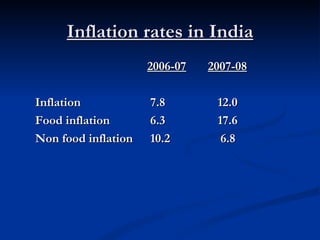
The document discusses various types and measures to control inflation. It defines inflation as a continuous rise in price levels and identifies different types including open inflation where no control measures are taken, suppressed inflation where prices are controlled, wartime inflation to fund war expenses, and creeping inflation where prices rise slowly. Measures to control inflation include monetary policies like controlling money supply and credit, and fiscal policies like decreasing expenditures, increasing taxes, and encouraging production, savings, and proper investment. The document concludes with an example of hyperinflation in Zimbabwe in 2008 that reached 355,000% and severely damaged the economy.