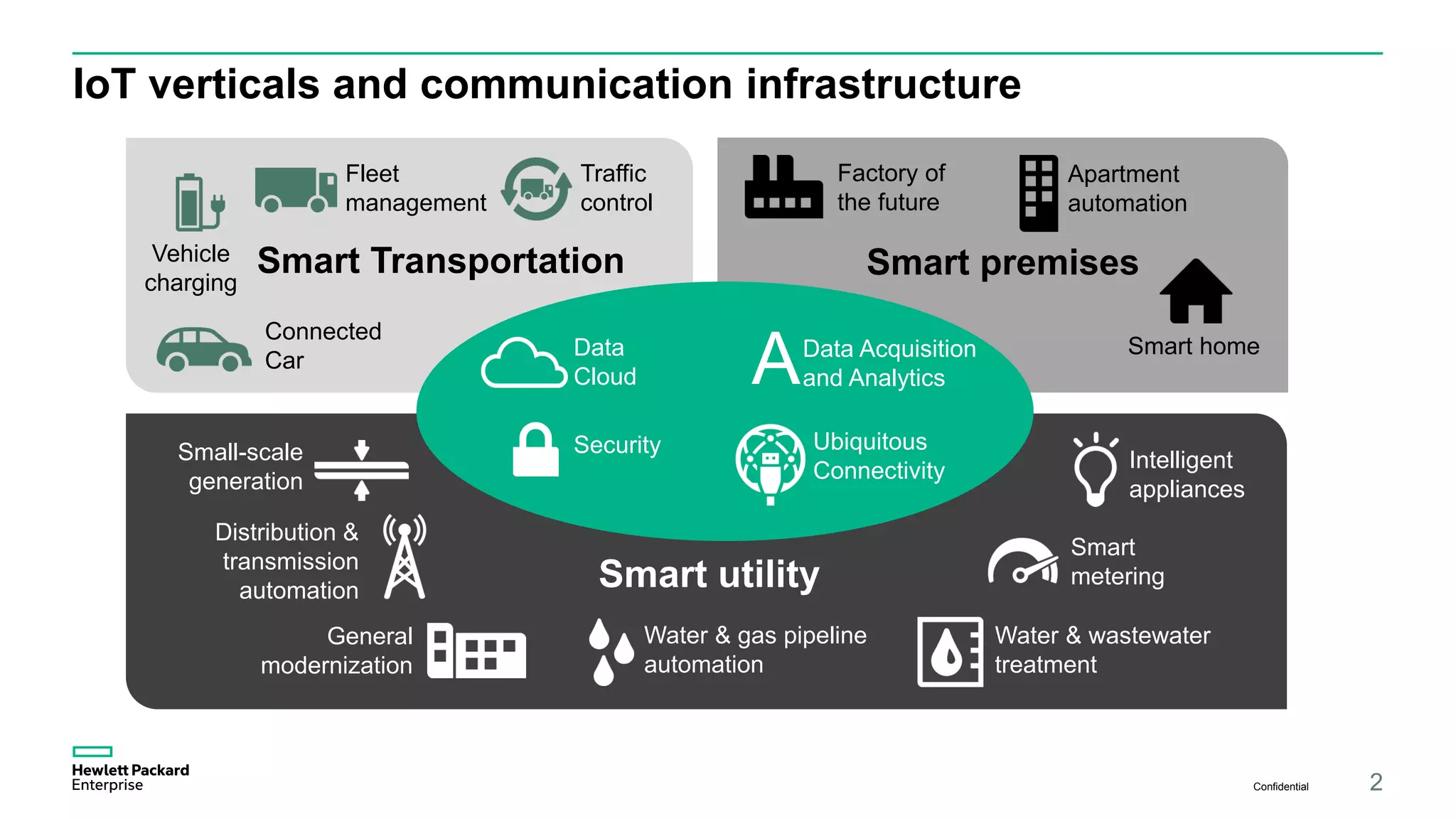
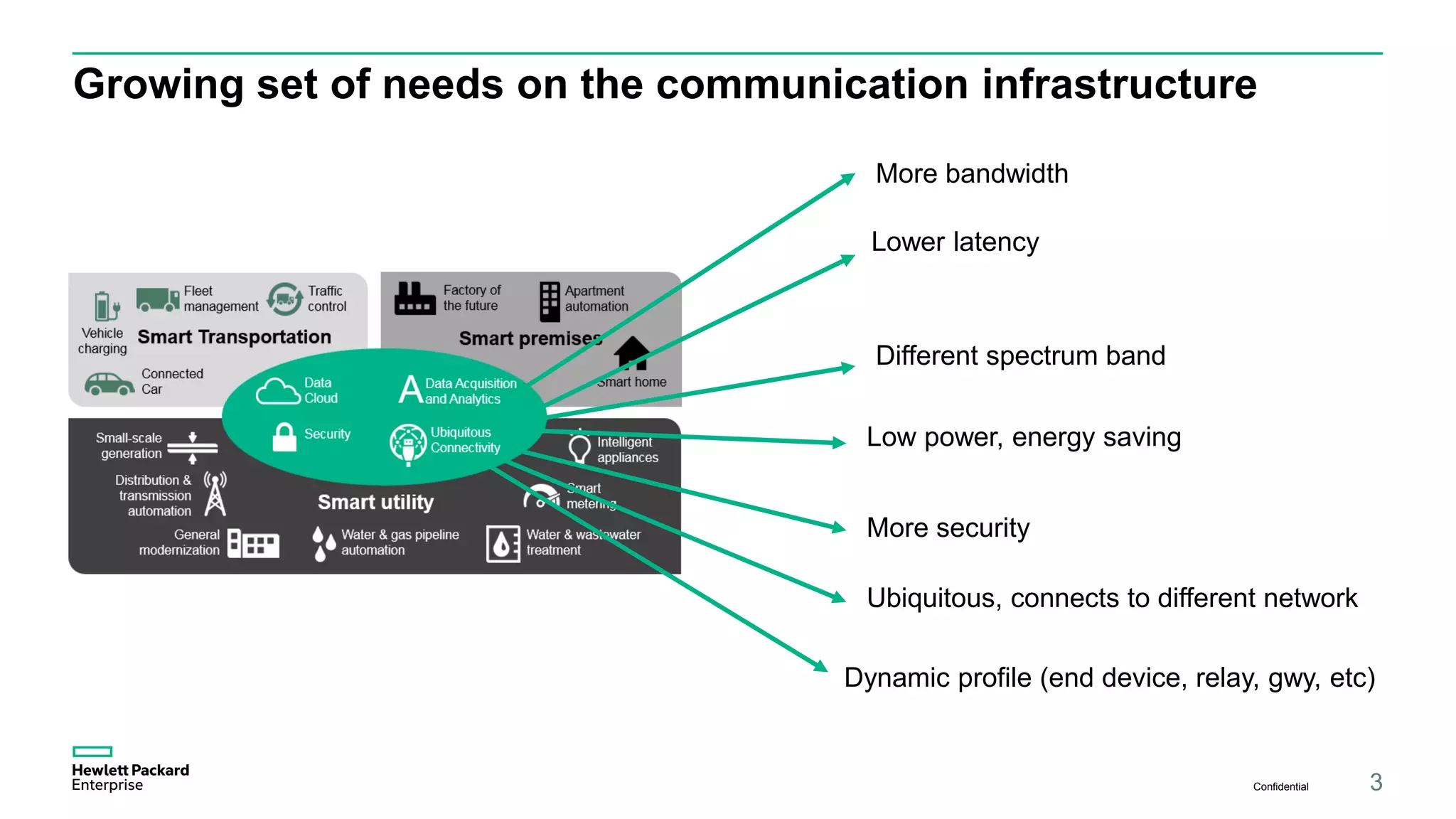
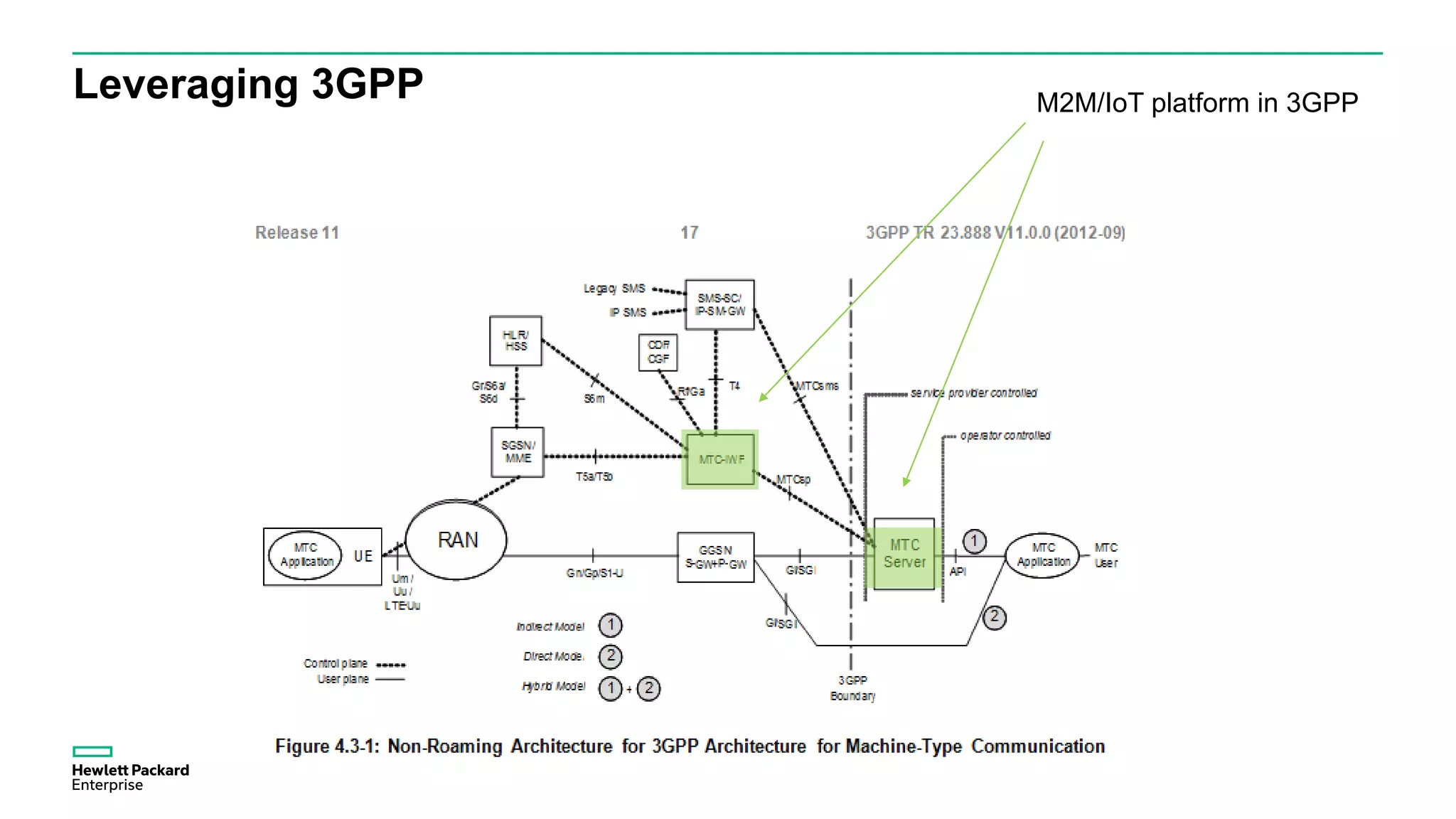
