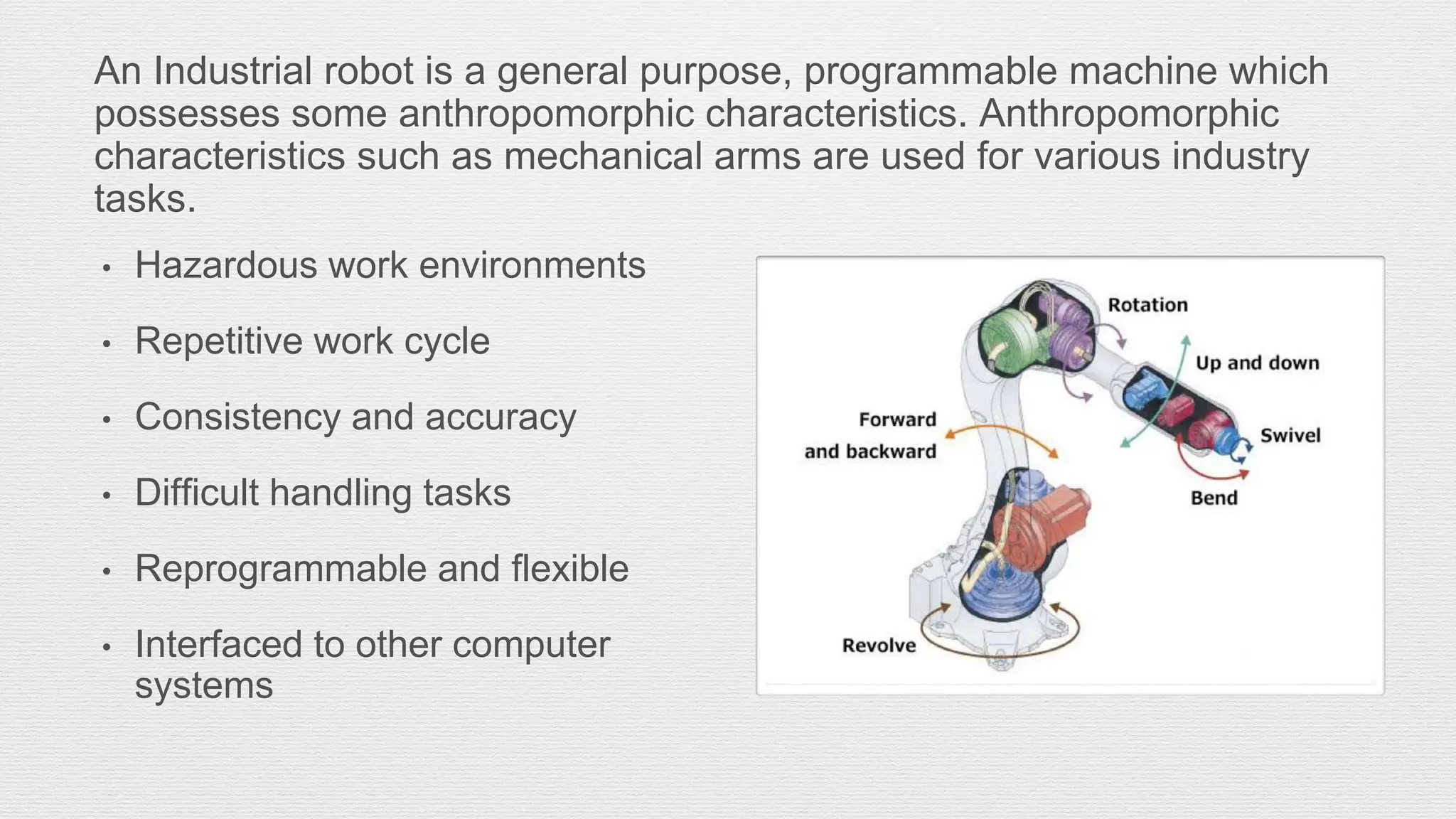
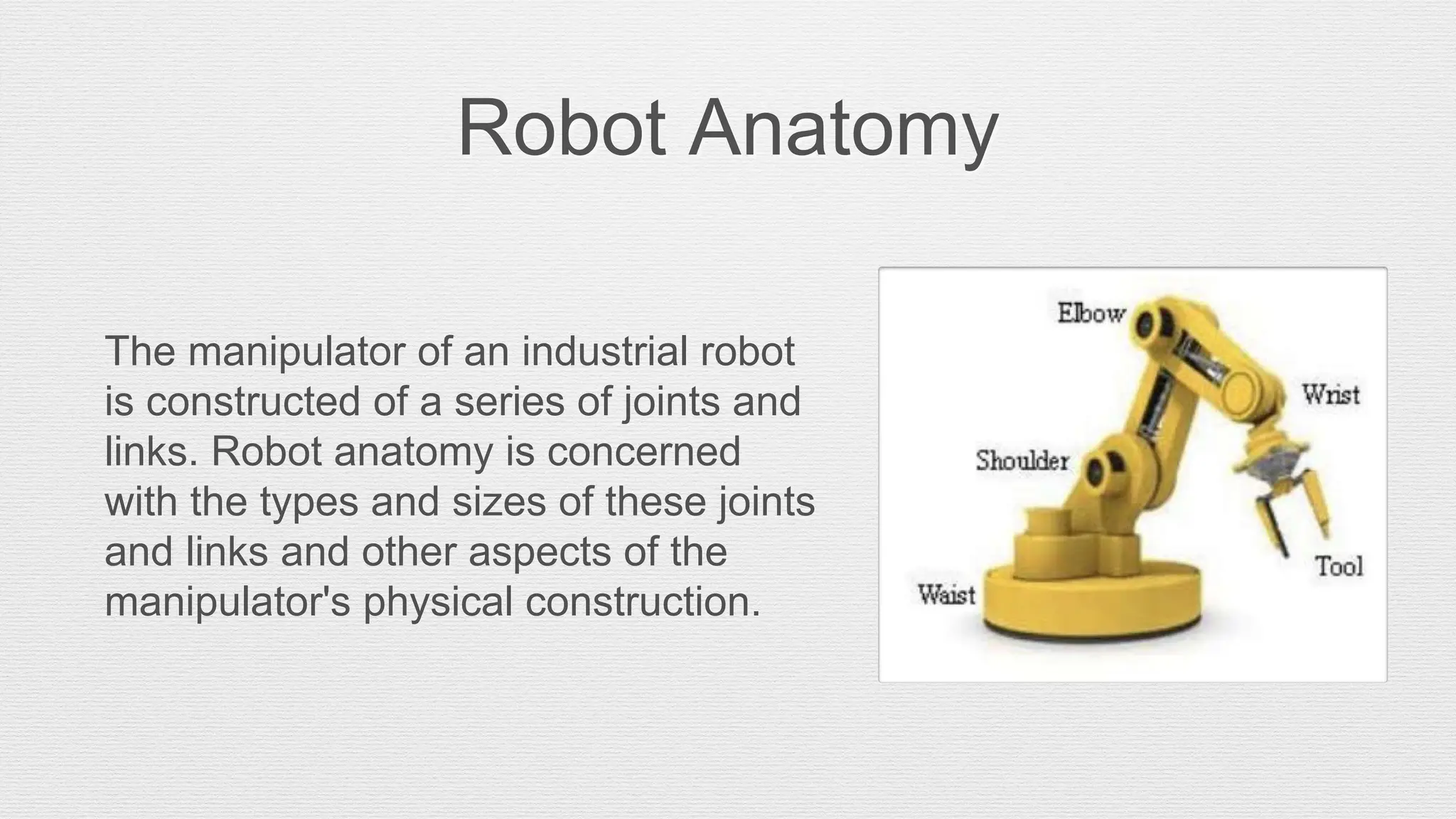
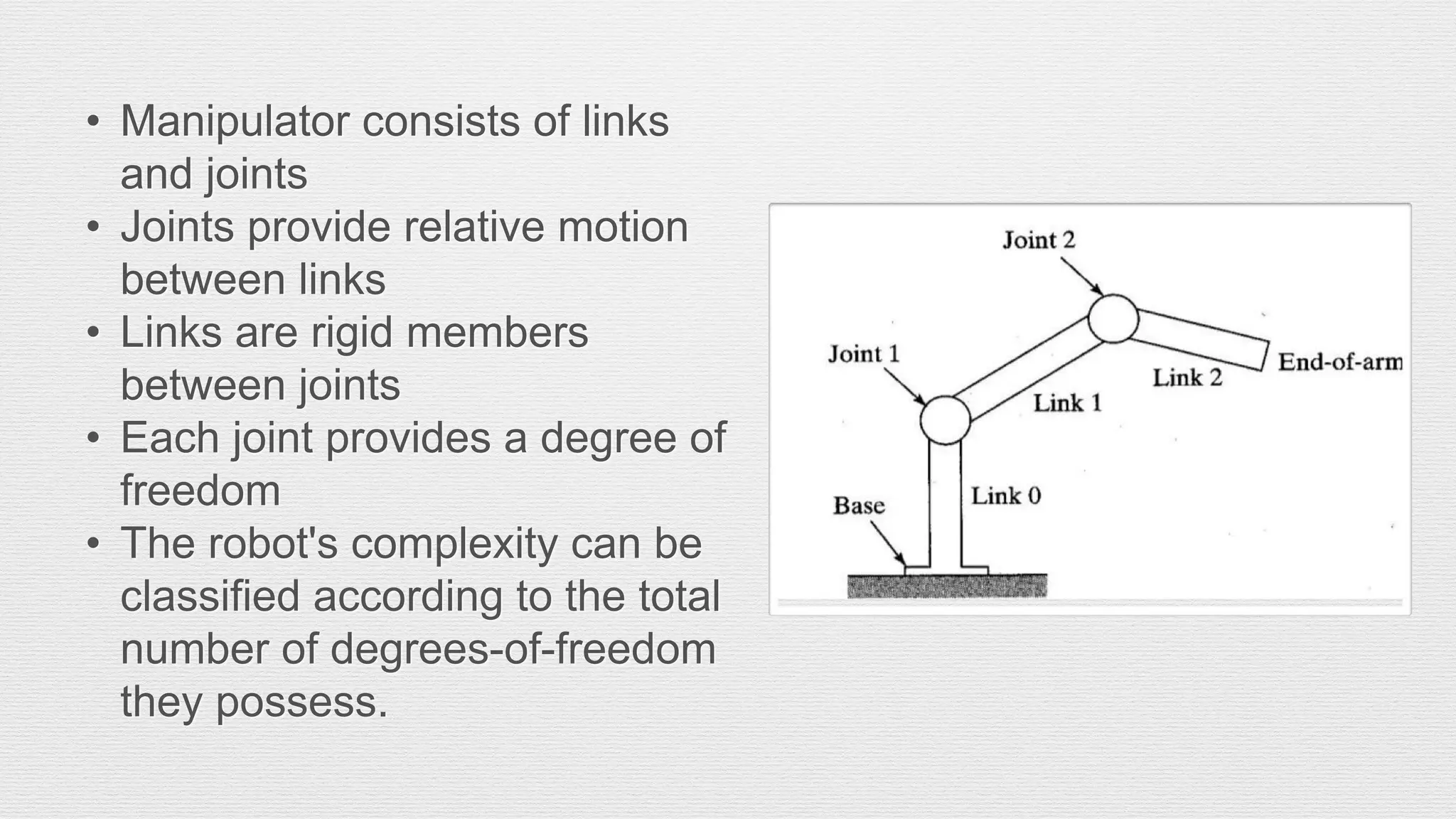
