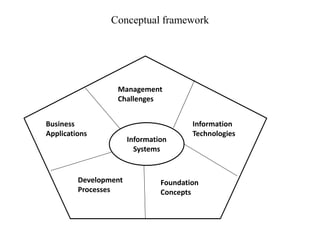
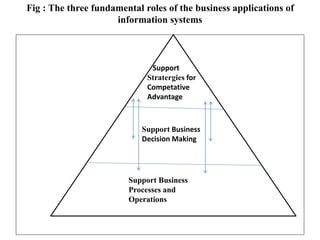
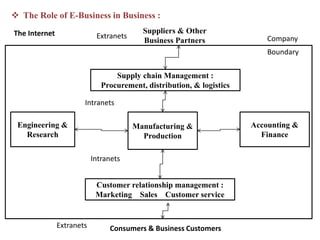
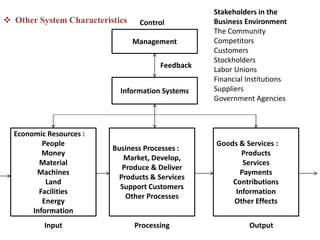
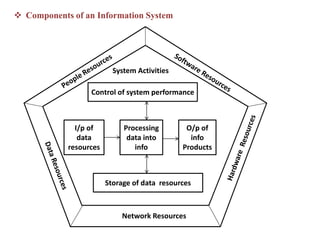
1. An information system is a set of interrelated components that collect, process, store, and distribute information to support decision making and control in an organization. It includes hardware, software, data, people, processes, and technologies.
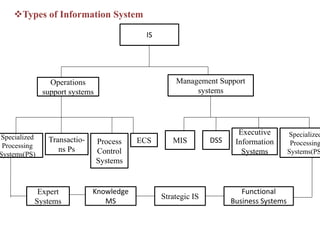
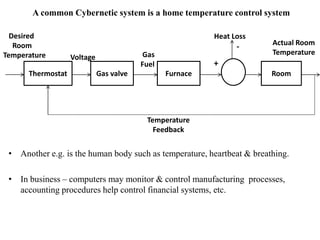
2. Information systems have three main components - input, processing, and output. They also involve feedback and control to monitor performance. Common examples of information systems include transaction processing systems, decision support systems, and executive information systems.
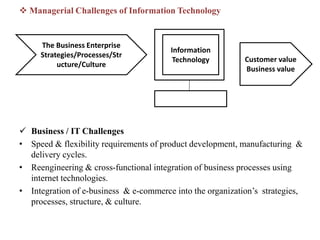
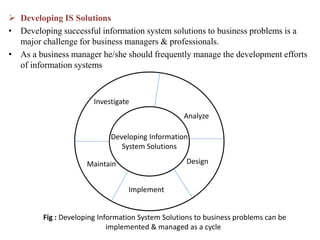
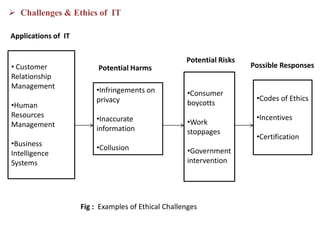
3. Managing information systems effectively presents challenges related to business processes, technology development, goals and ethics. Developing successful information system solutions involves analyzing needs, designing, implementing, and maintaining systems through continuous improvement.