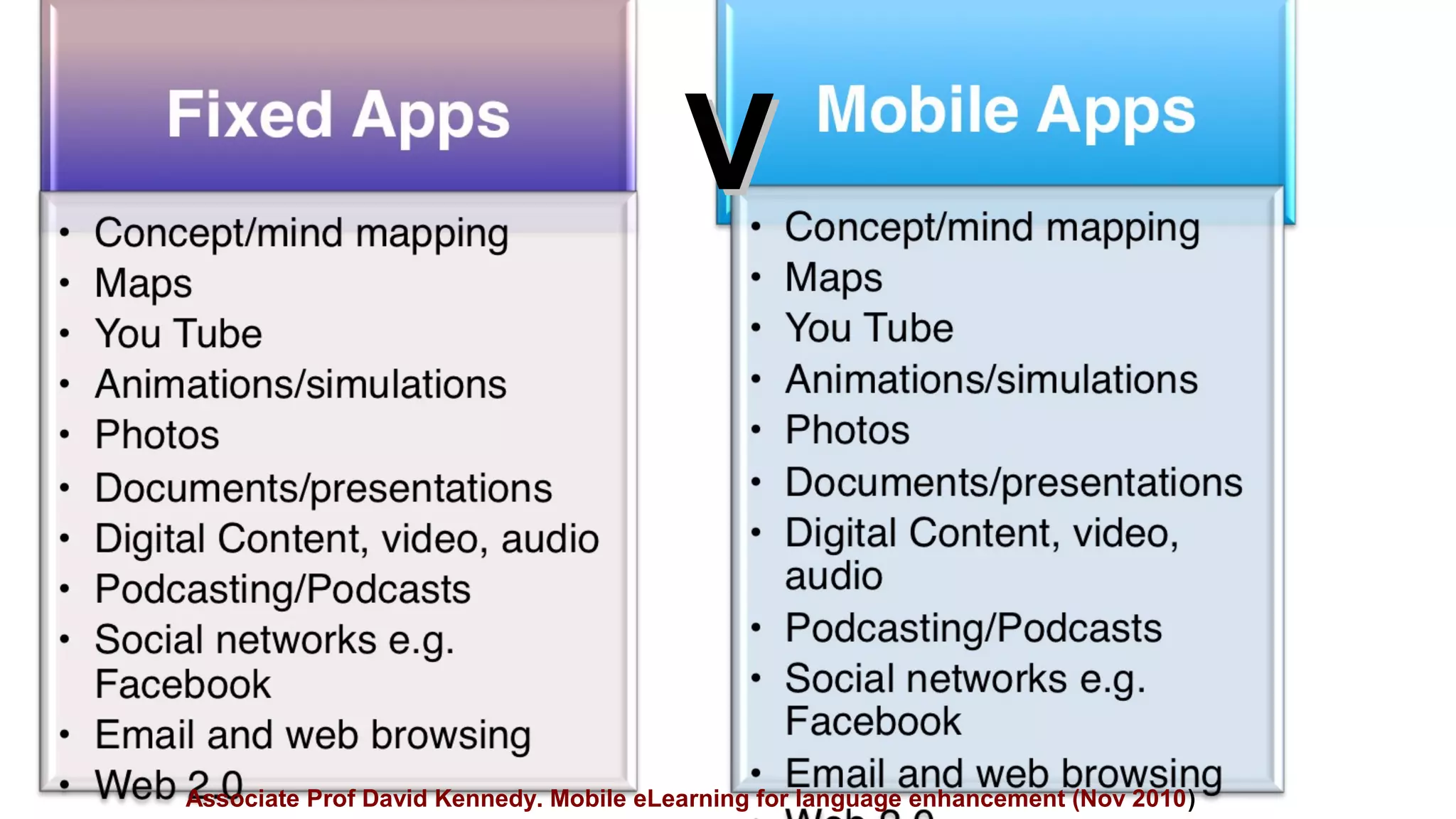
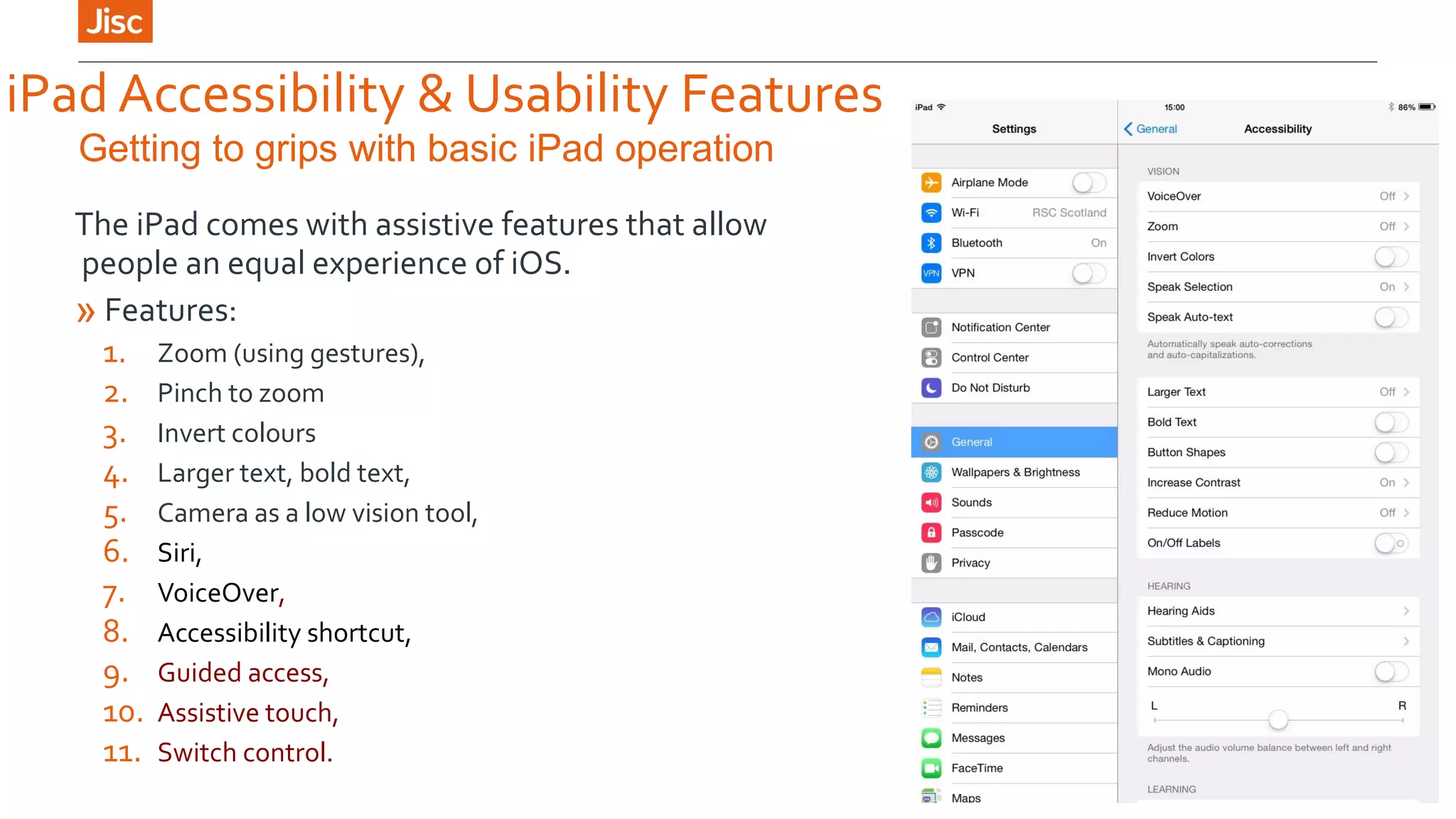
