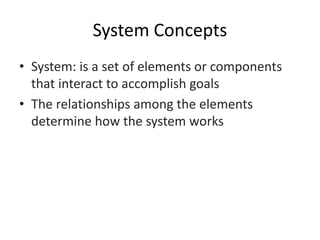
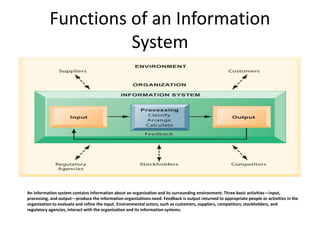
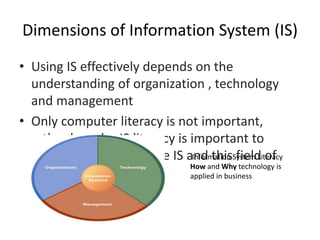
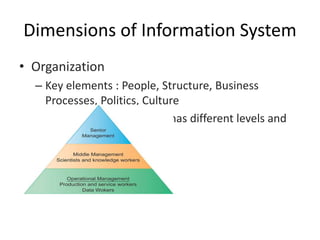
The document provides an overview of information systems in organizations, highlighting their importance in transforming businesses and supporting decision-making. It details the roles of data, information, knowledge, and system concepts, and outlines six strategic business objectives that organizations aim to achieve through effective information systems. Additionally, it discusses globalization's impact on information systems and presents a case study on UPS, illustrating how technology enhances operational excellence and customer intimacy.