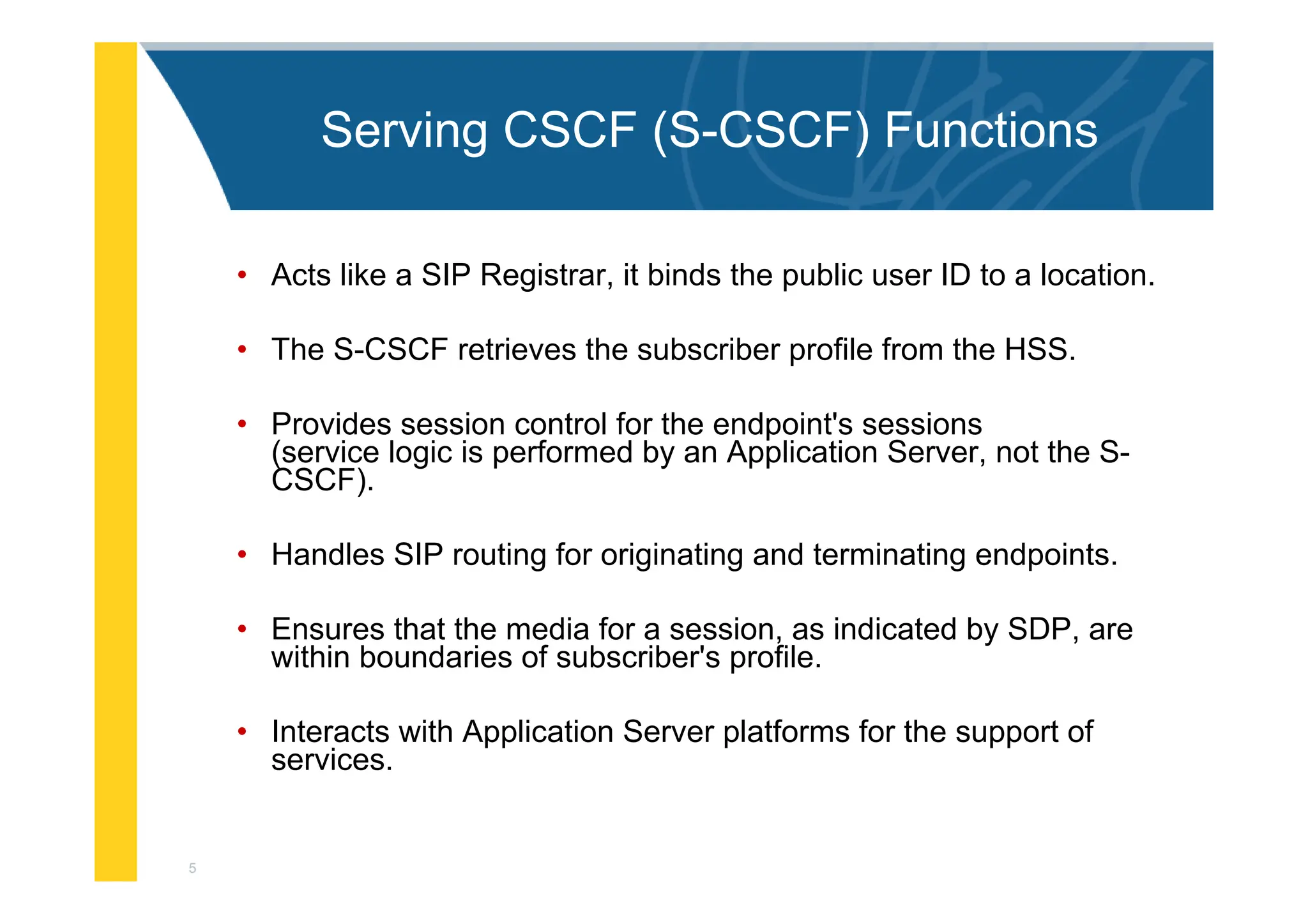
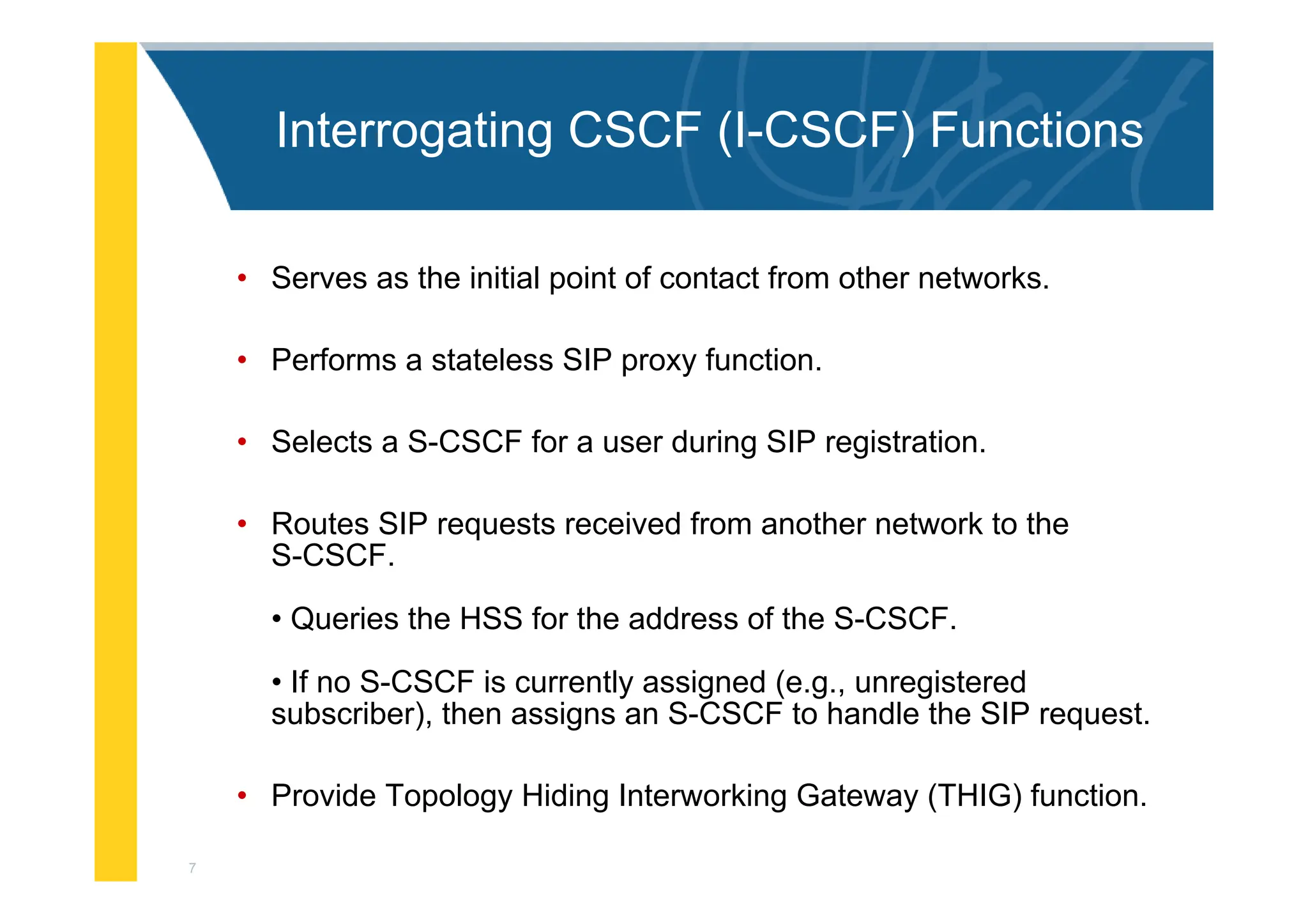
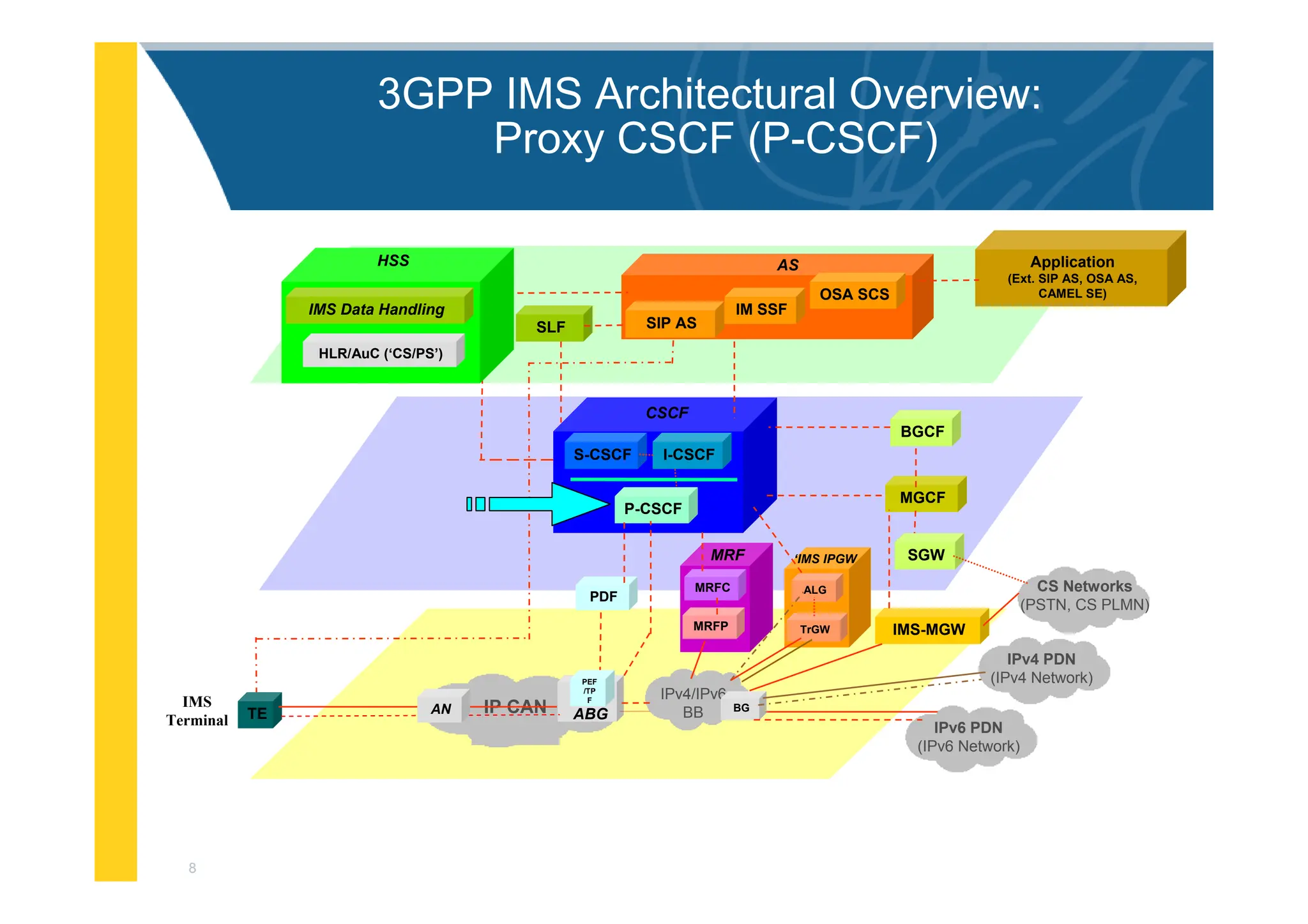