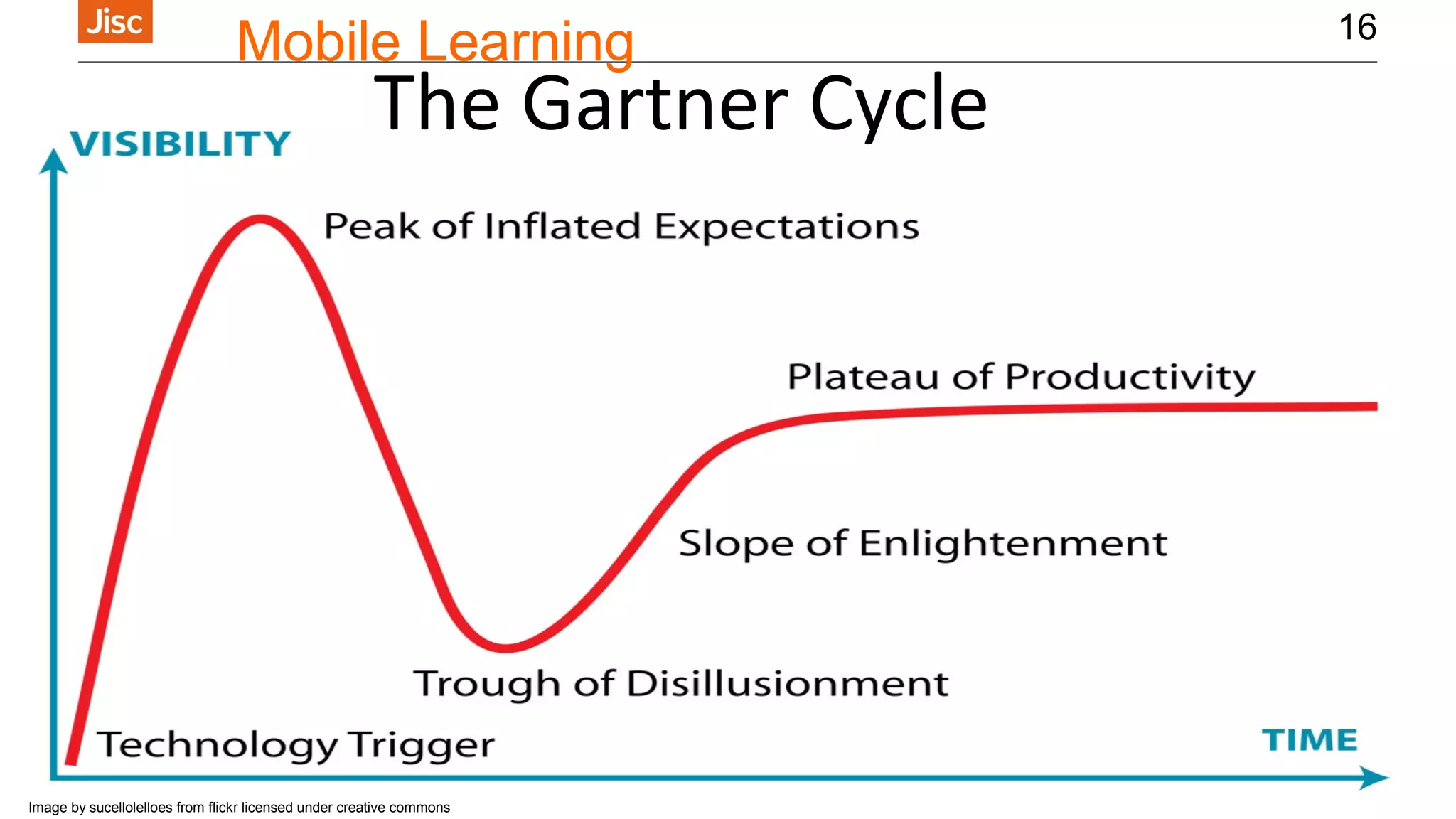
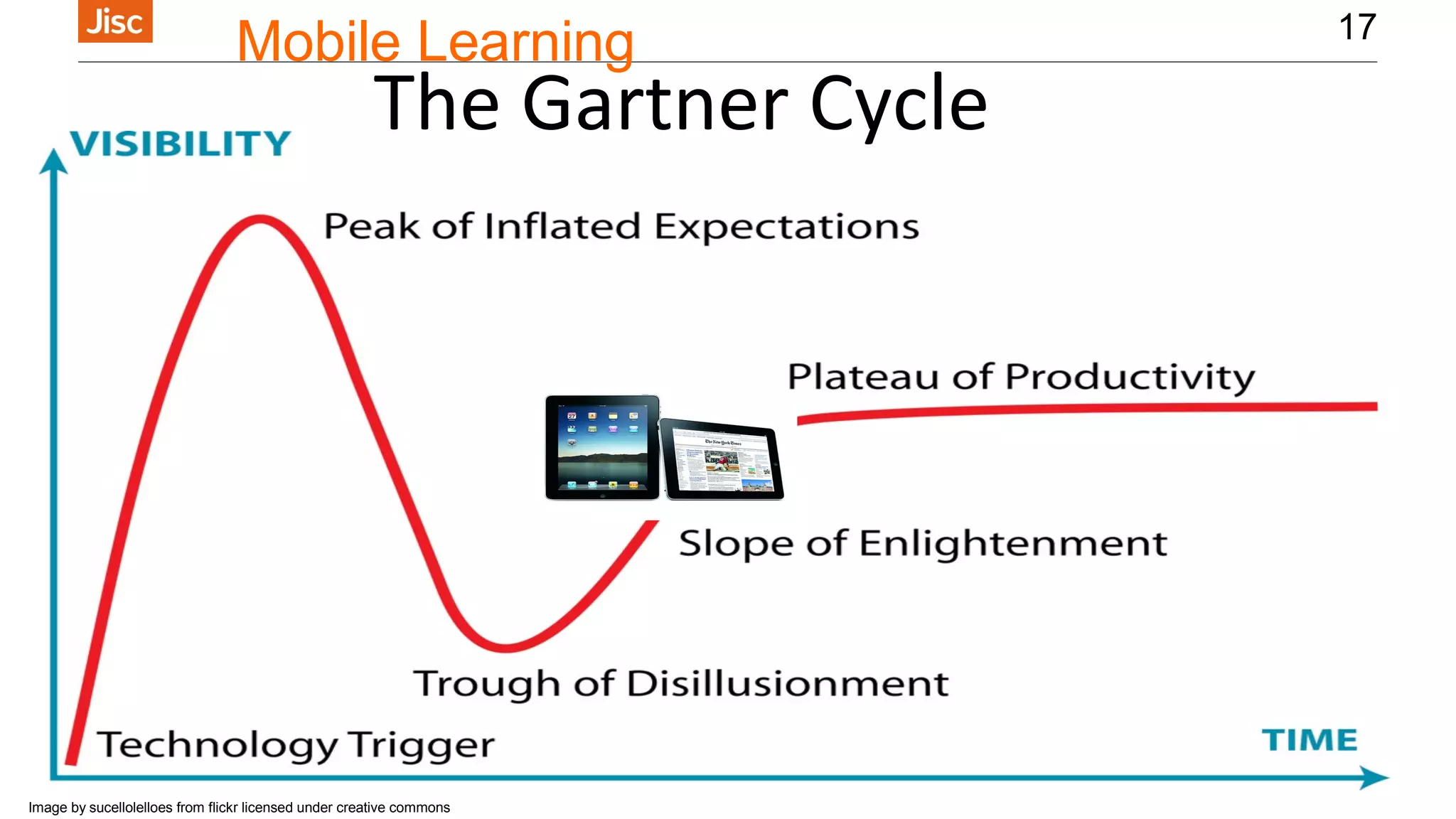
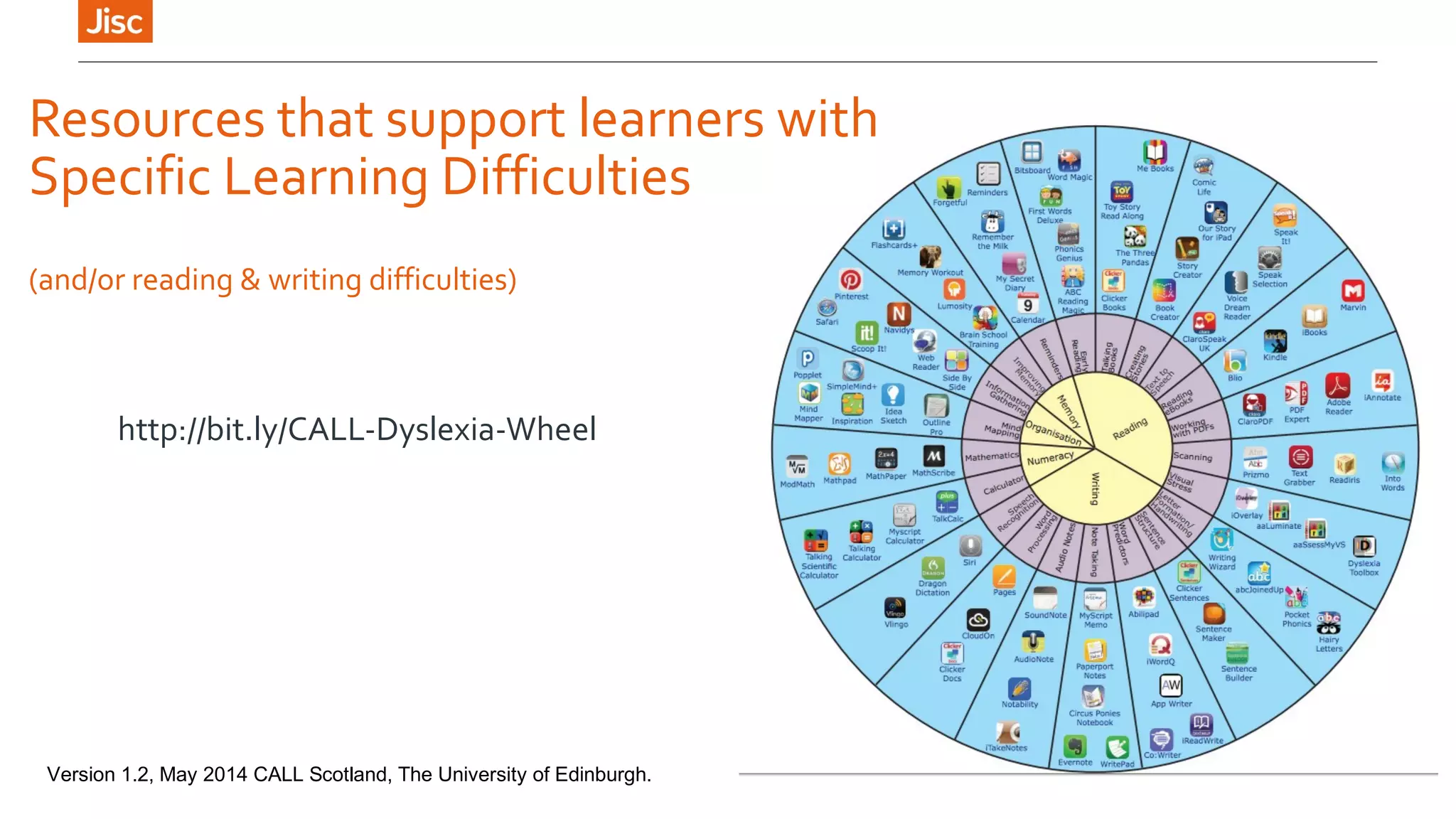
