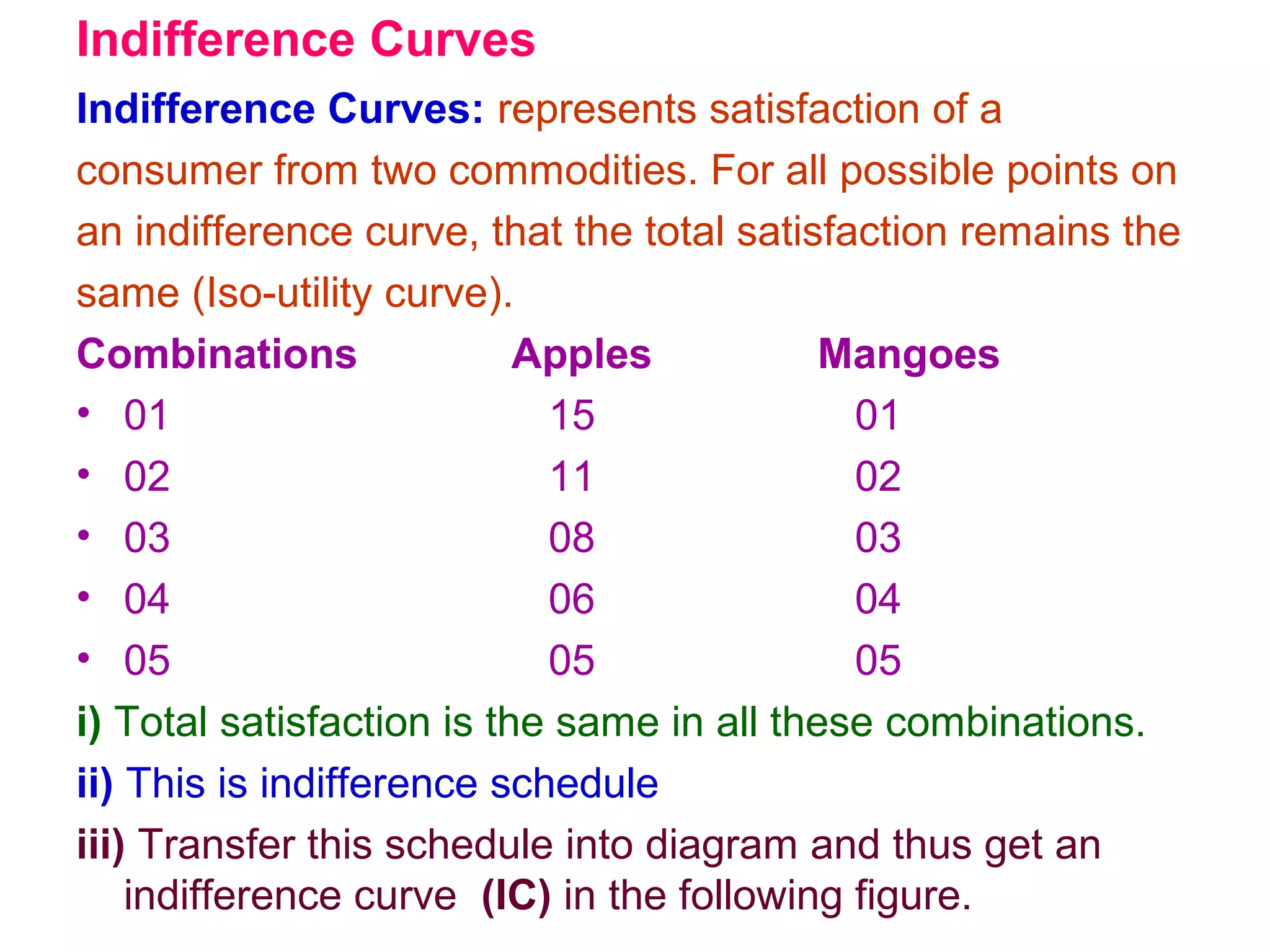
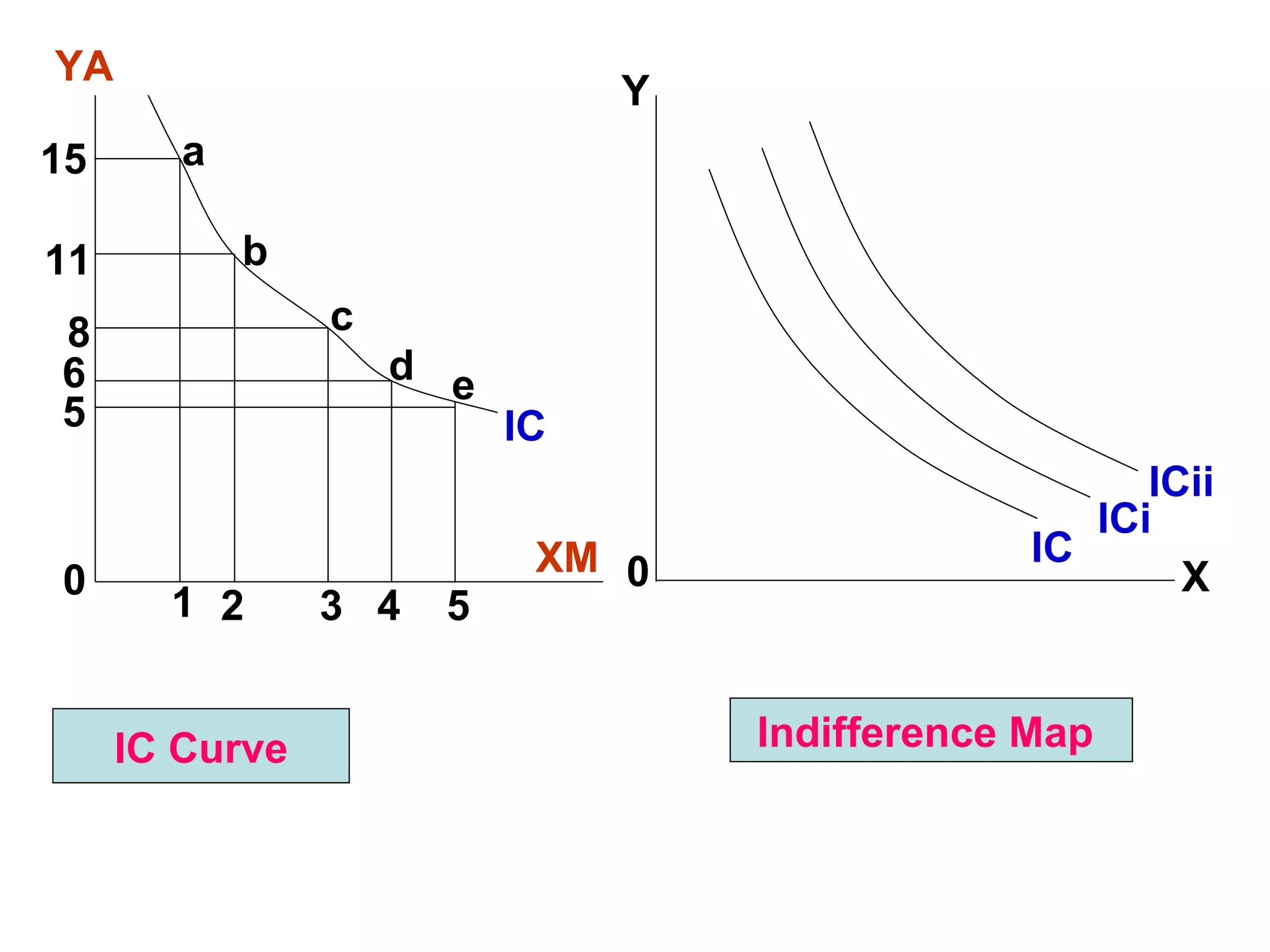
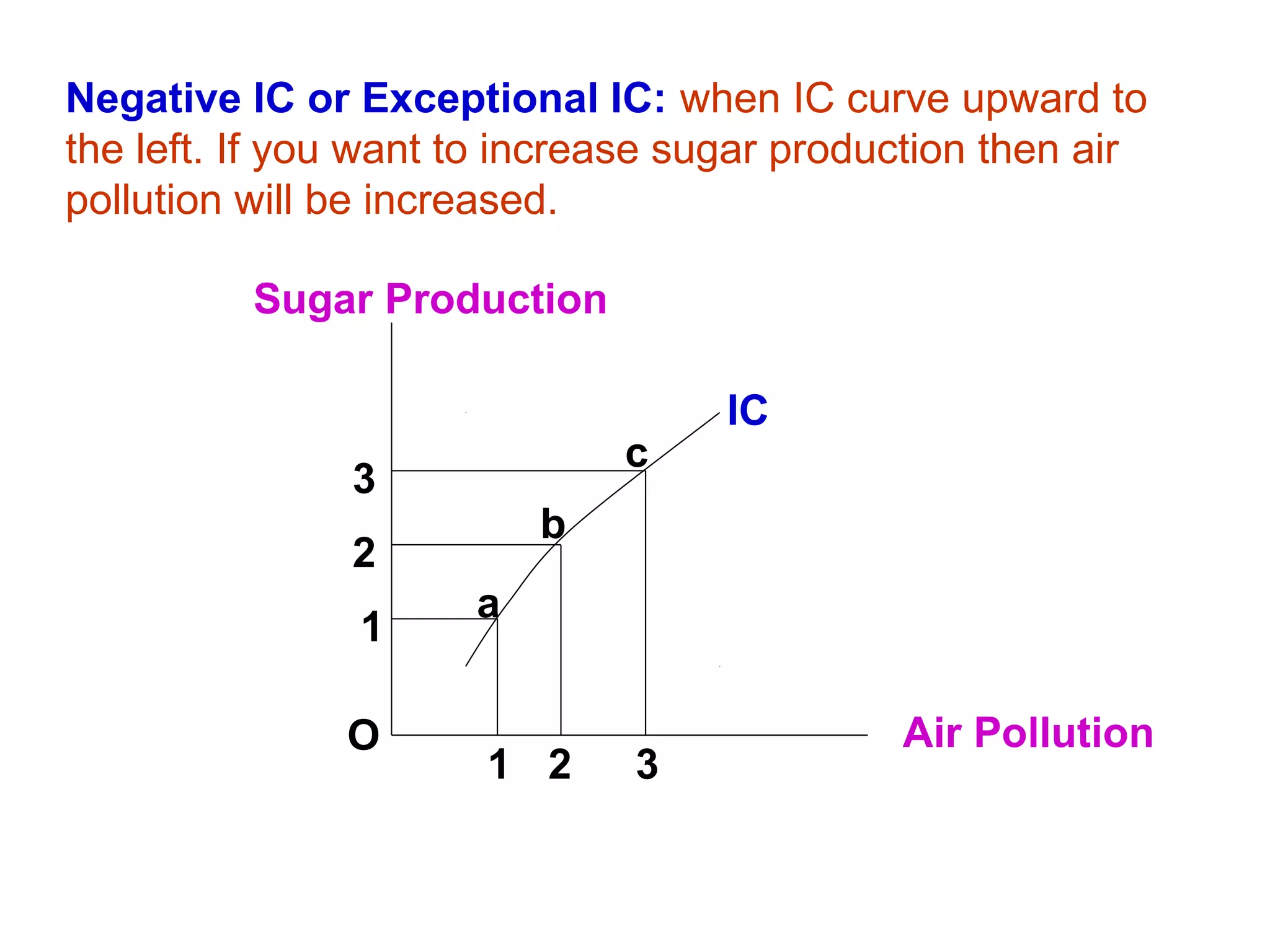
i) Indifference curve analysis examines how consumers develop preferences among alternatives based on factors like income, tastes, and marketing. It represents equal satisfaction from different combinations of two goods using indifference curves.
