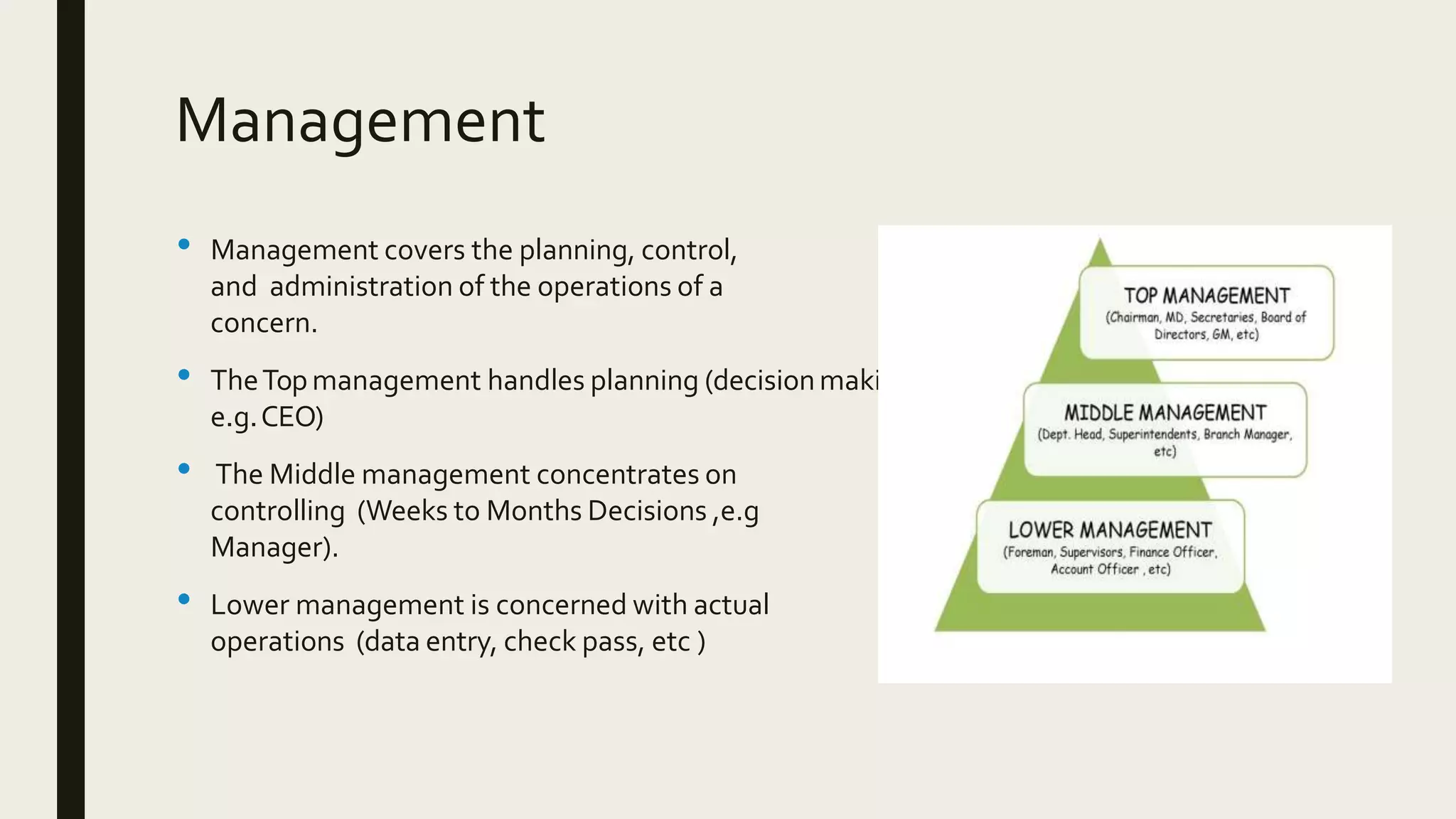
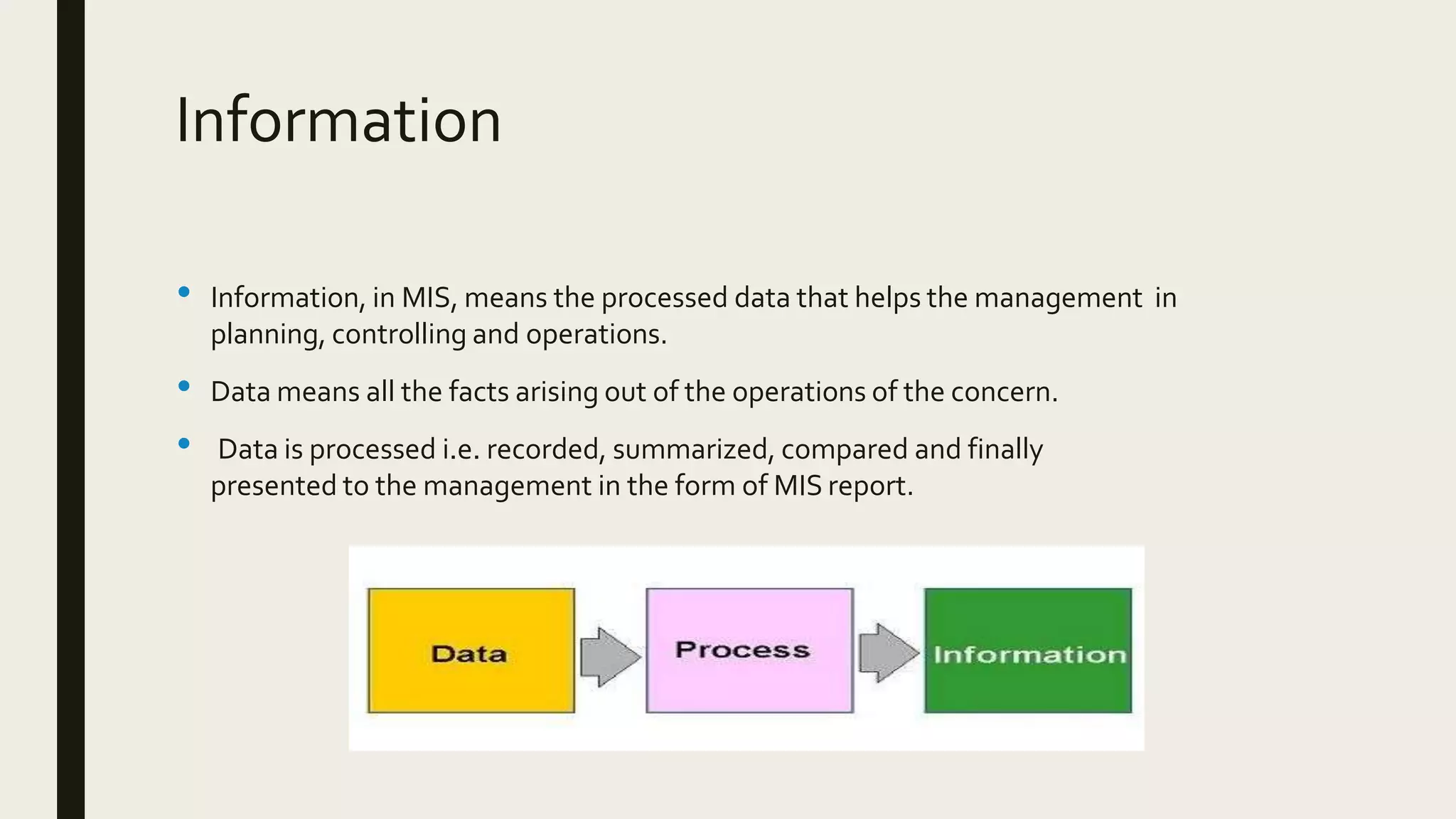
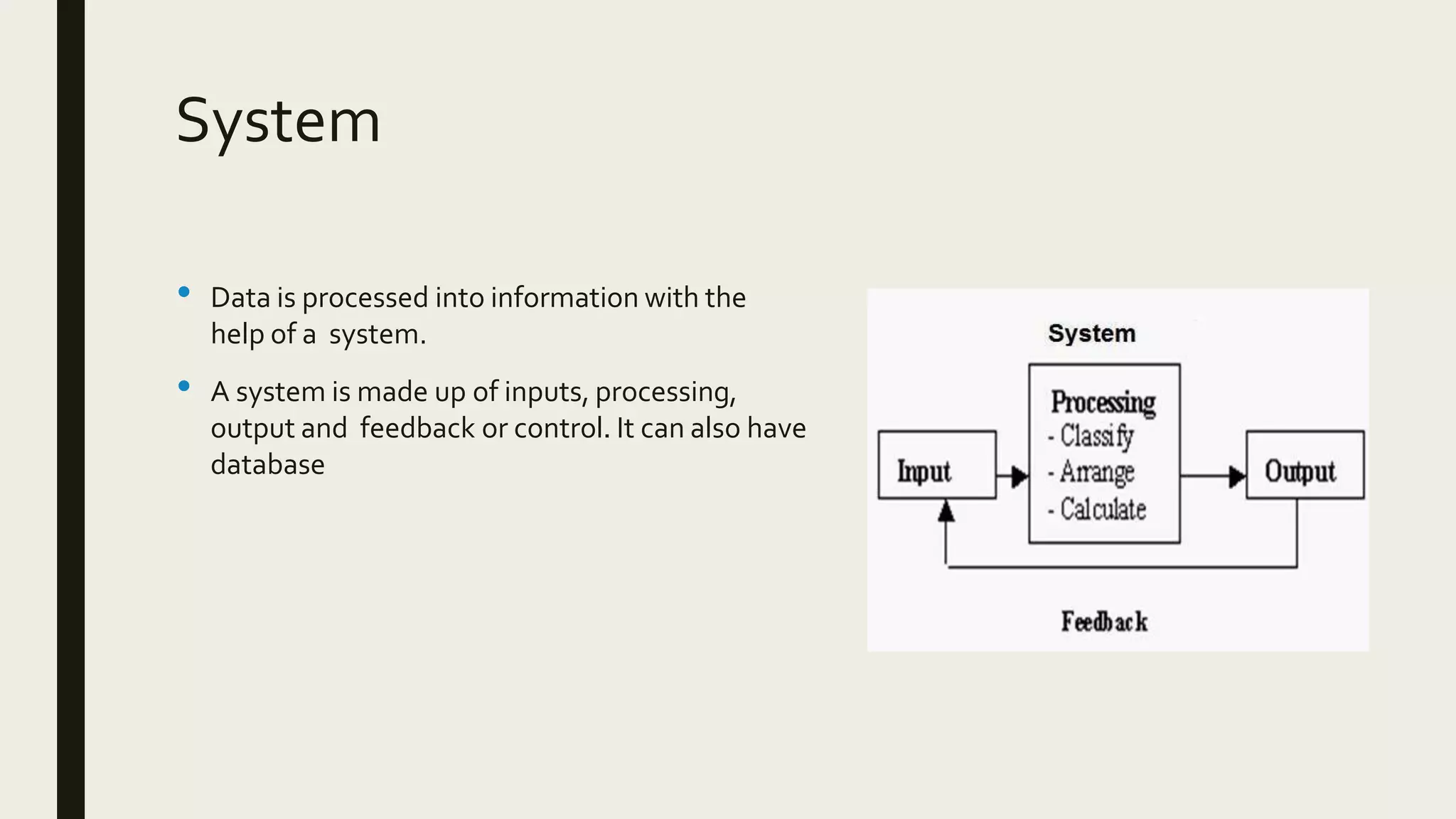