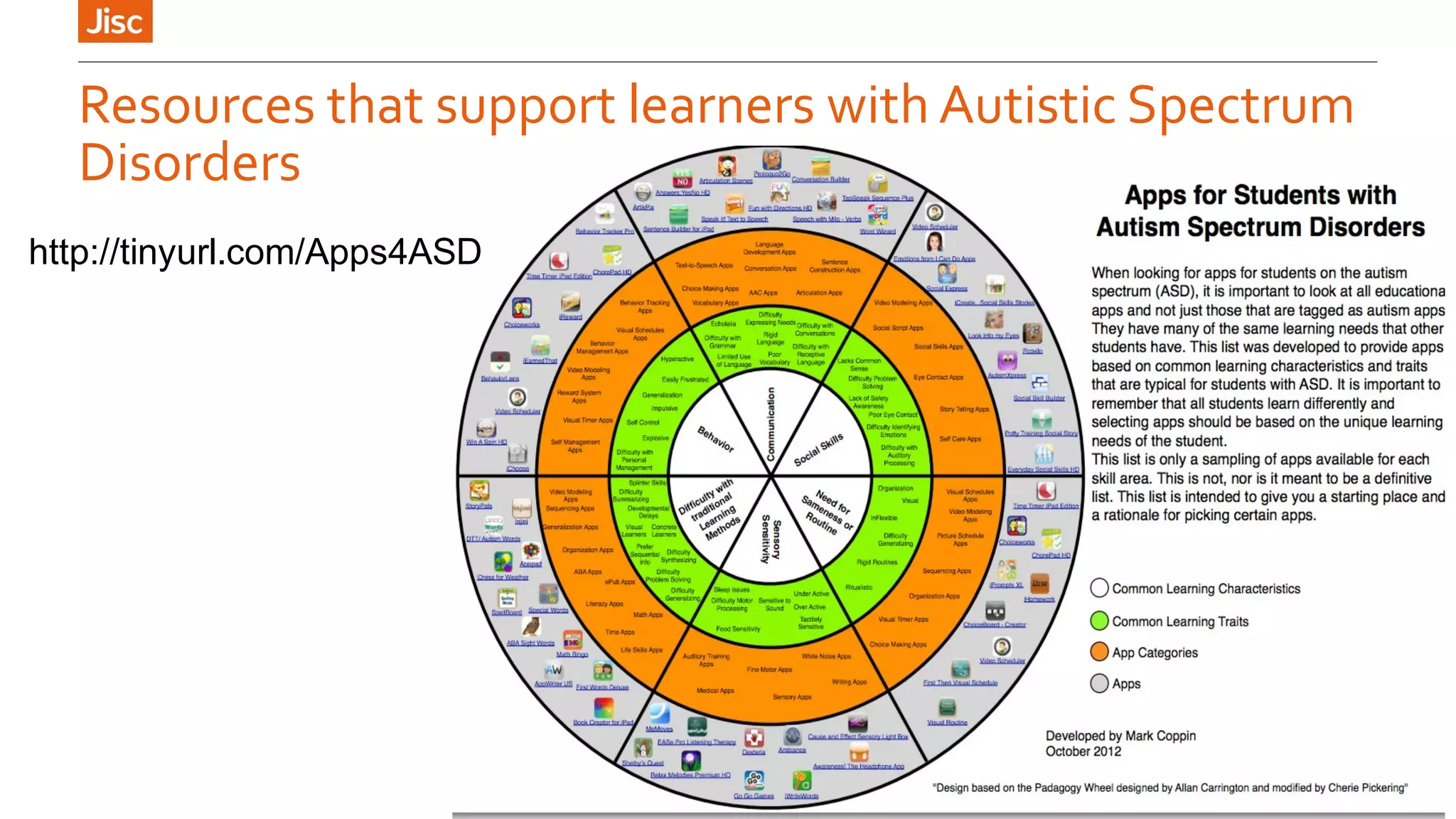
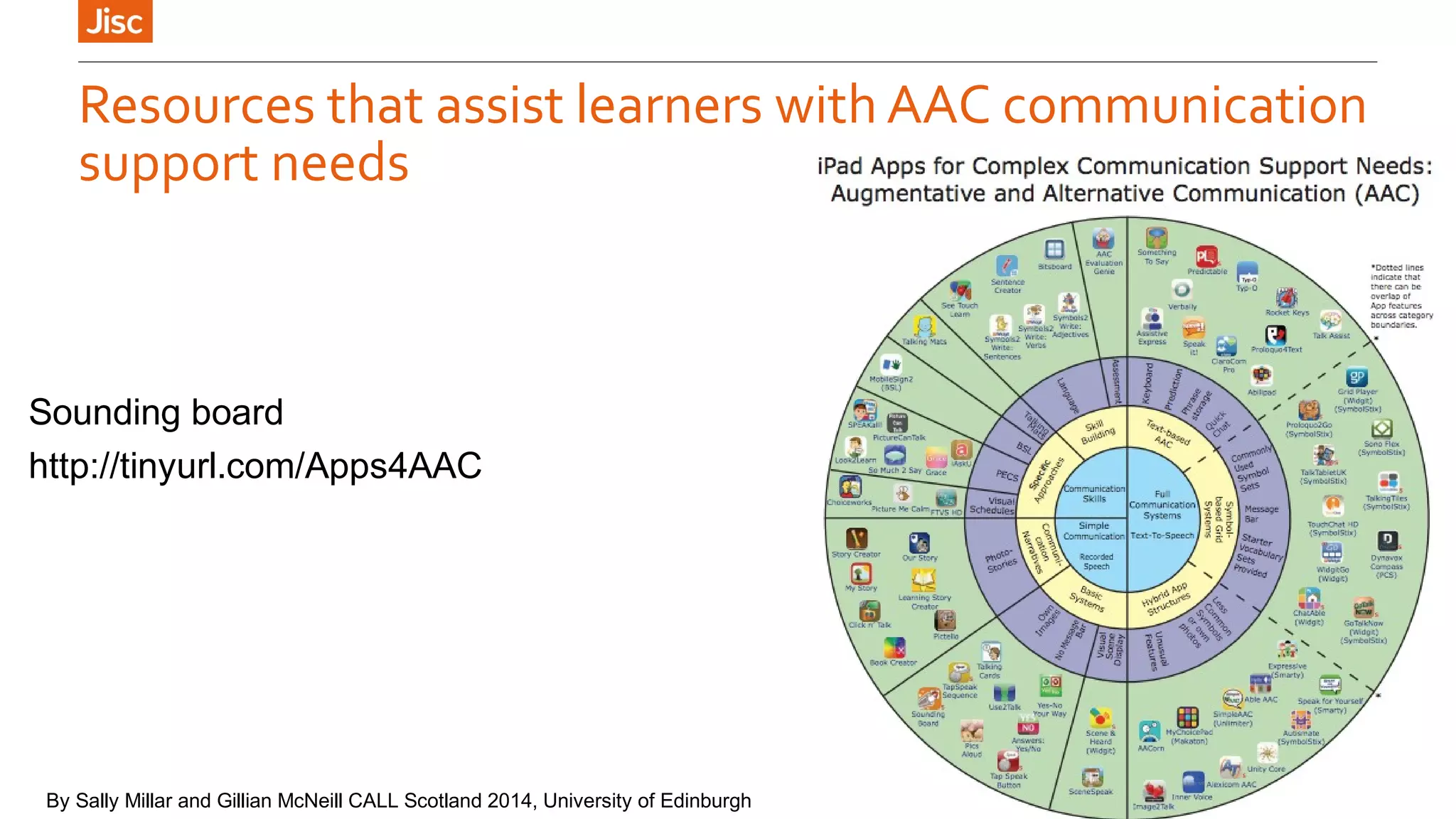
The document provides an introduction to using iPads for mobile learning, emphasizing the benefits of ubiquitous handheld devices and accessibility features. It outlines essential operations and assistive functionalities tailored for various learner needs, including those with disabilities. Furthermore, it highlights apps that support planning, organization, reading, writing, note-taking, and specific learning difficulties.