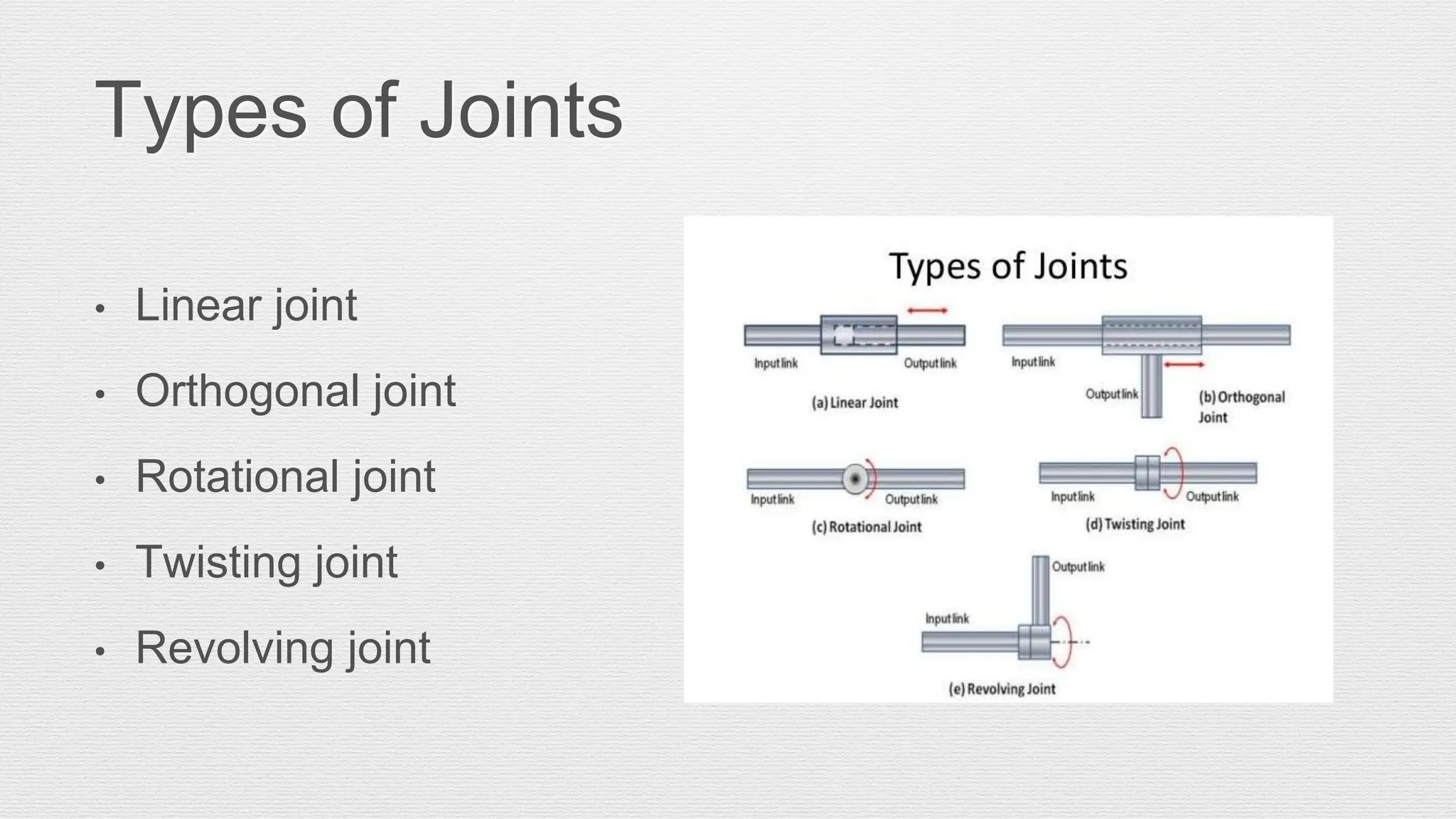
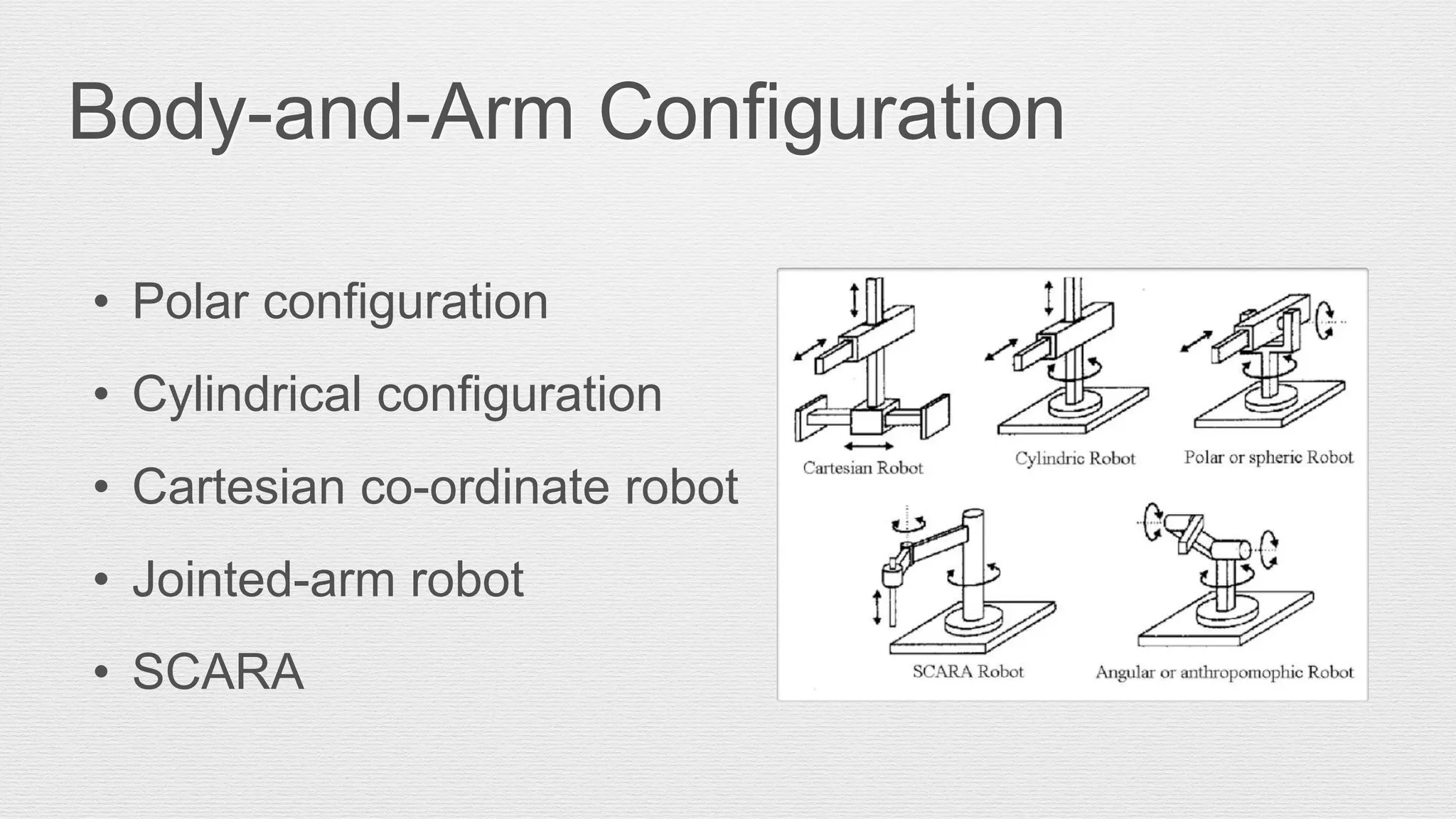
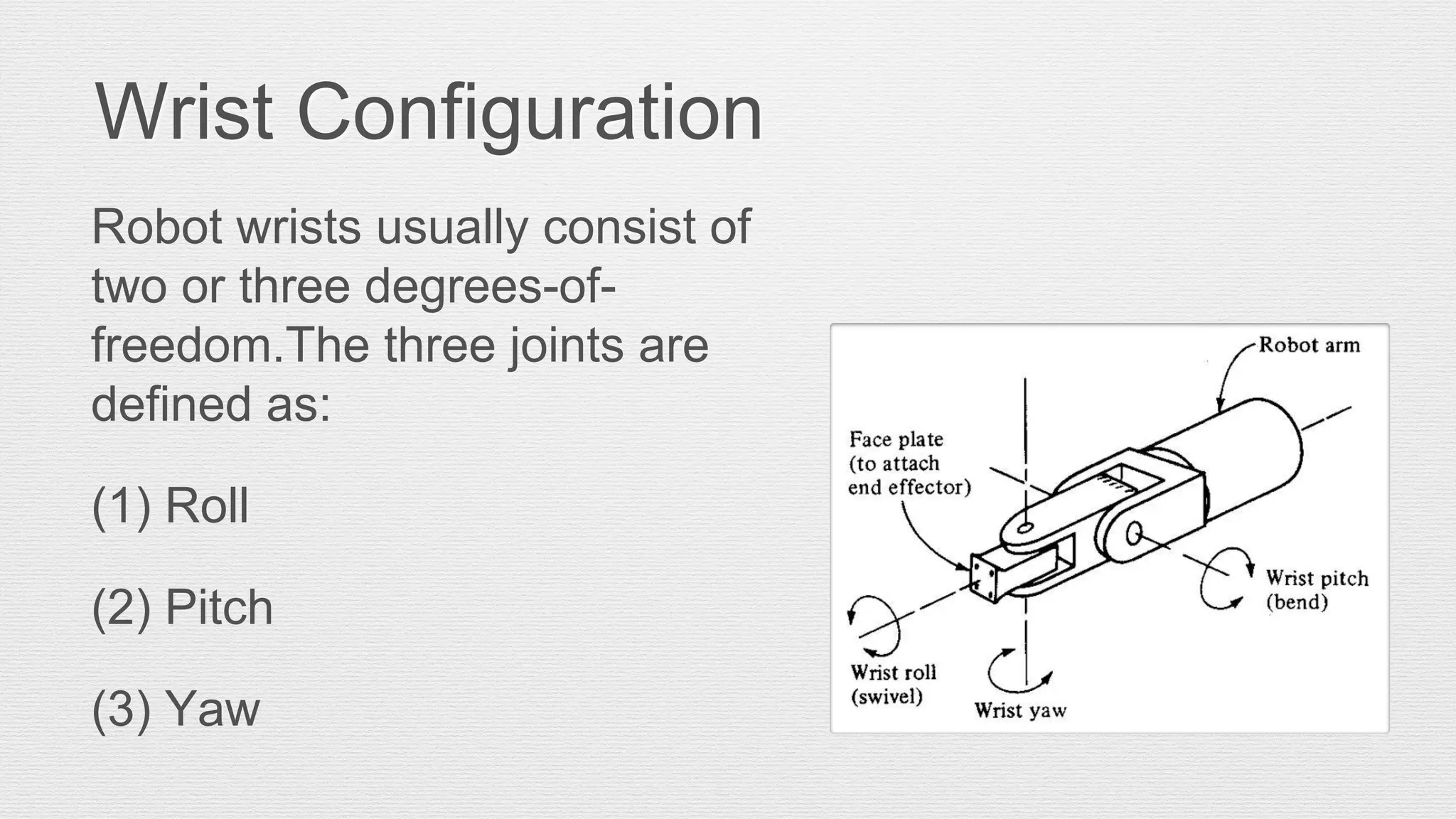
Robotics is an engineering and science field focused on the design, operation, and manufacture of robots, often inspired by nature. Robots are utilized in hazardous environments for tasks requiring precision and repeatability, and can be reprogrammed for various functions. The anatomy of robots includes components like manipulators, sensors, actuators, and various joint configurations, with common applications in industries such as automotive for welding and assembly.