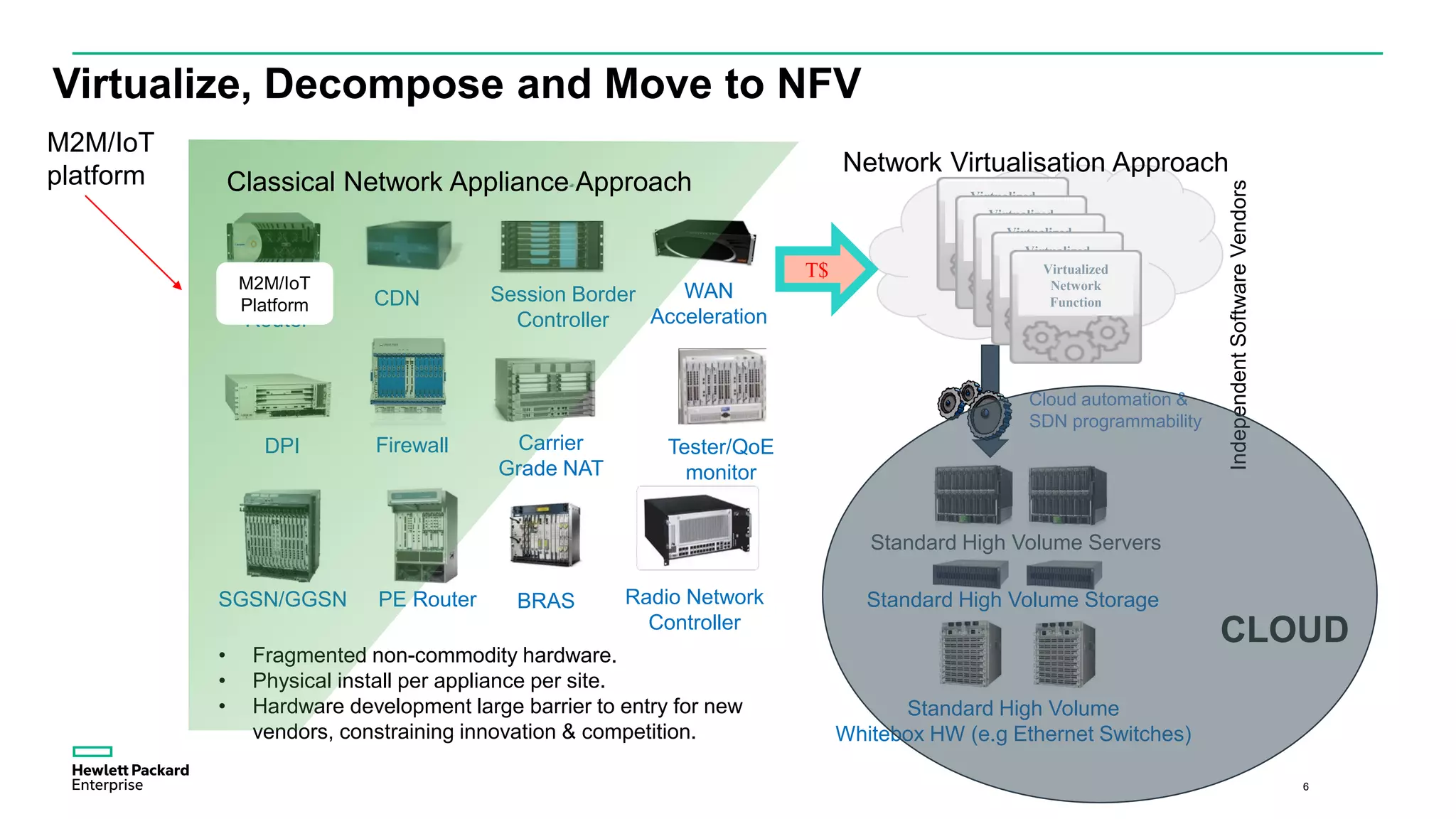
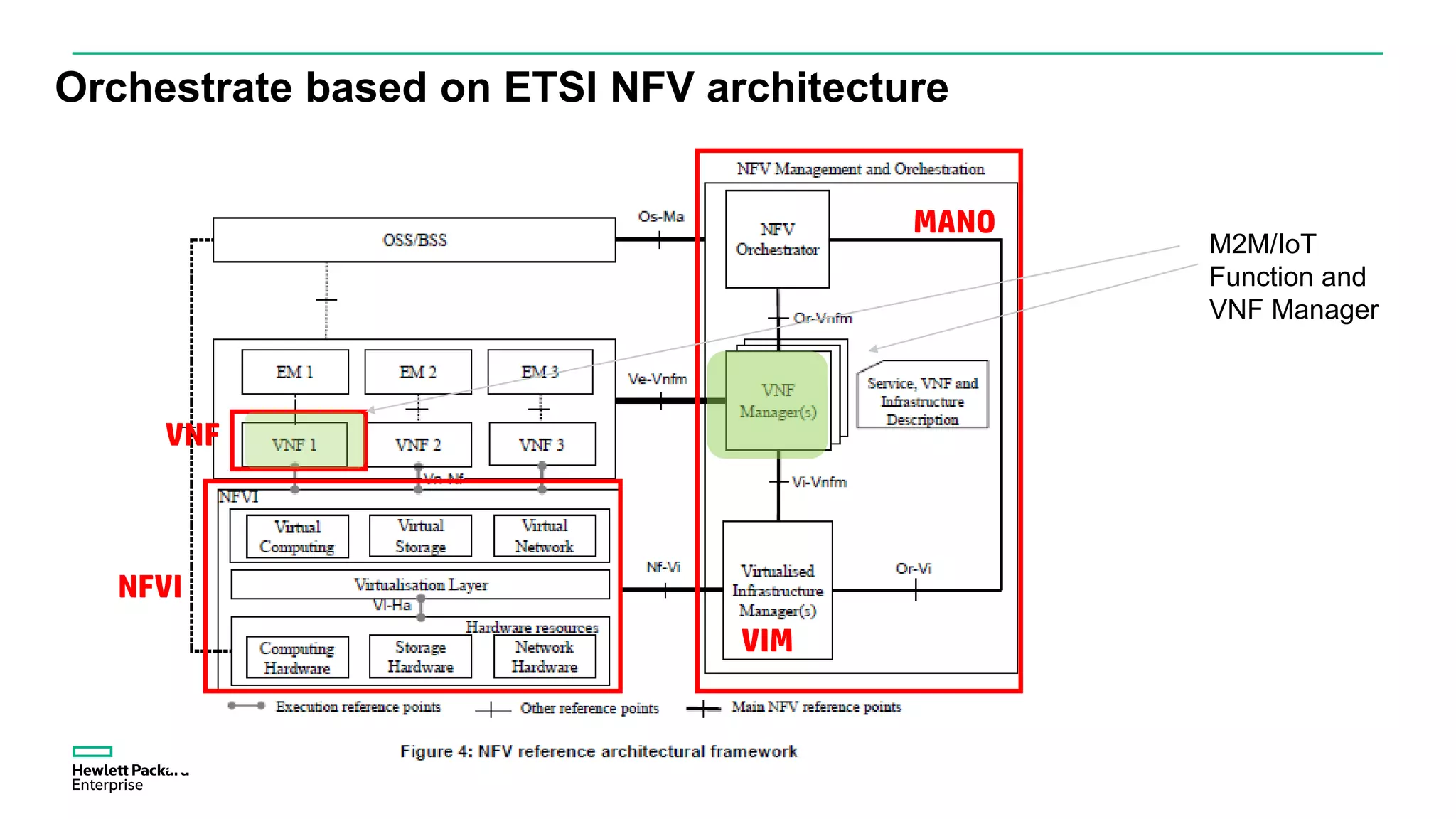
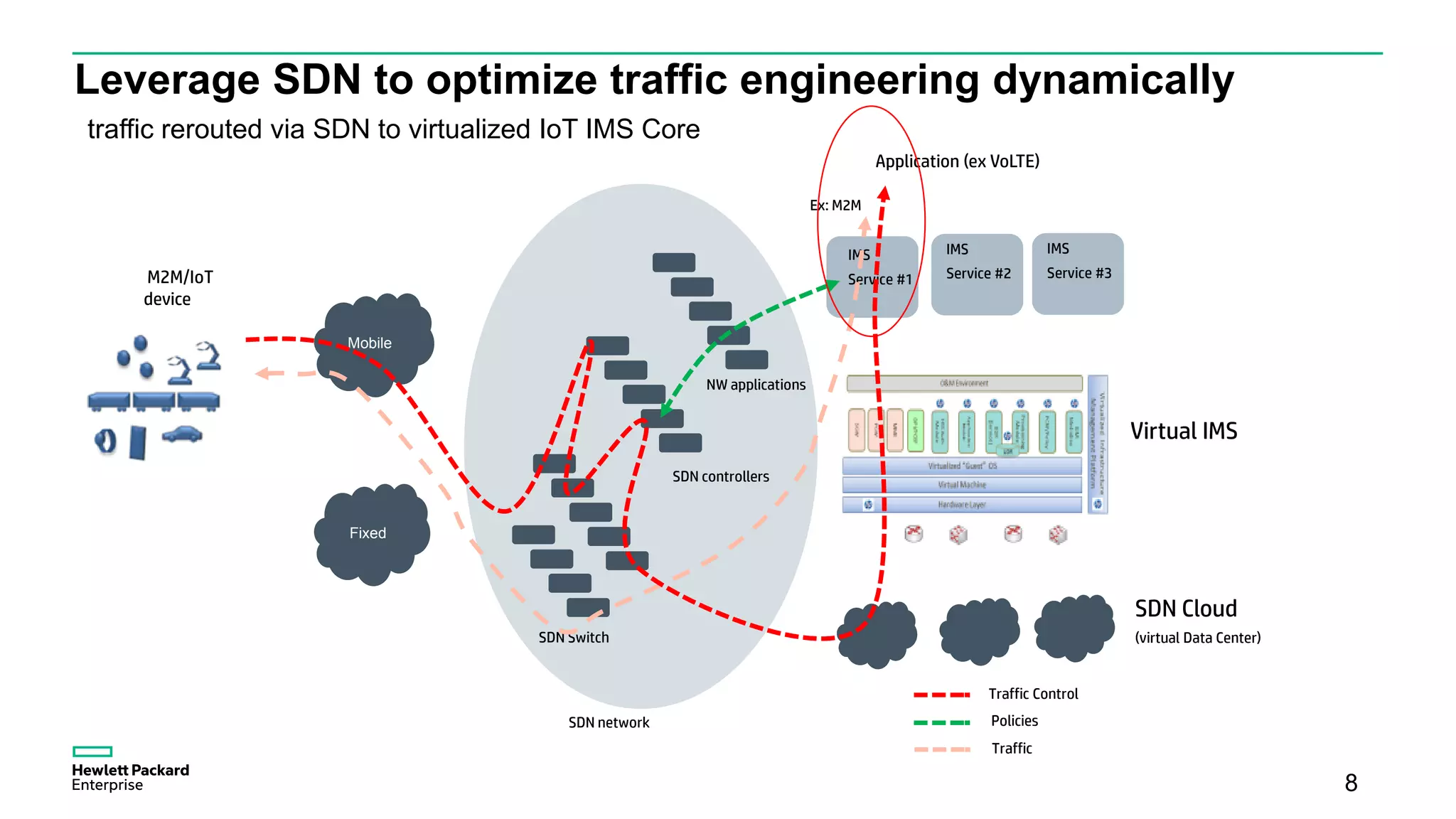