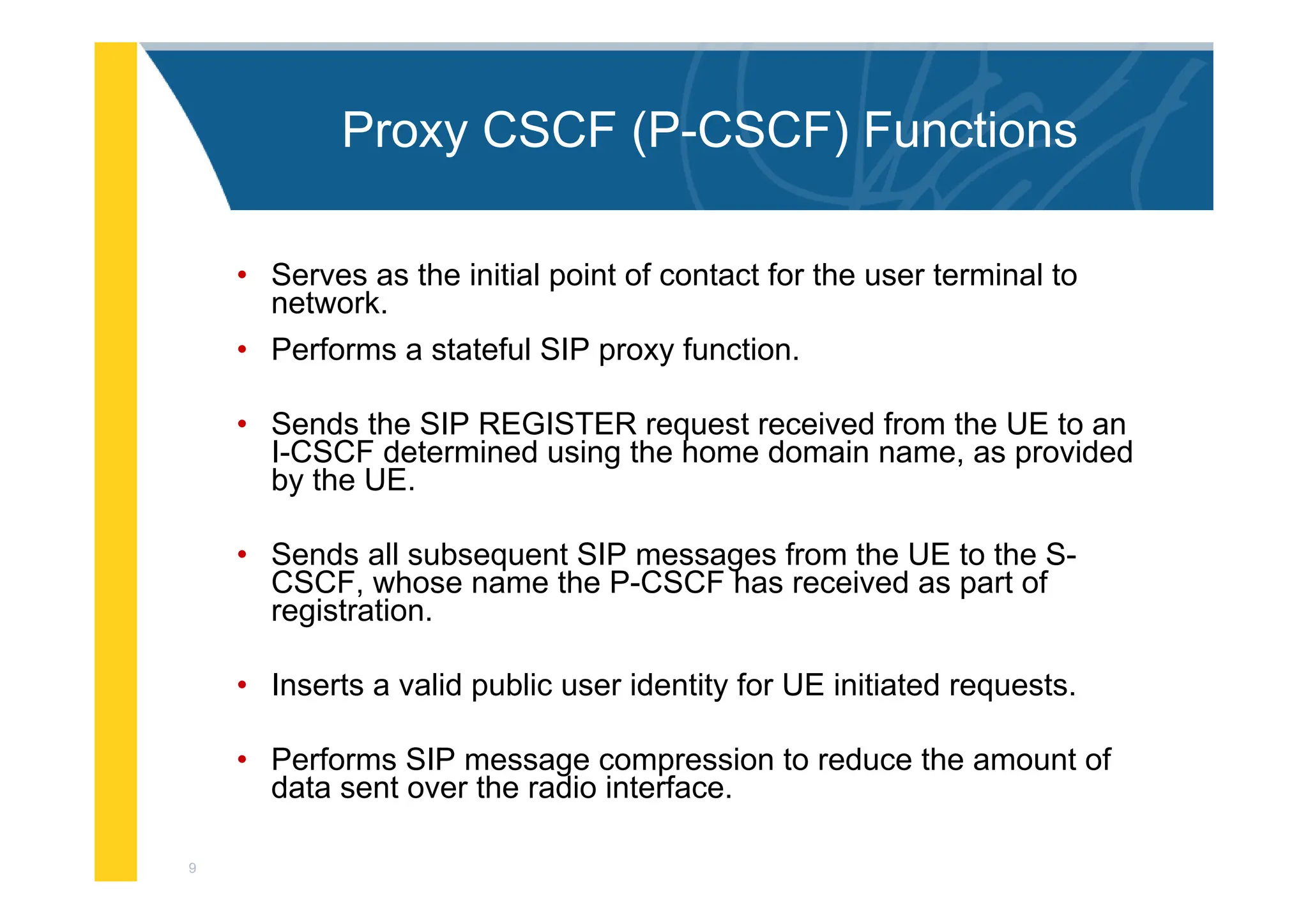
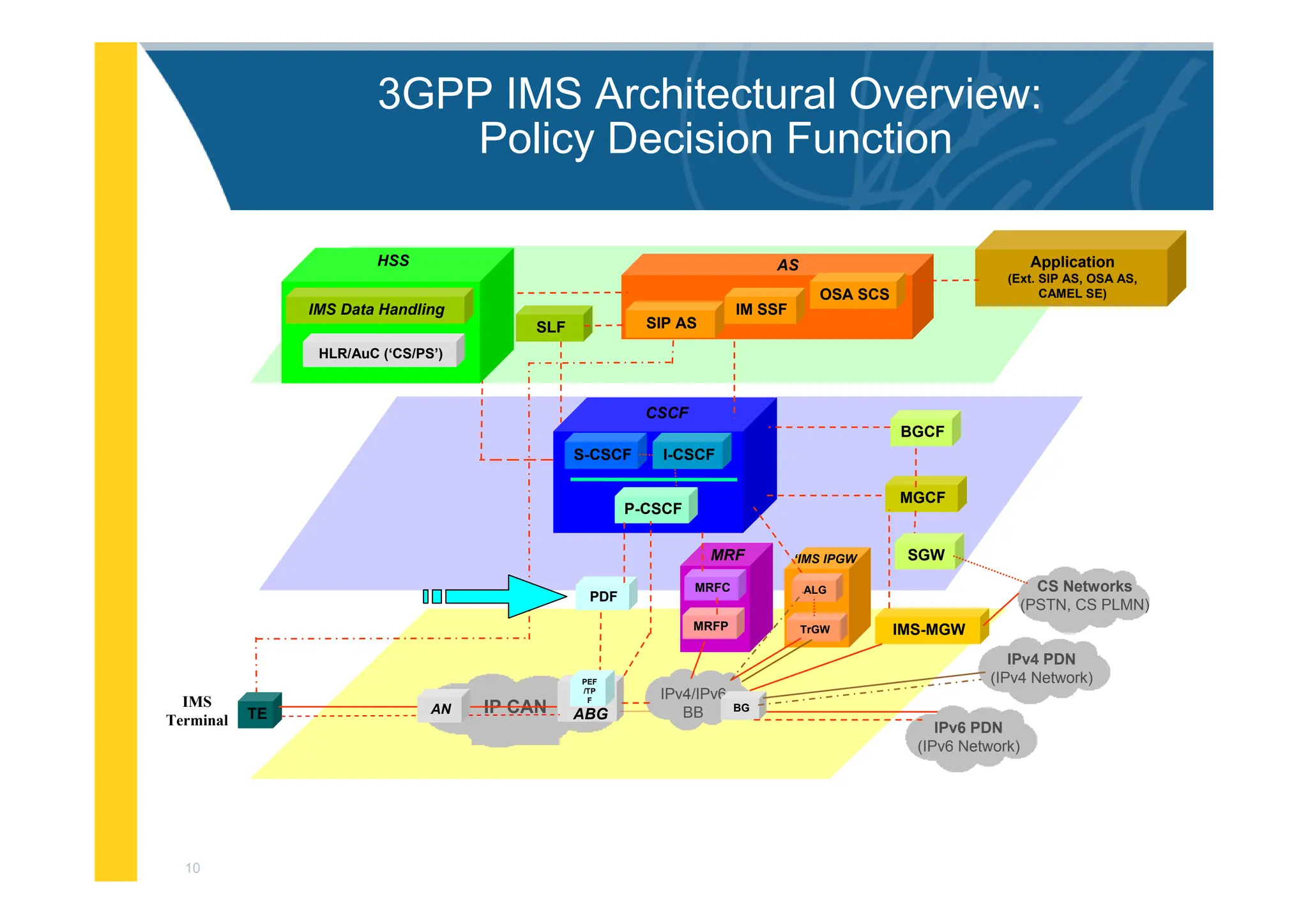
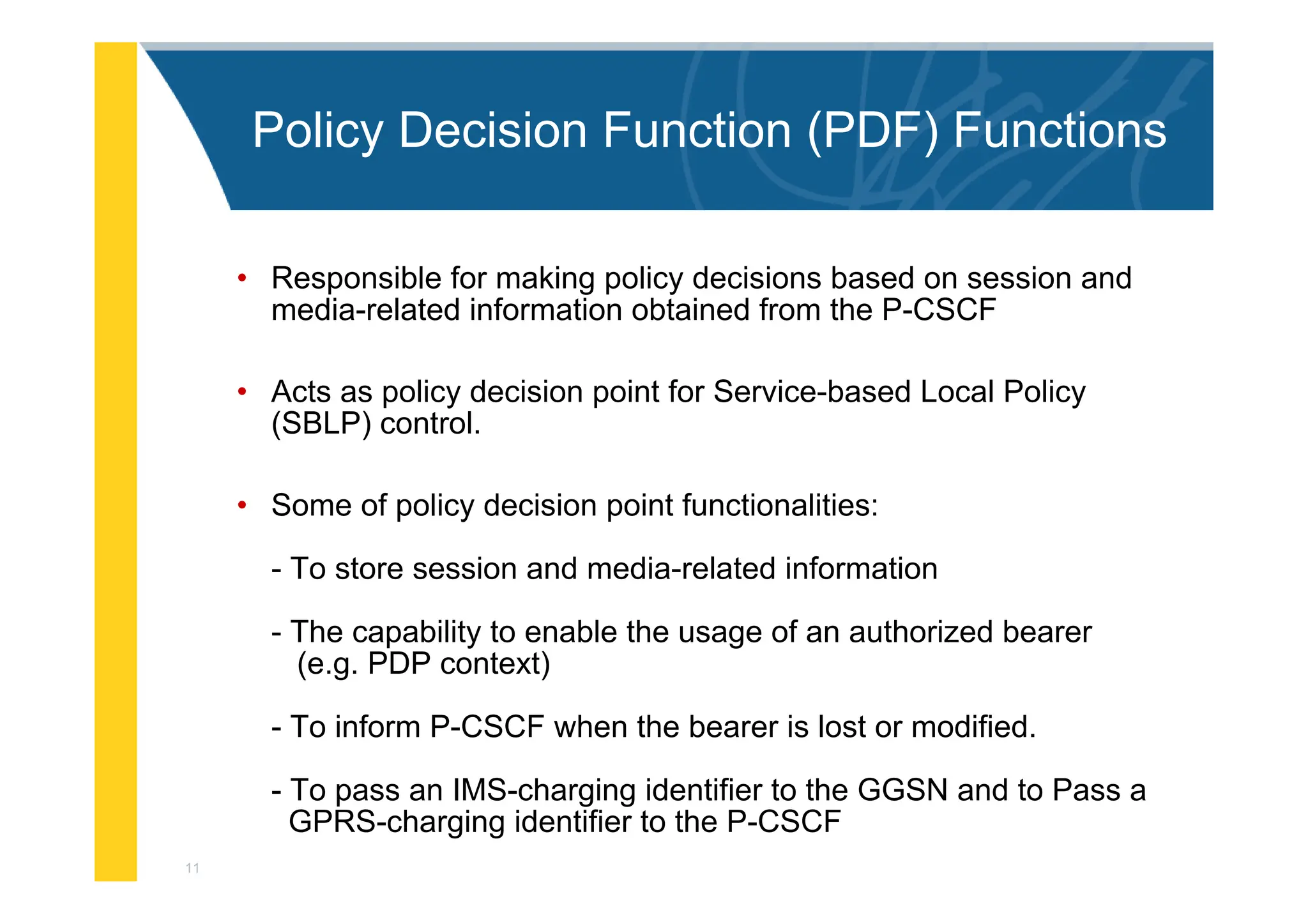
