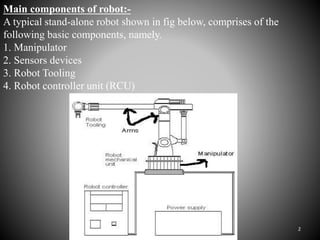
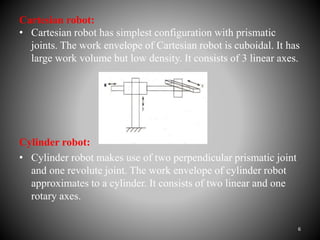
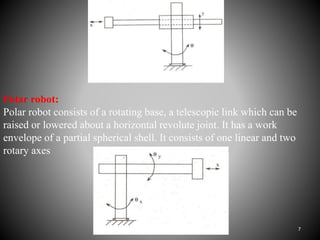
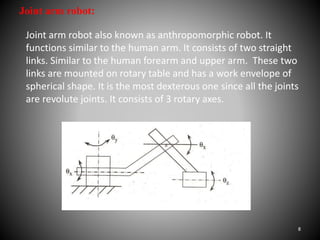
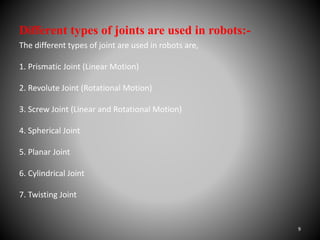
The document summarizes the main components of a typical robot, including the manipulator, sensors, robot tooling, and robot controller unit. It describes the manipulator as consisting of linkages, joints, and end effectors that are activated by signals from the controller. Sensors provide information to the controller about the status of the manipulator. The robot tooling, or end effectors, can be designed depending on the task. The robot controller unit converts input programs into signals to activate the manipulator. Different types of robot arms are described, including Cartesian, cylinder, polar, and joint arm robots.