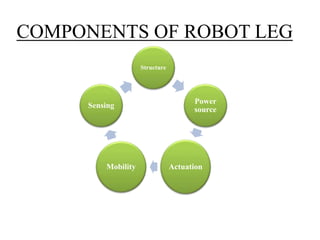
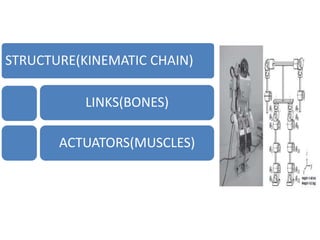
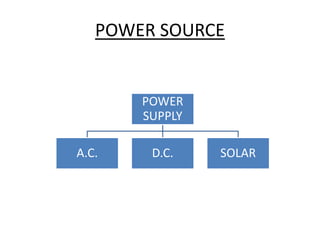
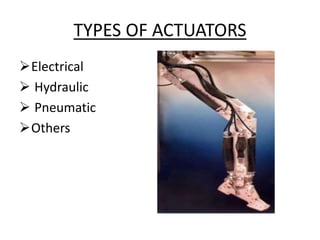
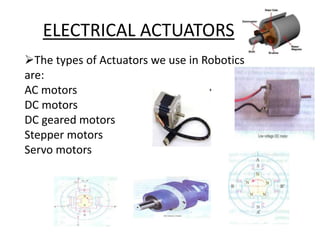
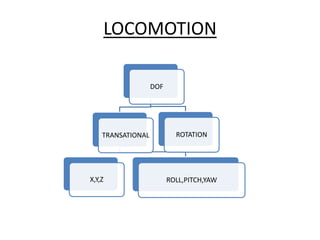
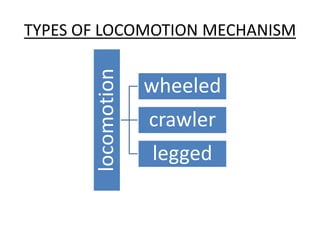
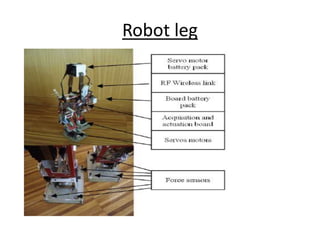
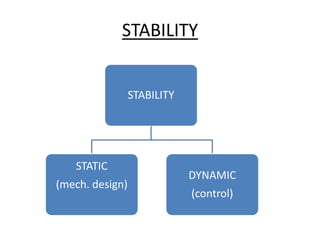
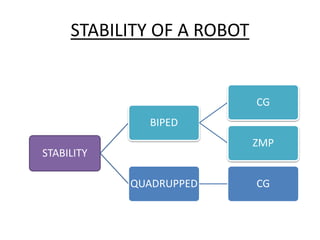
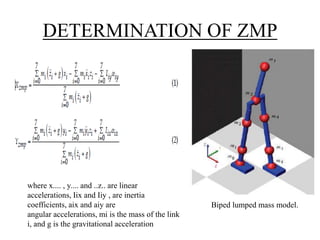
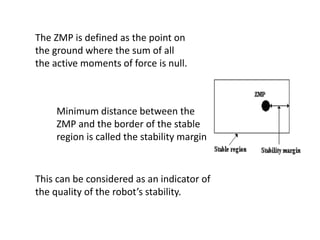
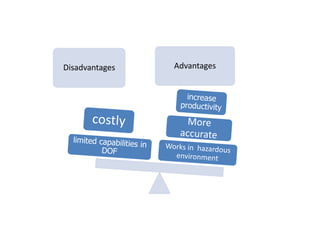
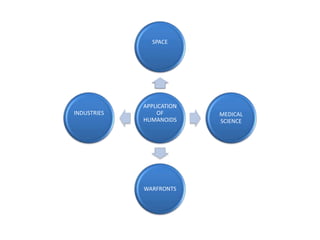
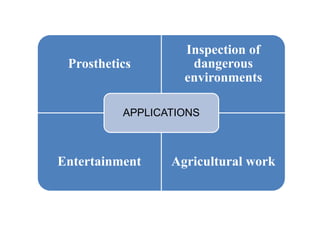
The document discusses the components and mechanisms of robot leg structures, highlighting types of actuators (including electrical, hydraulic, and pneumatic), various sensors, and control systems like PID. It also covers locomotion types and stability aspects of humanoid robots, mentioning the Zero Moment Point (ZMP) and its importance in assessing a robot's stability. Finally, the document outlines the applications of humanoids across various fields like space, medical sciences, and entertainment.