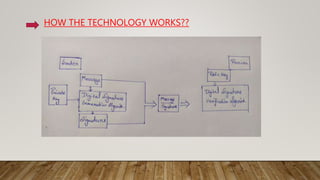
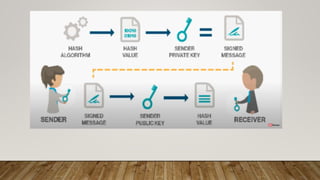
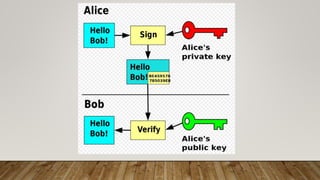
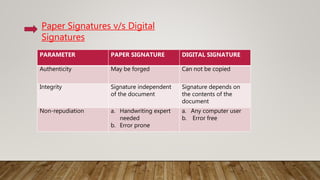
This document discusses digital signatures, which provide authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation for electronic documents. A digital signature is a mathematical scheme that uses public key encryption to verify that a digital message was created by a known sender and was not altered in transit. The document outlines the basic requirements of private and public keys, and how the technology works. It compares digital and paper signatures, and lists some applications of digital signatures such as electronic mail, data storage, and software distribution.