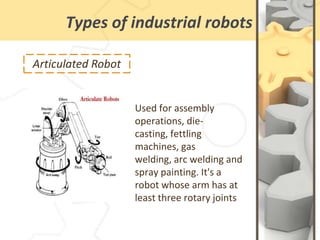
This document defines robots and describes different types of industrial robots. It begins by defining a robot as a machine that can carry out complex actions automatically through programming to resemble human movements and functions. The main components of a robot are then outlined as the robot arms, sensors, end parts, controller, and drive. Several common types of industrial robots are also described, including Cartesian, cylindrical, spherical/polar, SCARA, articulated, and parallel robots. Each robot type is suited for different assembly or manufacturing tasks.