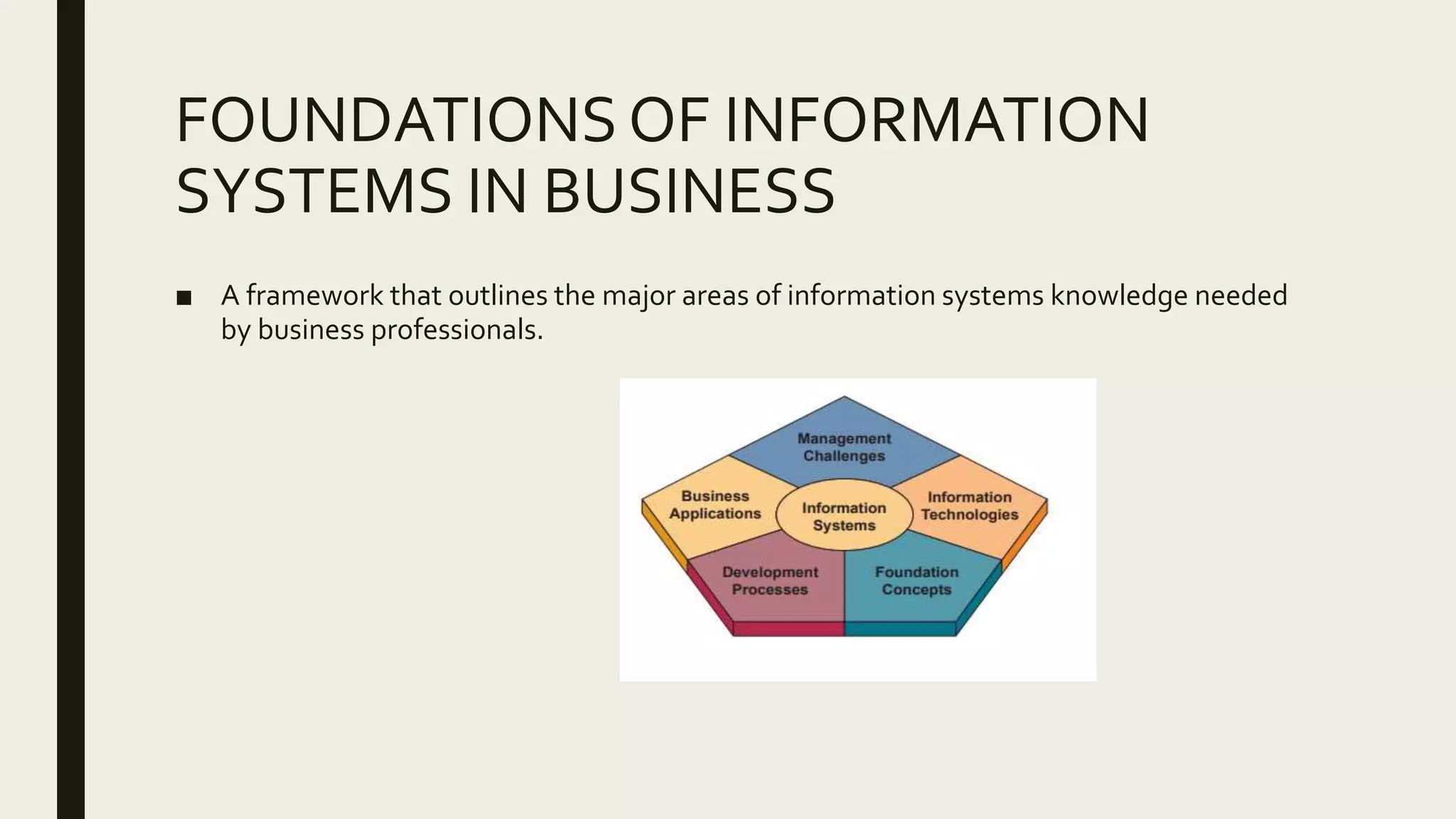
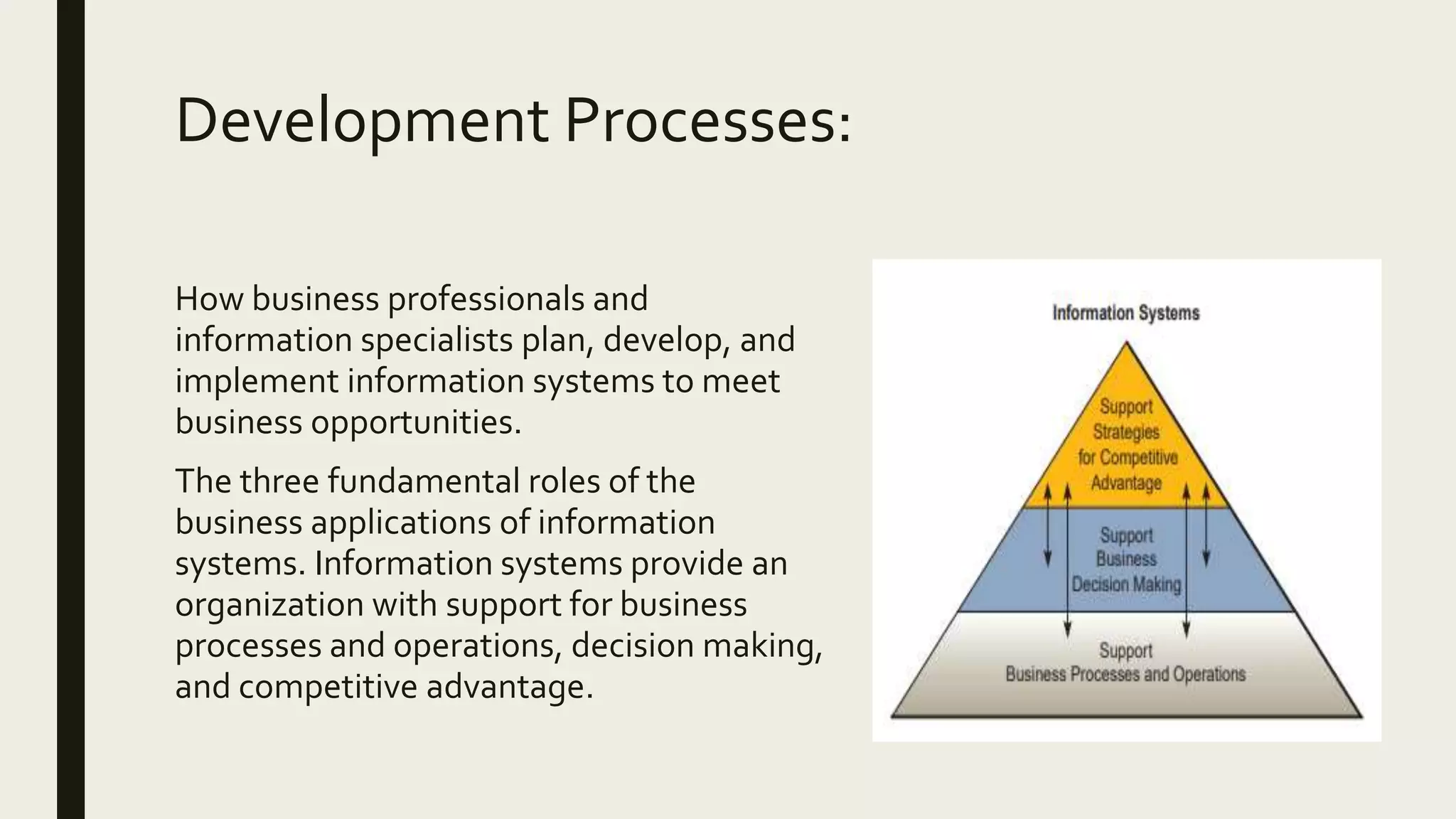