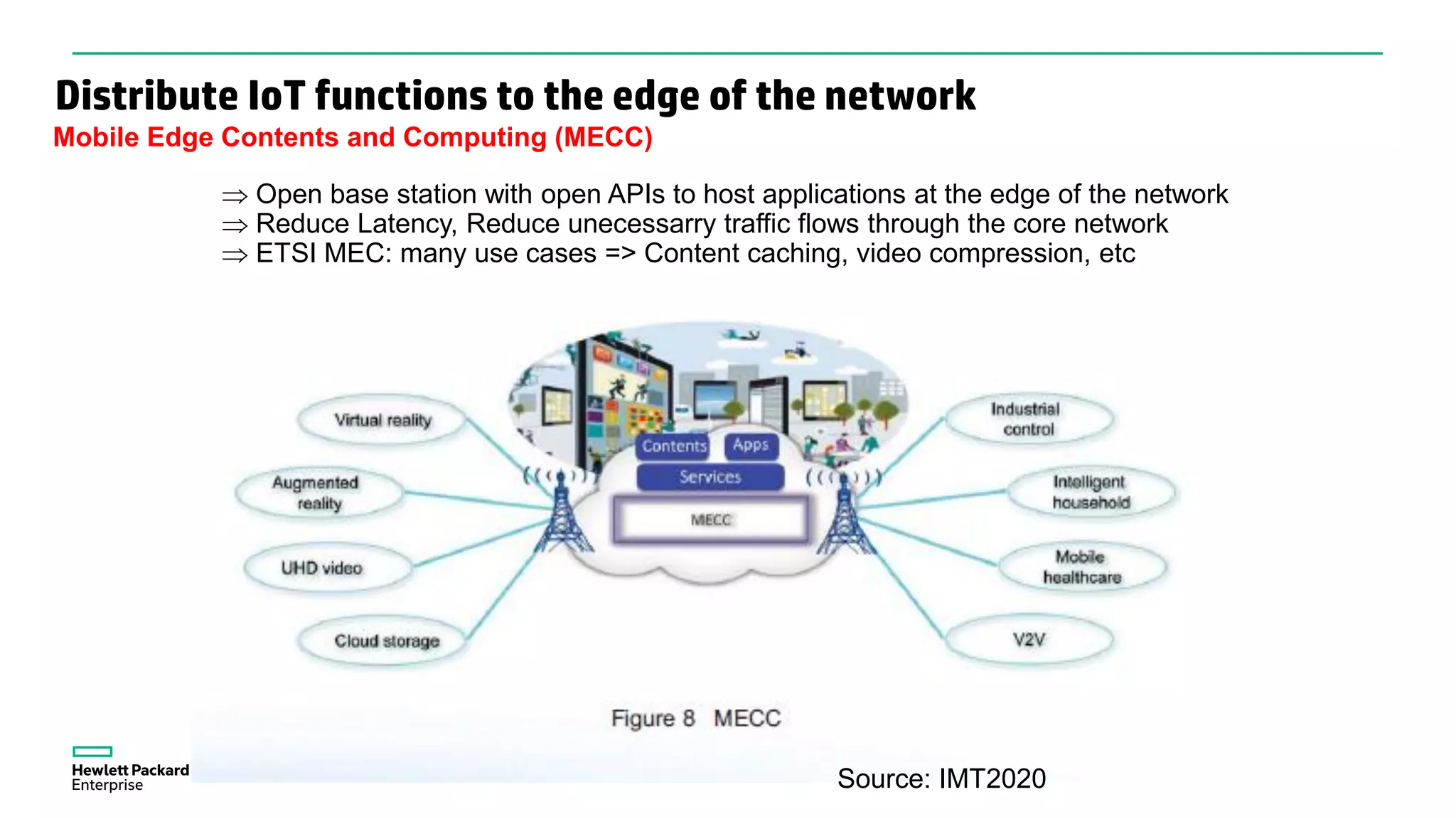
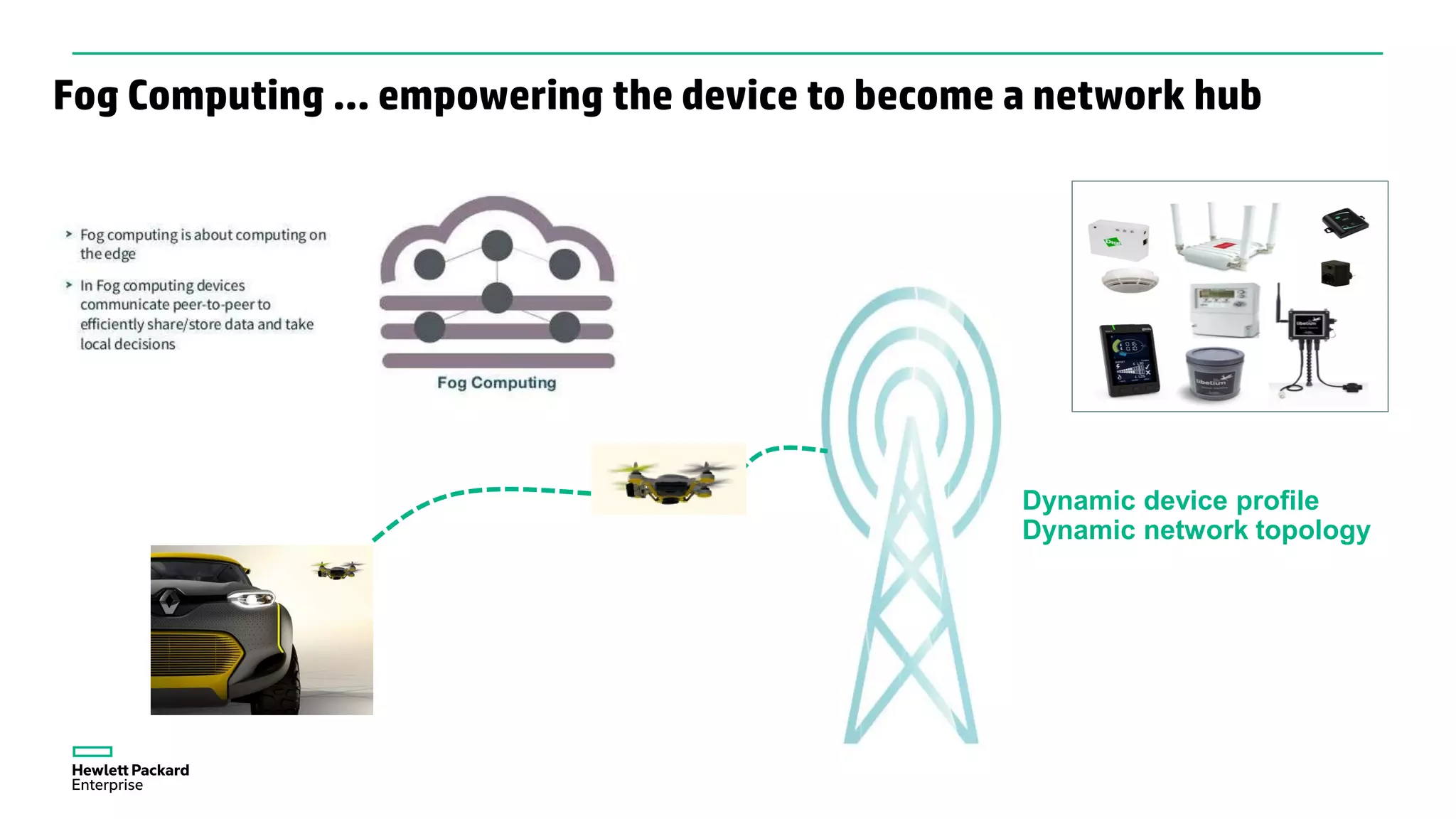
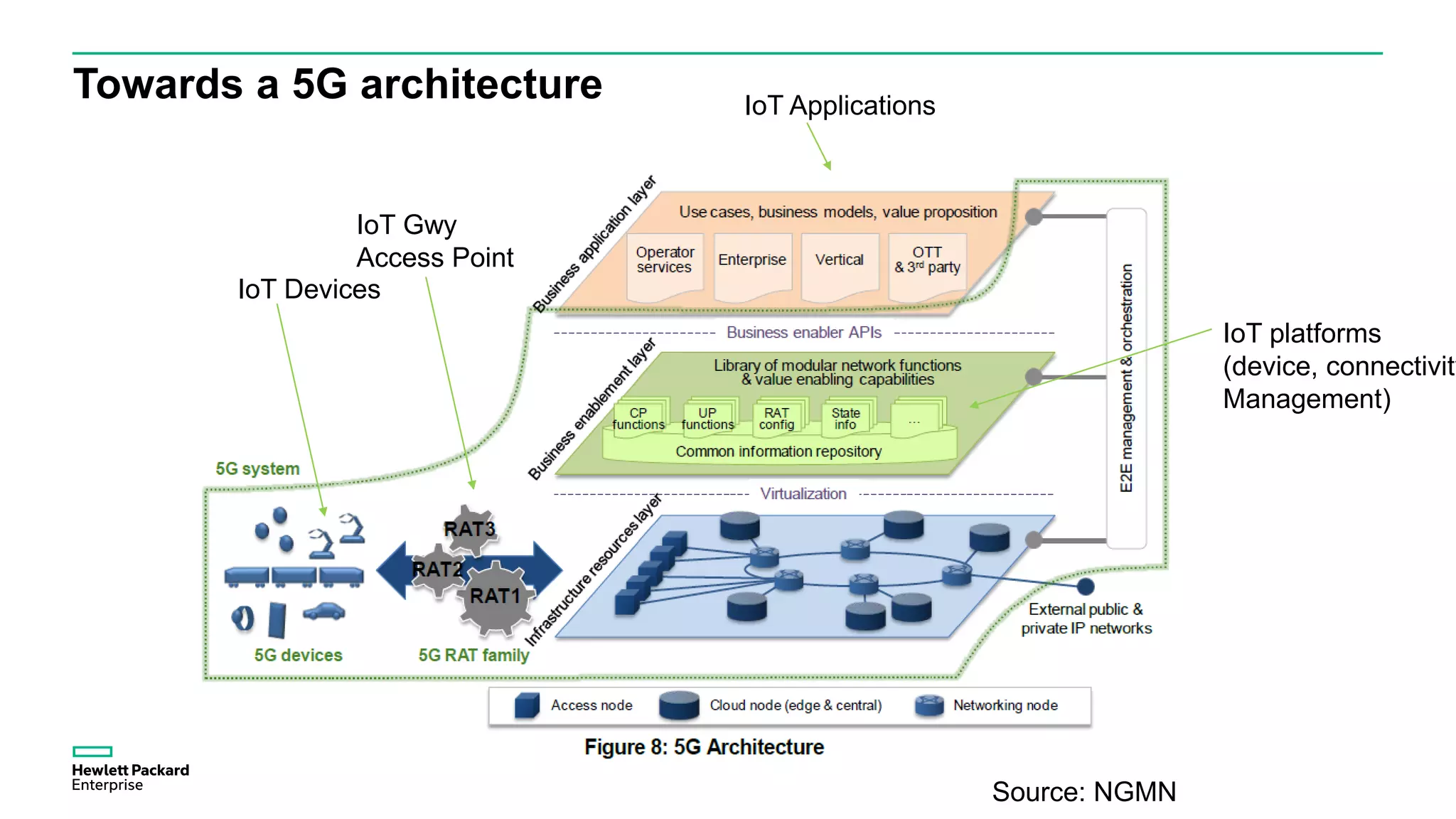
