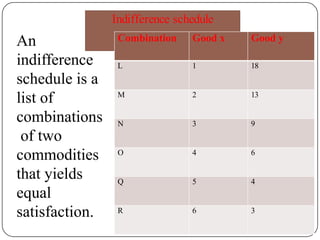
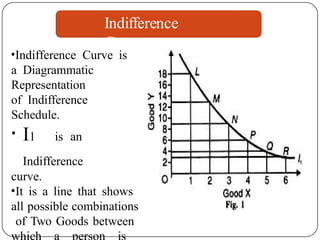
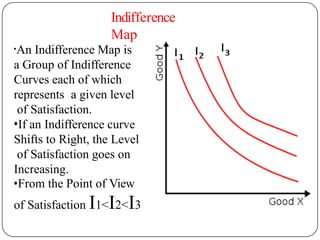
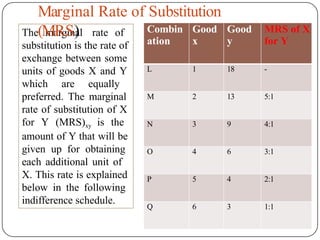
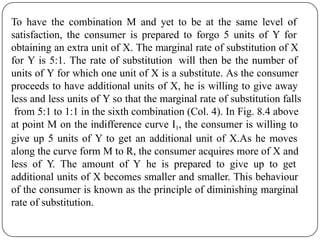
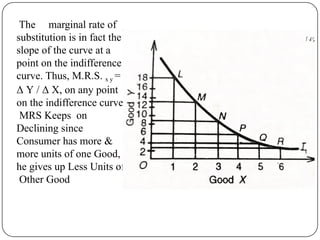
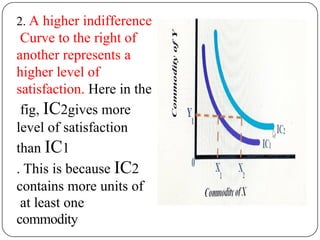
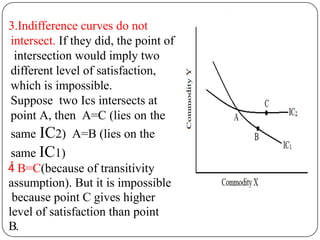
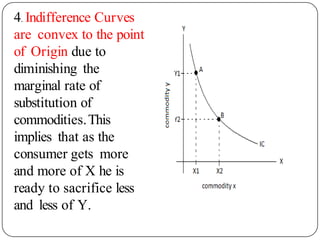
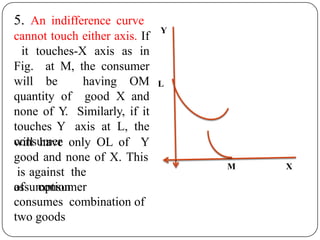
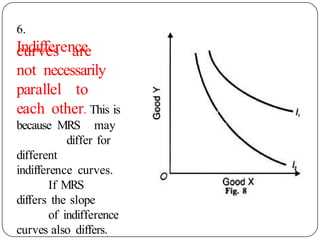
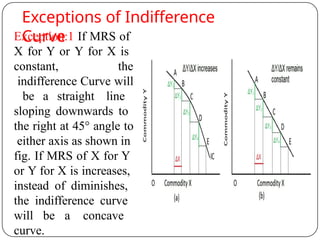
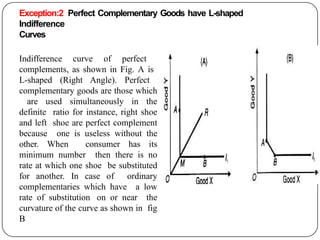
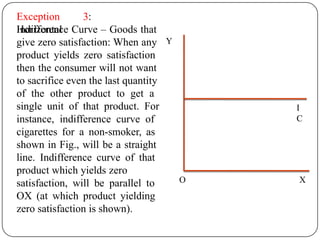
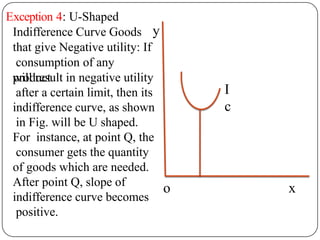
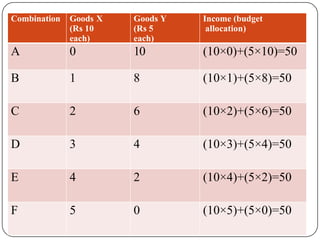
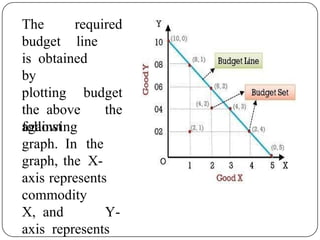
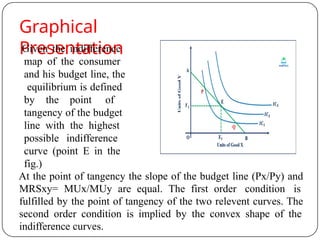
Indifference curve analysis, developed by Hicks and Allen, examines consumer behavior by representing preferences for combinations of two goods, measuring utility ordinally. An indifference curve is created from an indifference schedule, indicating all combinations that yield the same satisfaction, while properties include a negative slope, non-intersecting curves, and convexity due to diminishing marginal rate of substitution. Consumers achieve equilibrium when they maximize utility under a budget constraint, represented by the tangency of the budget line with the highest indifference curve.