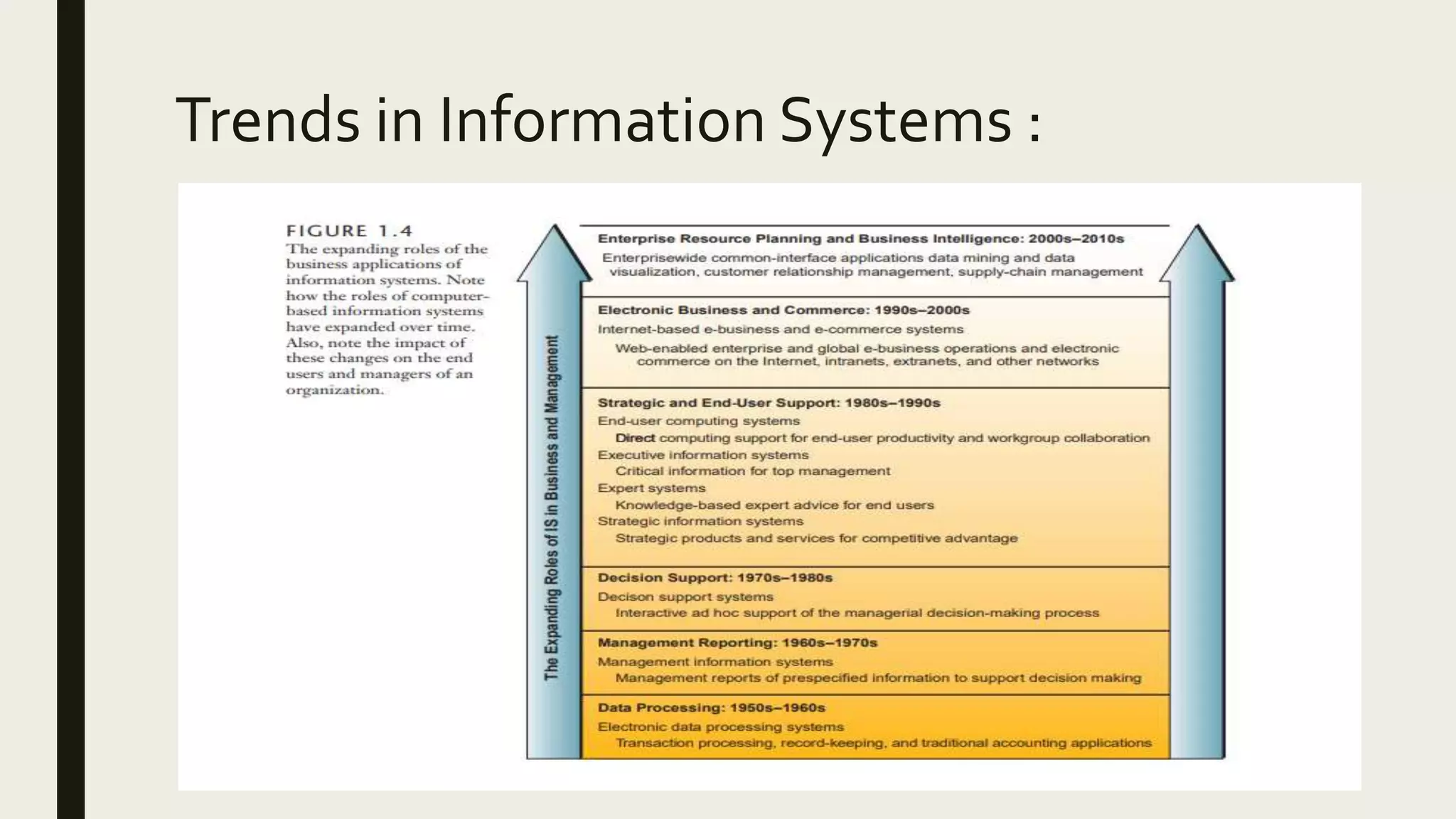
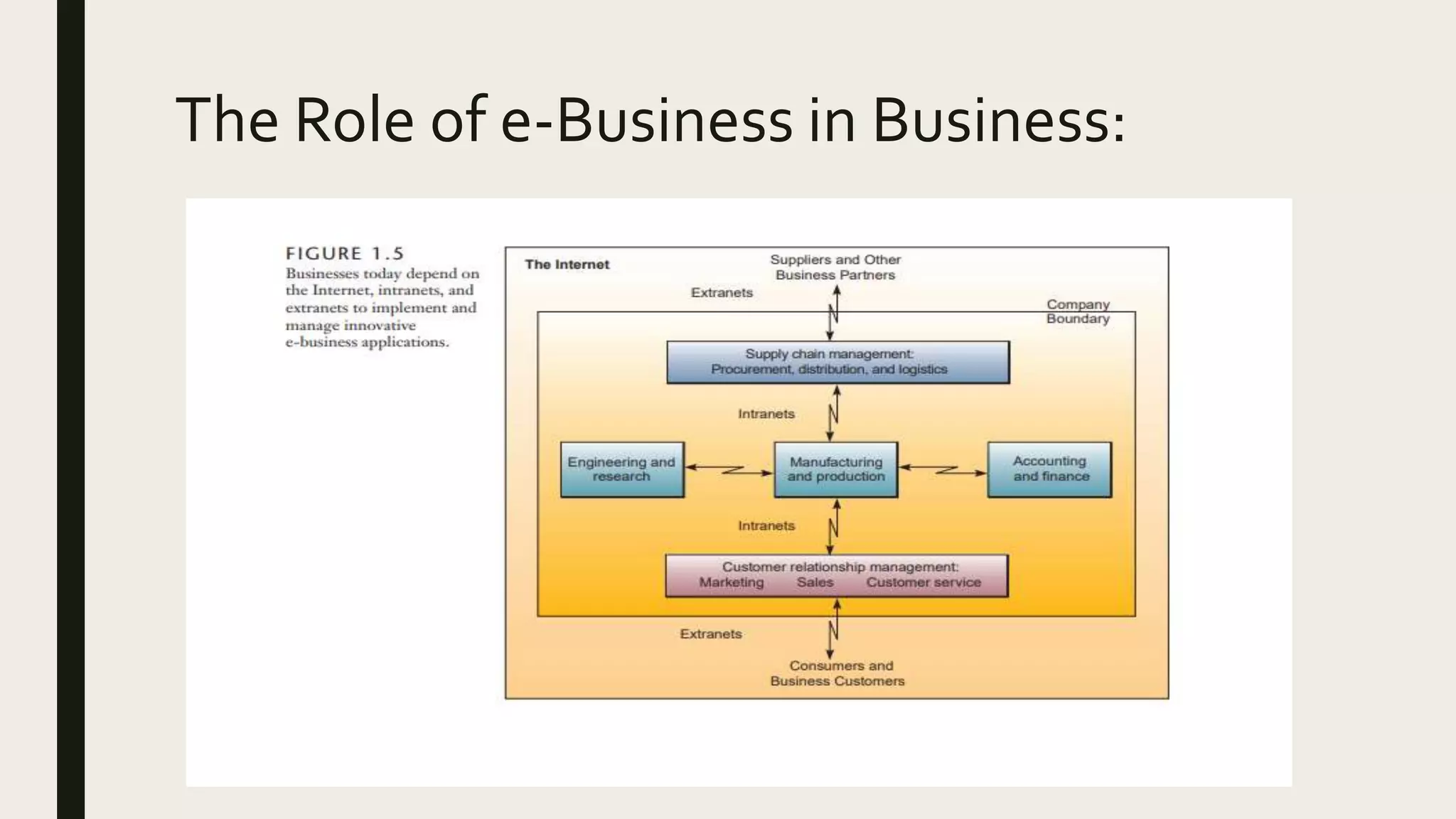
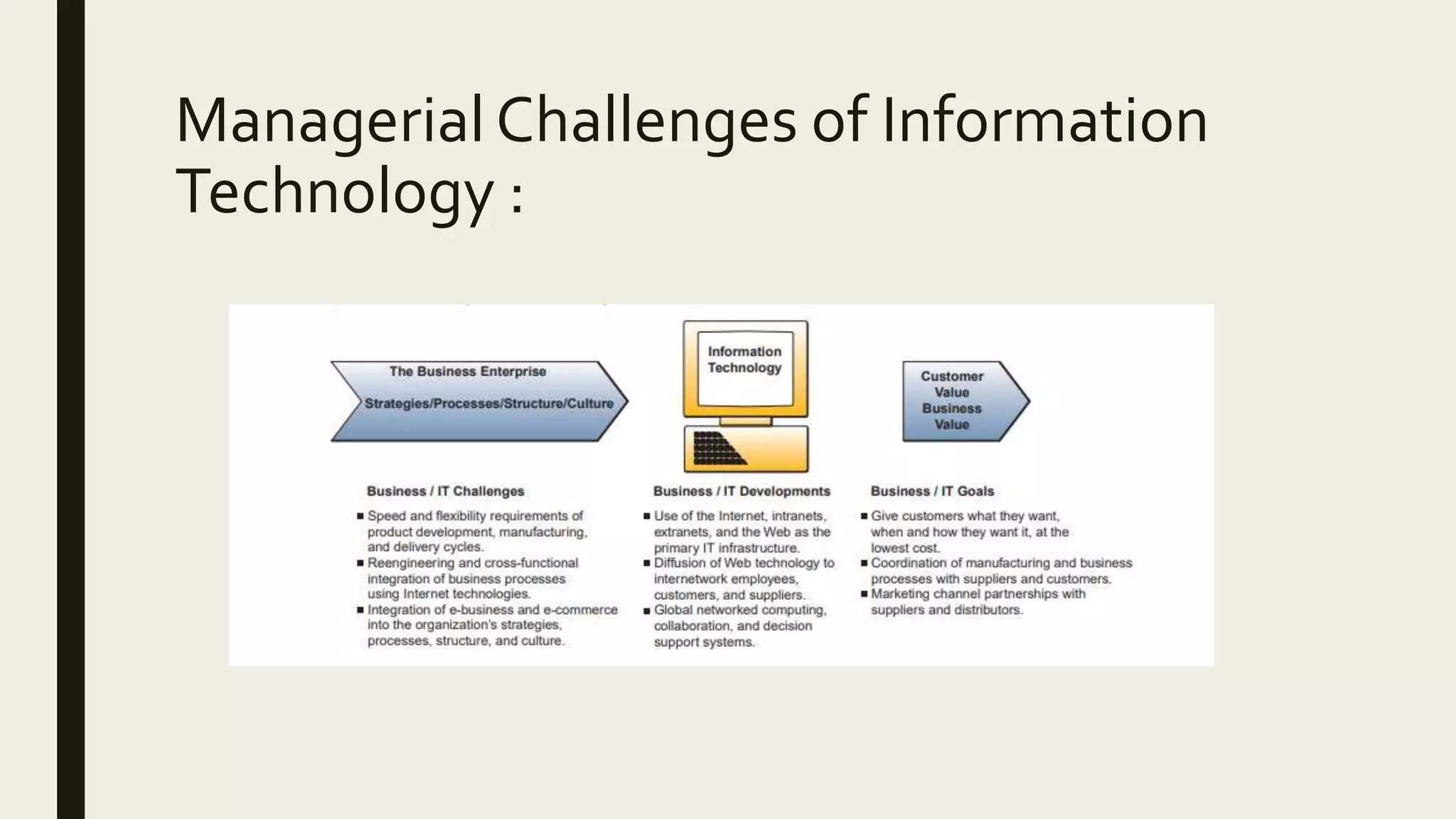