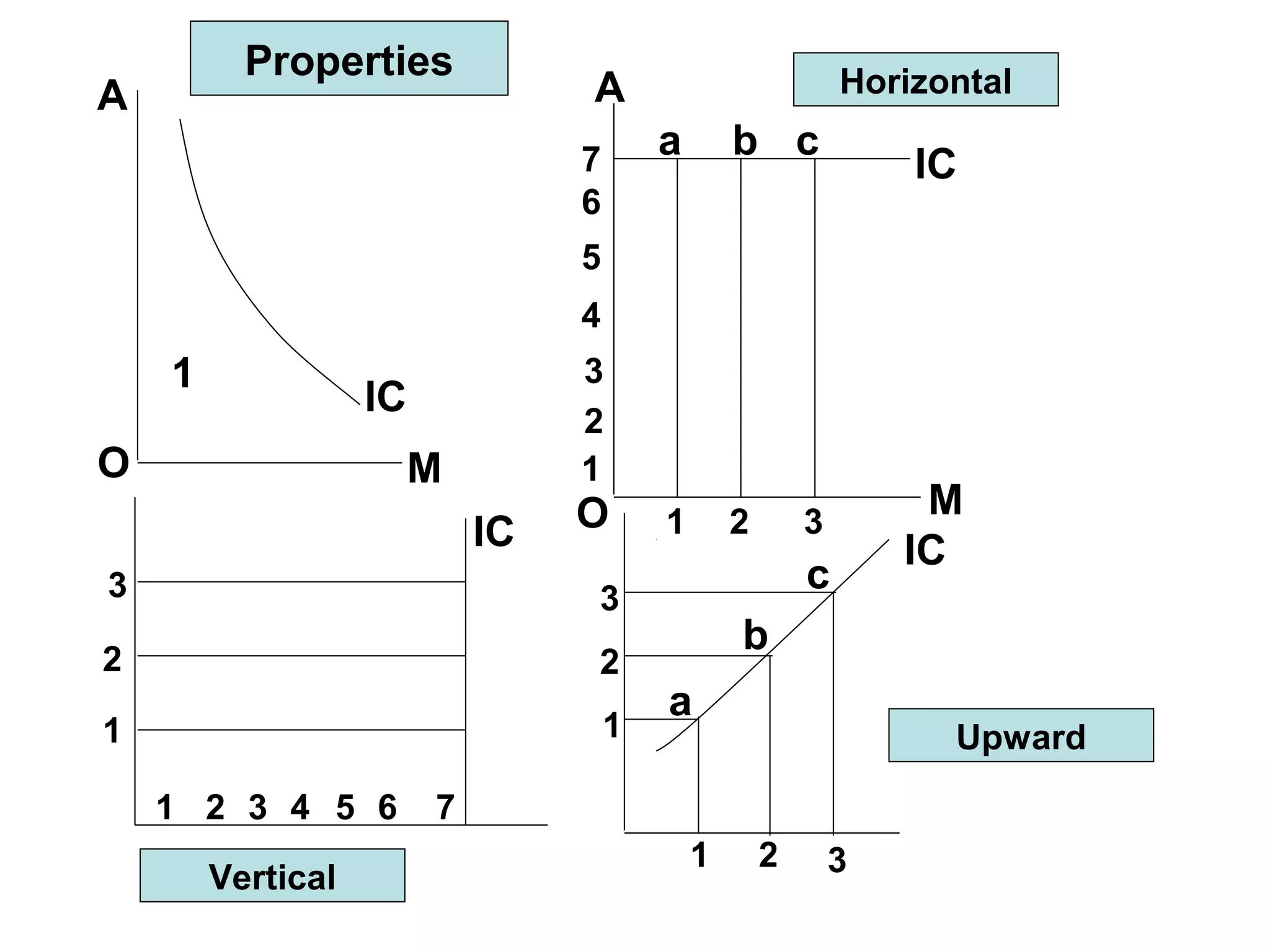
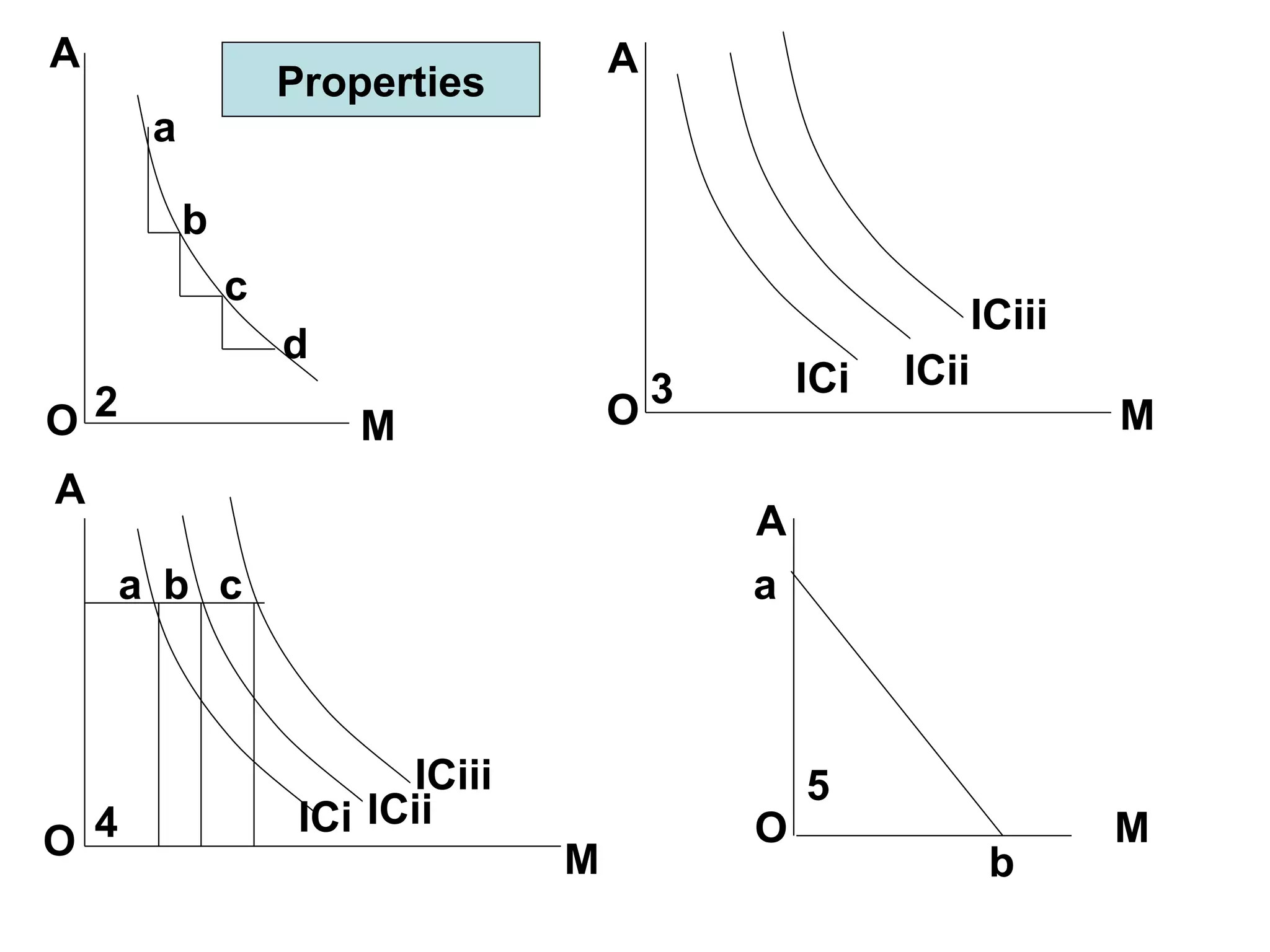
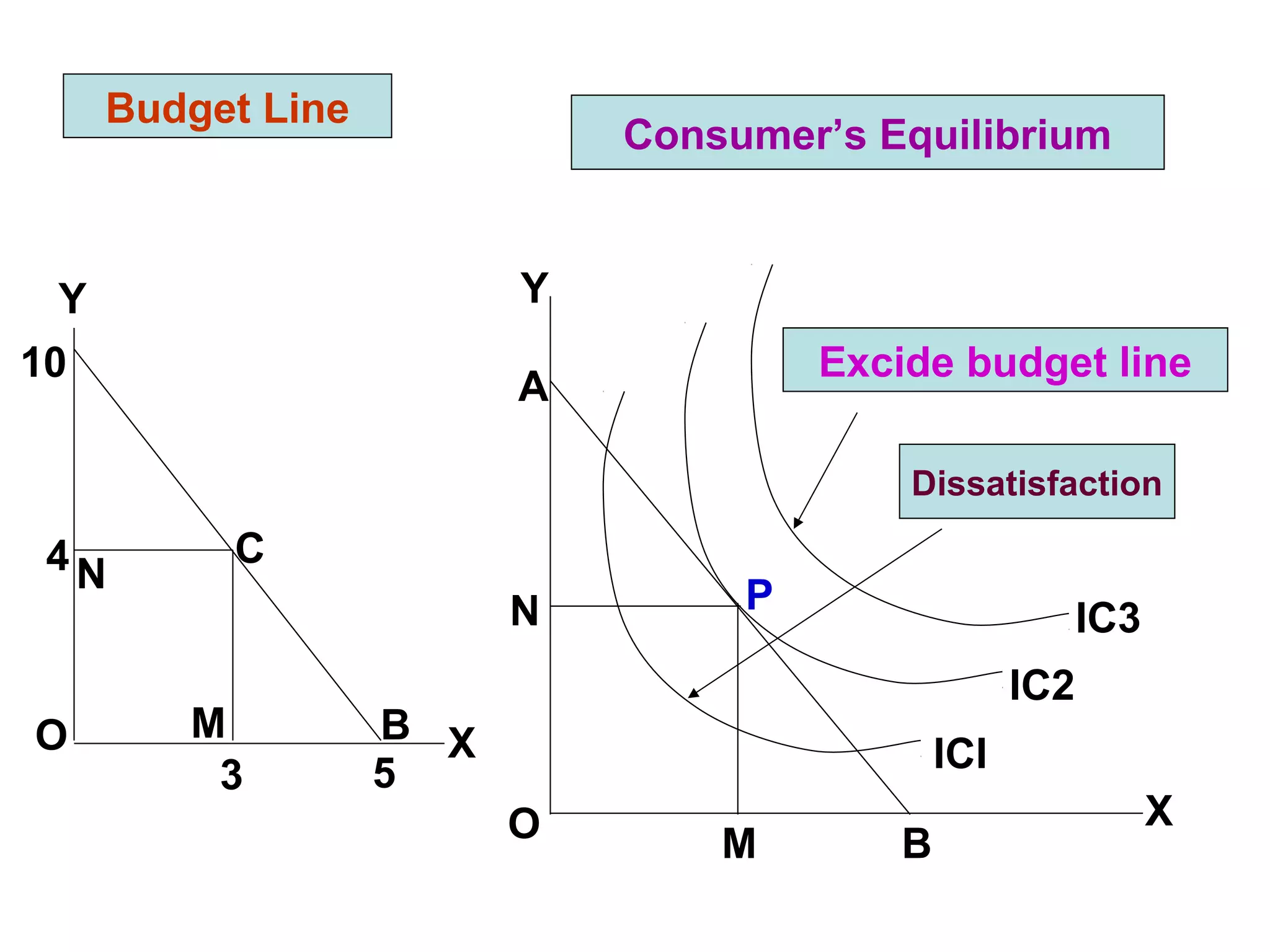
ii) Indifference curves slope downward, are convex, do not intersect, and represent higher satisfaction the higher up they are. A budget line shows the combinations of two goods that can be purchased with a limited income.
iii) Consumer equilibrium occurs at the highest indifference curve that a budget line can reach, where consumers get the maximum satisfaction possible within their budget constraints.