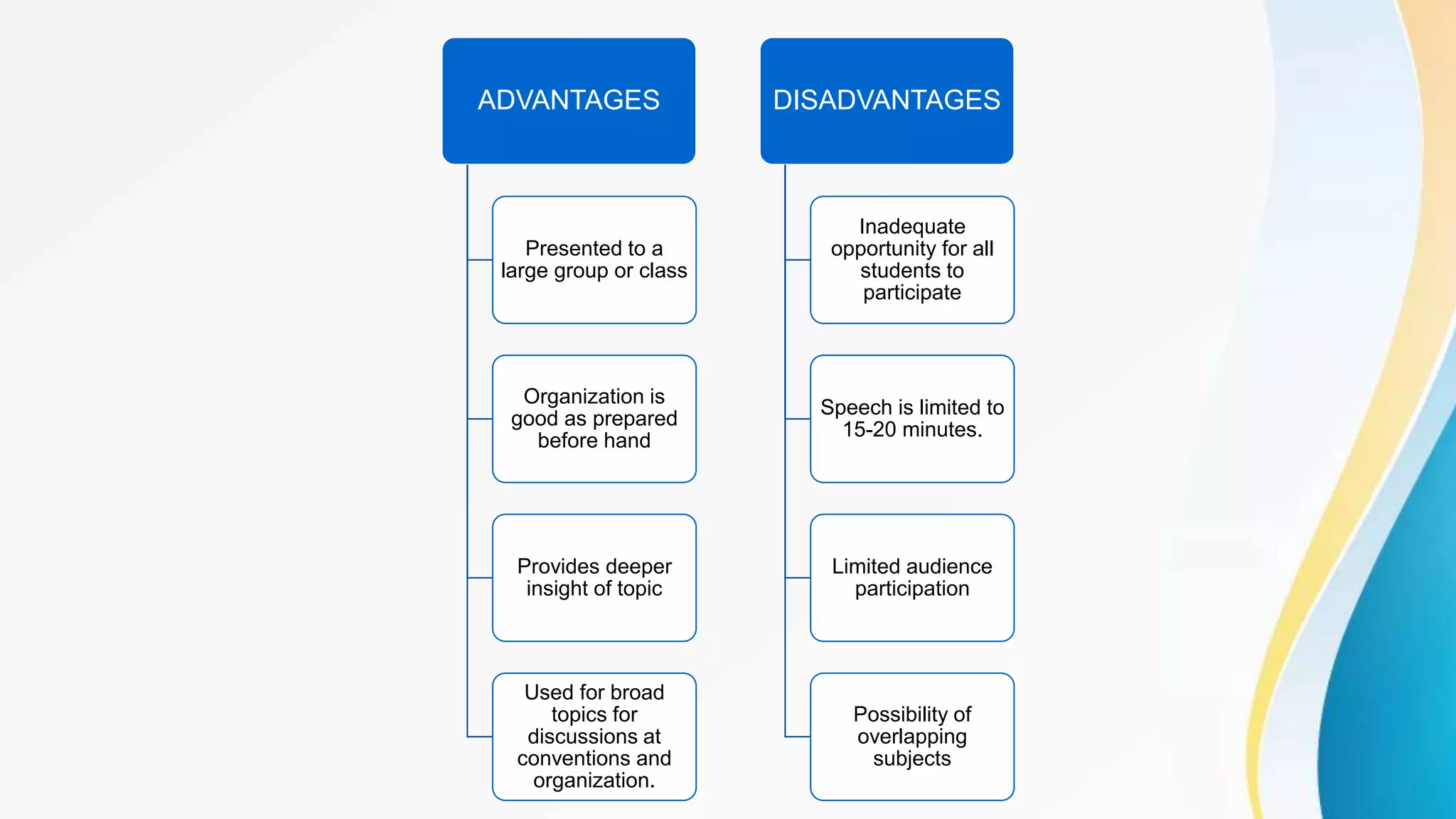
This document outlines various clinical teaching methods used in nursing education. It begins with definitions of clinical teaching and objectives. It then describes many methods including nursing clinics, bedside clinics, nursing rounds, nursing assignments, nursing care conferences, reports, individual/group conferences, process recording, field trips, the laboratory method, nursing care plans, seminars, case analysis, case incidents, role playing, symposiums, workshops, and panel discussions. For each method, it provides details on purpose, principles, advantages, and disadvantages. The document serves as a comprehensive reference for nursing instructors on approaches to teach clinical skills and apply theoretical knowledge.