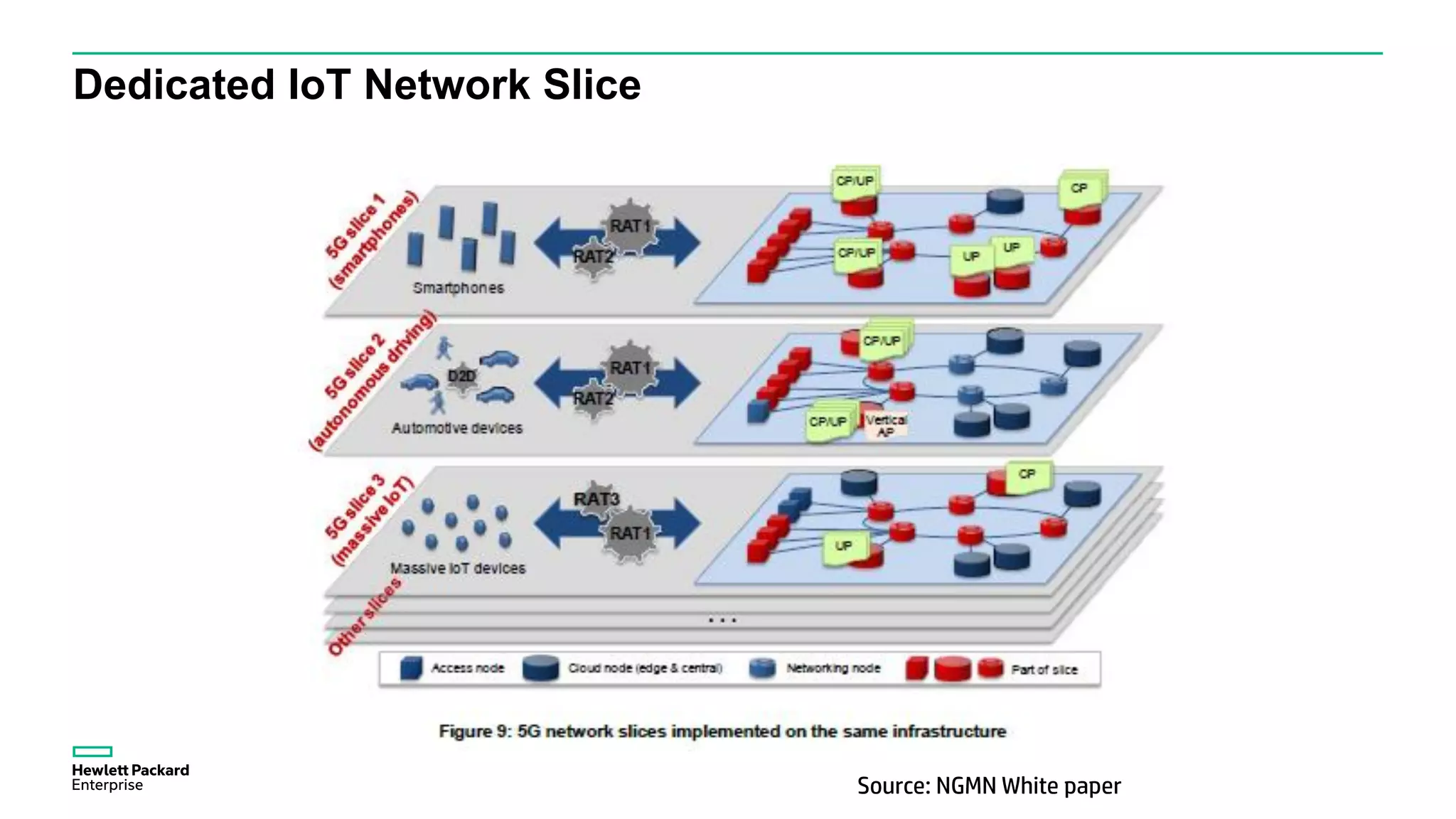
The document discusses advancements in IoT and M2M technologies aimed at enhancing smart city infrastructure, focusing on programmable cities that leverage SDN and NFV for improved connectivity. It highlights the need for lower latency, increased bandwidth, and greater security for communication infrastructures to support various applications such as traffic control, smart utilities, and connected vehicles. The integration of cloud technologies and virtualized network functions is emphasized as a means to enable dynamic traffic management and edge computing, ultimately enhancing the livability of cities.