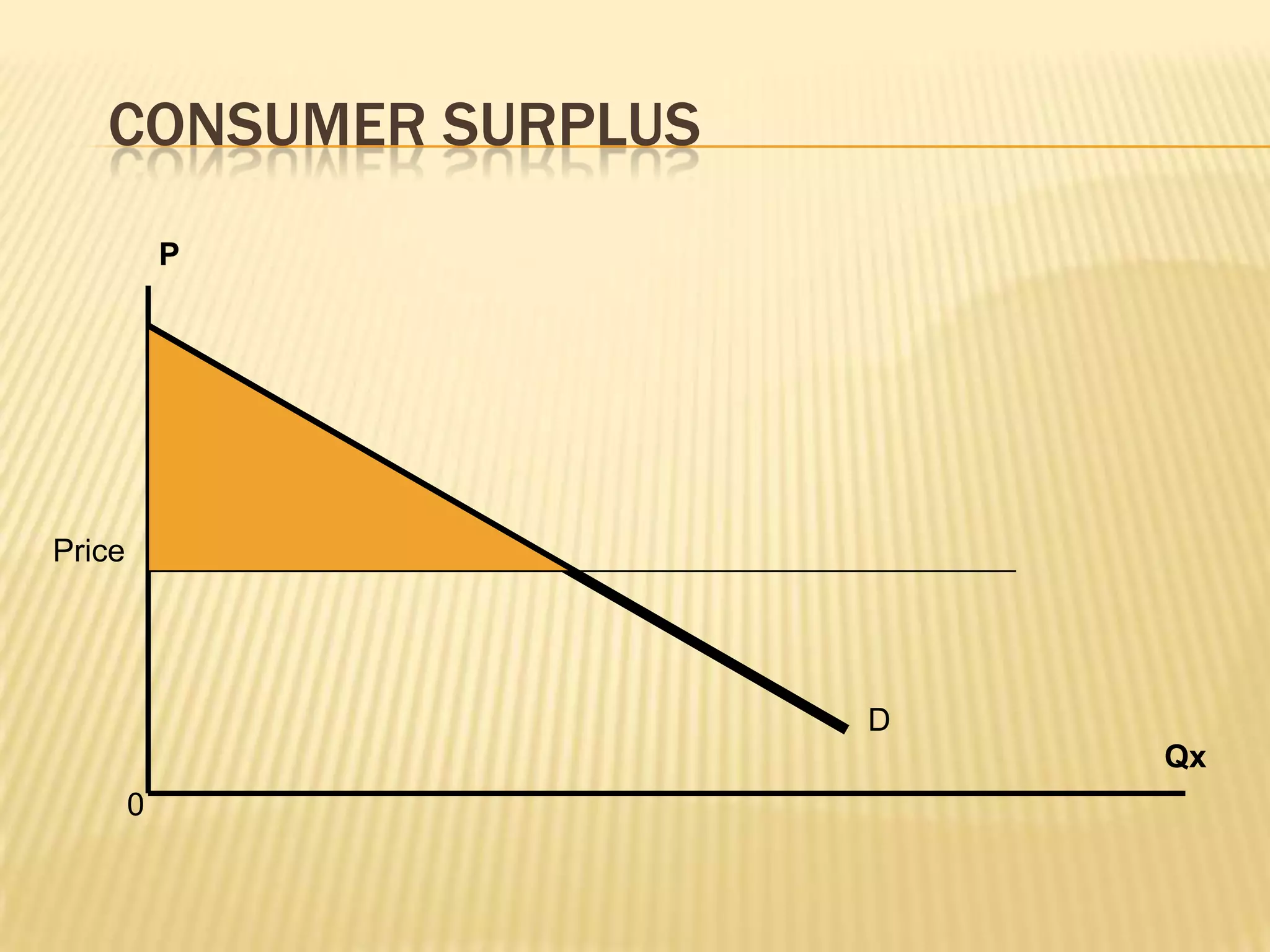
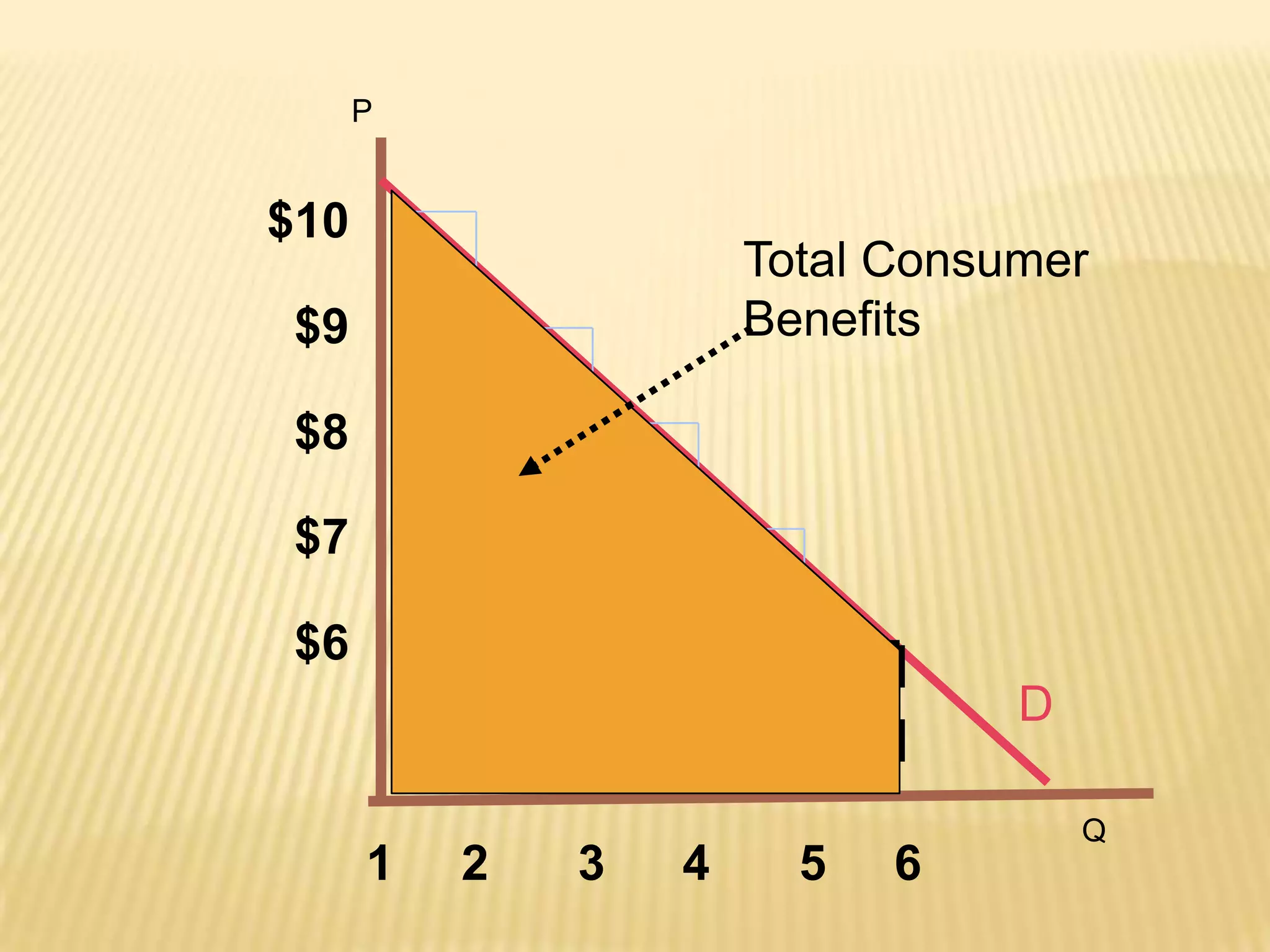
1) Consumer surplus measures how much better off consumers are from purchasing goods that provide them utility, which is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and the actual price they pay.
2) Consumer surplus can be measured for each unit purchased and is the total surplus from summing the surplus of each individual unit.
3) Graphically, consumer surplus is represented by the area above the price line and below the demand curve up to the quantity purchased. A lower price increases consumer surplus while a higher price decreases it.