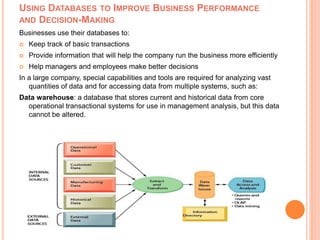
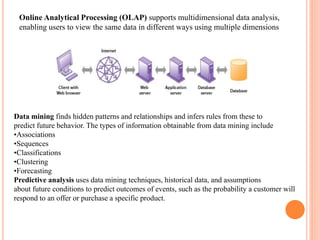
Information technology infrastructure includes physical hardware like transmission lines, routers, and software that manages transmission signals between connected computers and users. It is the integrated framework that digital networks operate on and includes components like data centers, computer networks, databases, and regulatory systems. The seven major coordinated components that make up a firm's IT infrastructure are computer hardware, operating systems, enterprise software, data management and storage, networking and telecommunications platforms, internet platforms, and consulting/integration services.