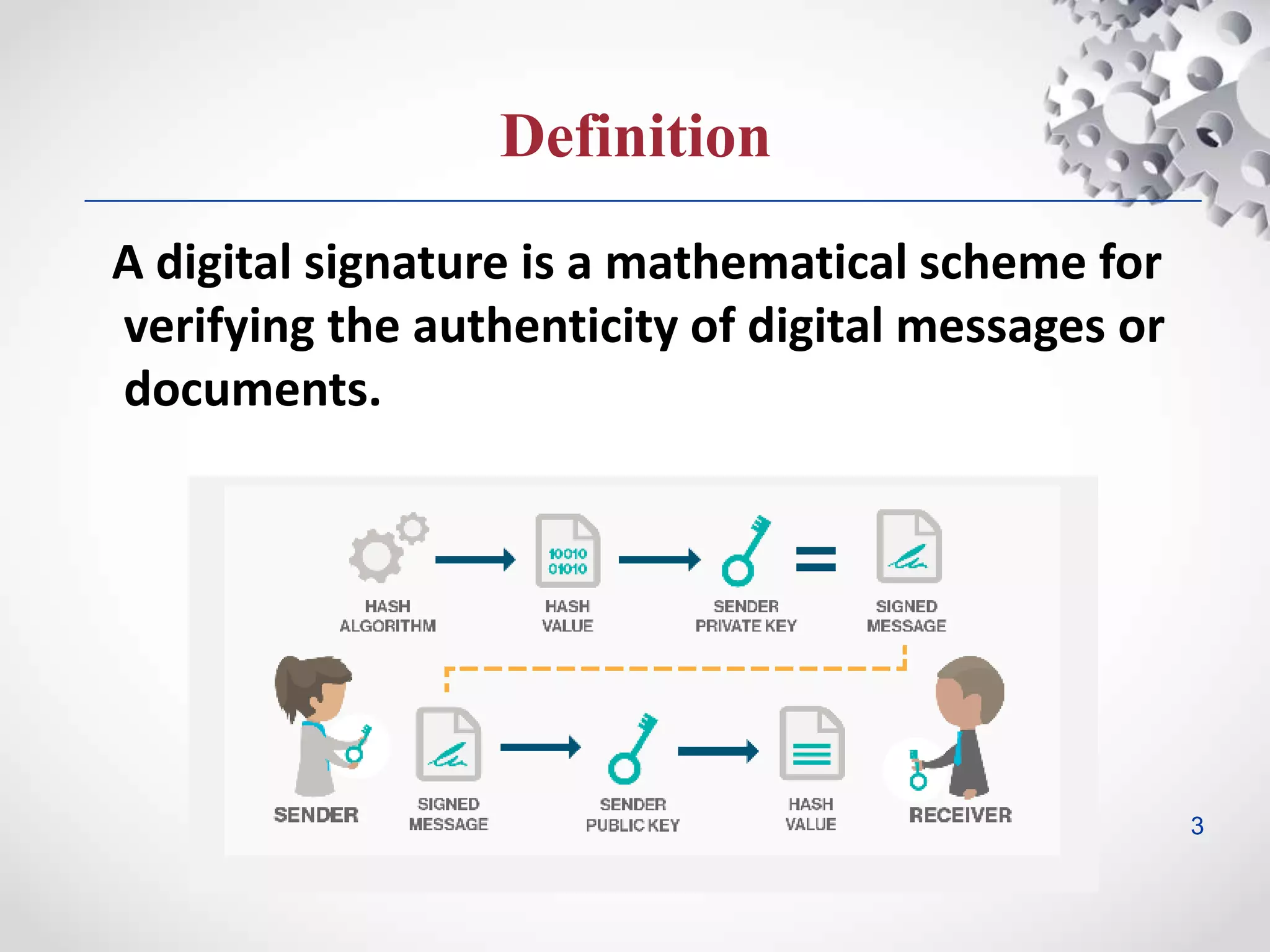
This document provides an overview of digital signatures. It defines a digital signature as a mathematical scheme for verifying the authenticity and integrity of digital messages. The document then discusses how digital signatures work, including the use of hash functions, public key cryptography, digital certificates, and certificate authorities. It explains that digital signatures prove a message was not altered by generating a unique hash of the message encrypted with the sender's private key, which the recipient can then use the sender's public key to decrypt and compare against their own hash of the message. If the hashes match, the signature is validated.