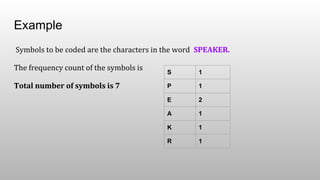
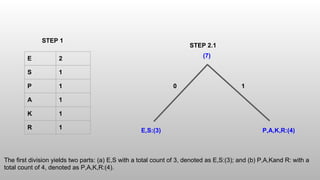
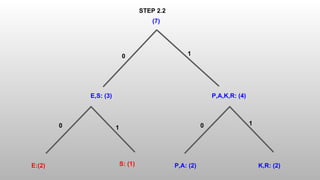
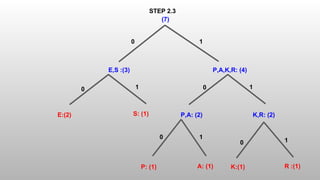
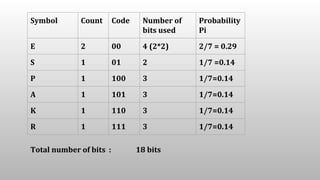
The Shannon-Fano algorithm is a variable-length coding technique developed by Claude Shannon and Robert Fano, which involves sorting symbols by frequency and recursively dividing them to create a binary tree for encoding. An example using the word 'speaker' illustrates the encoding, leading to a compression ratio of 3.11 and an average of 2.57 bits per symbol. The algorithm effectively compresses data while the entropy calculation indicates the minimum bits required to encode each character.


![Compression Ratio
If the total number of bits required to represent the data before compression is B0
and the total number of bits required to represent the data after compression is B1
,
then we define the compression ratio as
Compression Ratio = B0
/ B1
B0
= 8 * 7 Symbols Assume each character symbol require 8 bit
B1
= 18 bits
Compression Ratio = 56/18 = 3.11 [ Positive Compression ]
Average number of bits used by 7 symbols in the above solution = 18 / 7 = 2.57](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shannon-fanoalgorithm-180304074217/85/Shannon-Fano-algorithm-8-320.jpg)
![= 0.29 * log2
(1/0.29) + [ 0.14 * log2
(1/0.14) ] * 5
= 0.29 * log2
(3.45) + [ 0.14 * log2
(7.14) ] * 5
= 0.29 * log2
(3.45) + [ 0.14 * log2
(7.14) ] * 5
= 0.29 * 1.79 + [ 0.14 * 2.84) ] * 5
= 0.52 + 0.40 * 5 = 0.52 + 2.00 = 2.52
This suggests that the minimum average number of bits to code each character in the
word SPEAKER would be at least 2.52. The Shannon-Fano algorithm delivers
satisfactory coding results for data compression.
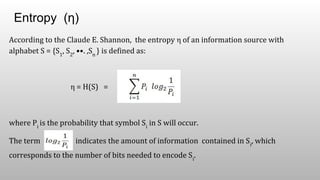
Entropy (η)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shannon-fanoalgorithm-180304074217/85/Shannon-Fano-algorithm-10-320.jpg)
