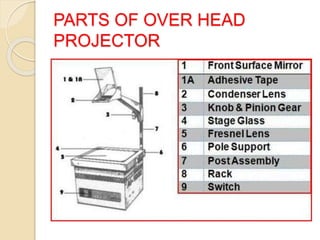
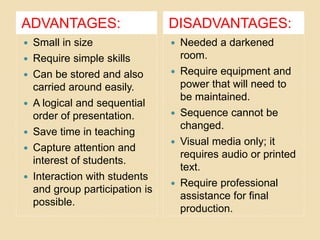
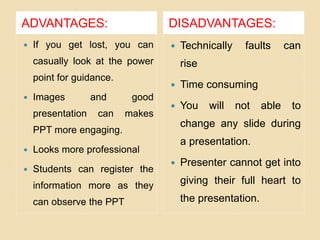
This document discusses different types of projected aids used in education, including overhead projectors, slide projectors, and PowerPoint. It provides definitions, functions, classifications, parts, guidelines for use, advantages, and disadvantages of each type. Overhead projectors allow teachers to write on transparencies to simultaneously project concepts. Slide projectors display small photographic images sequentially. PowerPoint offers flexibility in content and display but requires careful formatting of text, fonts, and colors for readability. Proper use and care of the projection equipment is also outlined.