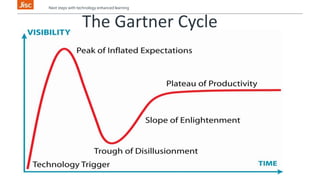
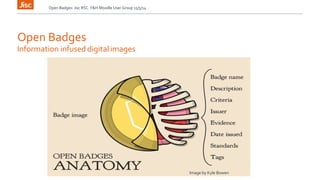
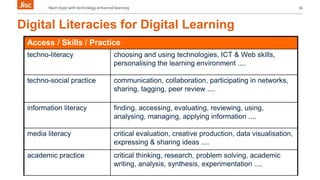
The document discusses emerging technologies and their potential impact on education over the next 1-5 years. It outlines technologies that may become widely used in the near future such as flipped classrooms, learning analytics, 3D printing, and virtual assistants. The document also discusses key drivers of change in education including new pedagogical approaches supported by technology, open education, and developing students' digital literacies.