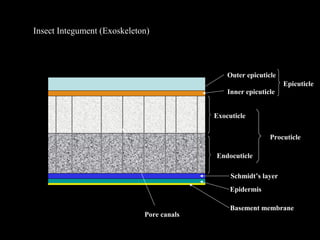
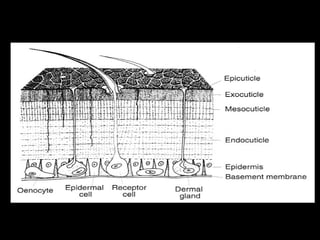
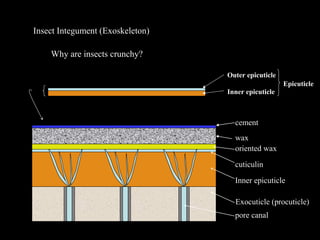
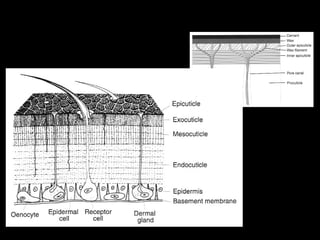
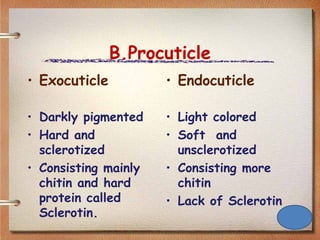
The insect integument, or exoskeleton, consists of three main layers:
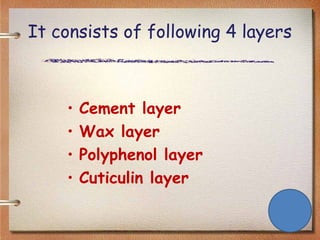
1. The cuticle, which is the outermost layer and provides protection. It has two regions - the epicuticle and procuticle.
2. The epidermis, which secretes the cuticle and aids in molting.
3. The basement membrane between the epidermis and organs.
The cuticle protects the insect, prevents water loss, and helps insects maintain their shape. It is rigid yet lightweight and allows for various modes of life.