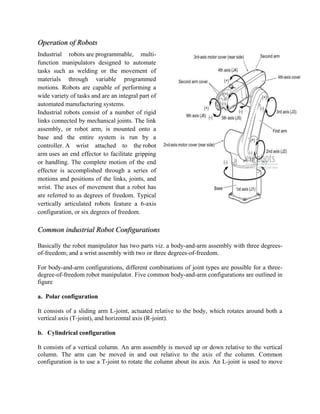
This document provides an overview of industrial robots, detailing their operation, types, and applications in modern industries. It defines industrial robots as programmable manipulators used for tasks such as welding and material handling, with advantages including increased quality and efficiency, but also noting disadvantages like job loss and high costs. The document further outlines five popular applications of industrial robots, including handling operations and welding.