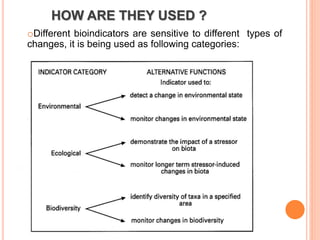
This document discusses insects as pollution indicators. It defines pollution and bioindicators. Insects are effective bioindicators because they are abundant, respond quickly to environmental changes, and are sensitive to detecting early changes. Certain insect groups like dragonflies, mayflies, caddisflies, and stoneflies indicate water quality, while beetles, collembolans, ants indicate soil quality. Light and noise pollution disrupt insect behaviors and life cycles. Industrial pollution can biomagnify through food chains. Honey bees, moths, and syrphid flies indicate air quality issues. Insects make good bioindicators to monitor overall ecosystem health.