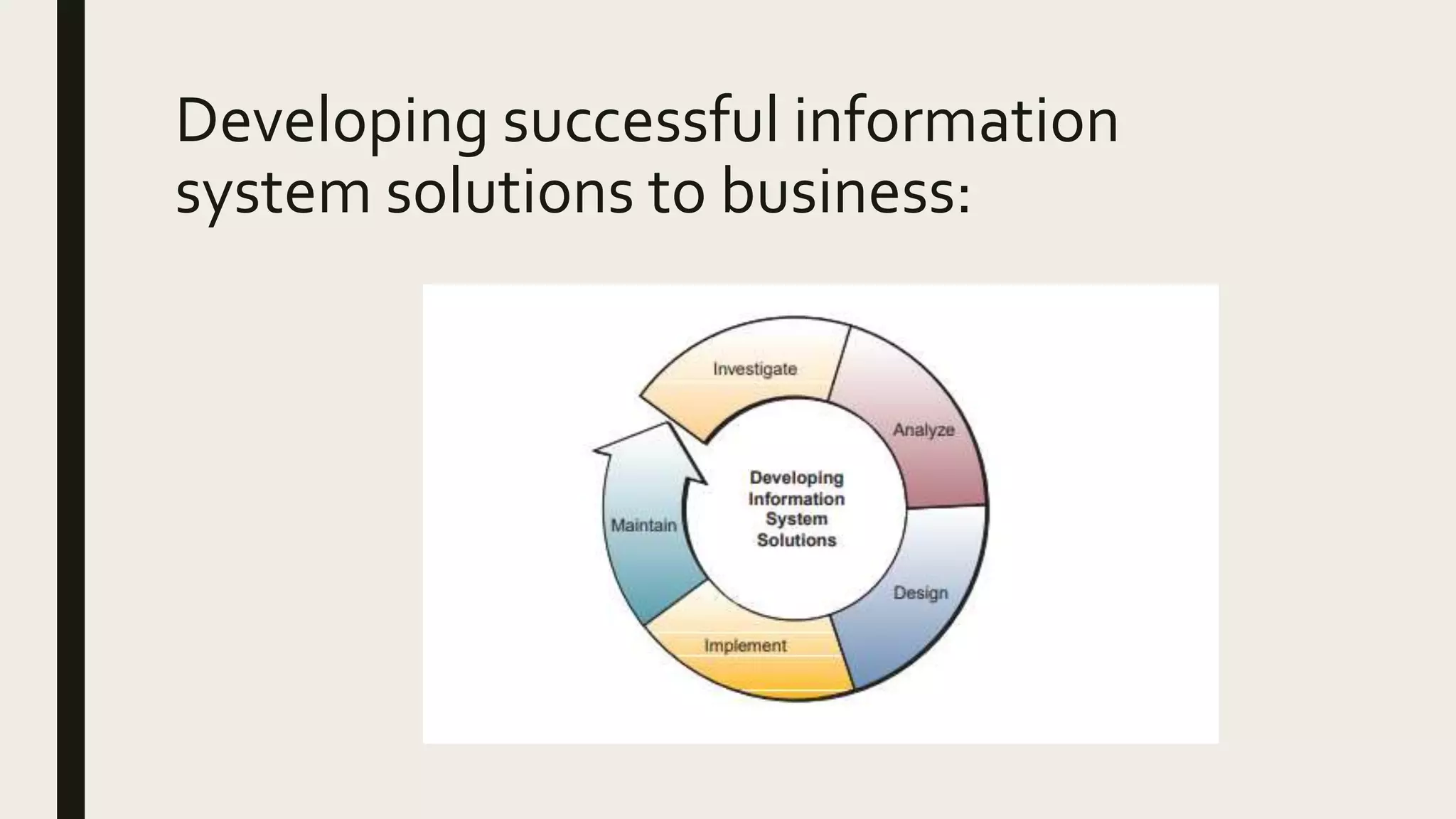
This document provides an introduction to management information systems. It defines MIS as a system that processes data to provide information to management for decision-making. It discusses the three components of MIS: management, information, and system. Management uses the information, information is processed data, and a system is used to process the data into usable information. The document also provides definitions of management, information, and system.