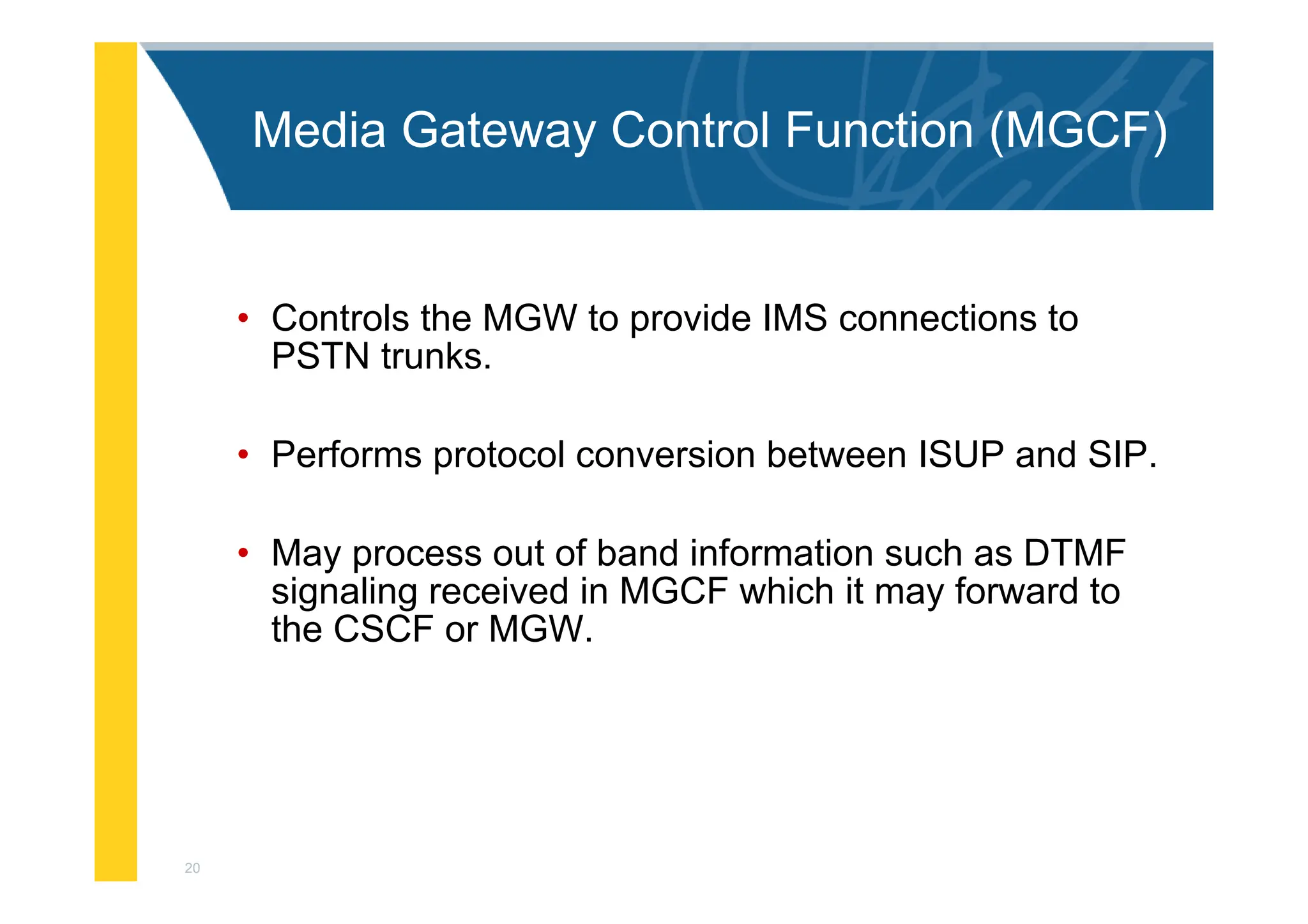
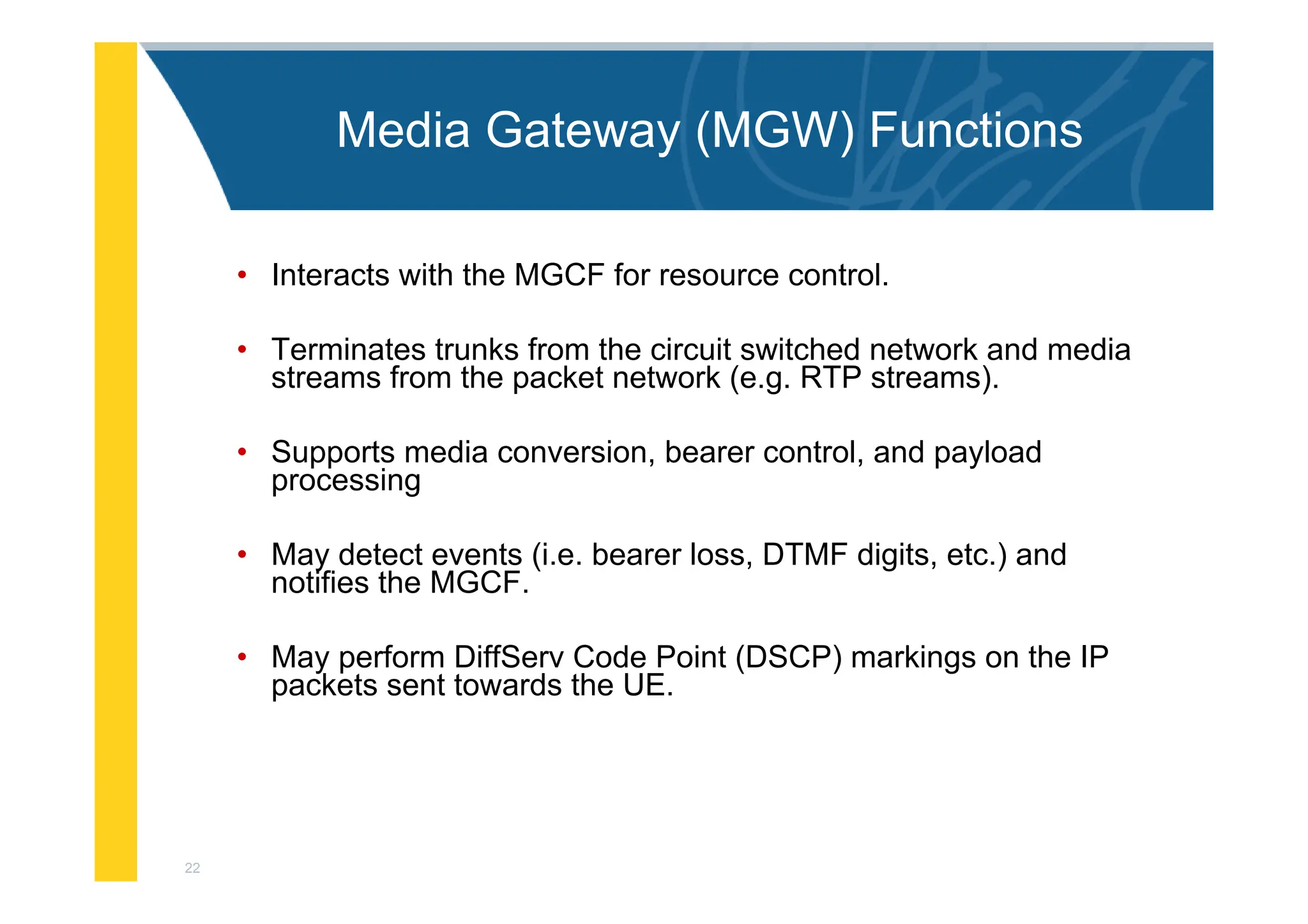
The document provides an architectural overview of the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), detailing various components such as the Serving CSCF, Interrogating CSCF, Proxy CSCF, and others, each with specific functions related to session control, registration, and signal processing. It also explains the roles of the Policy Decision Function, Home Subscriber Server, Application Server, and Media Gateway Control Function within the IMS framework. The IMS architecture is outlined to support multimedia services over IP networks, integrating various signaling and media resource functions.

![2
Simplified view of the layered
architecture in IMS
From [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-2-2048.jpg)
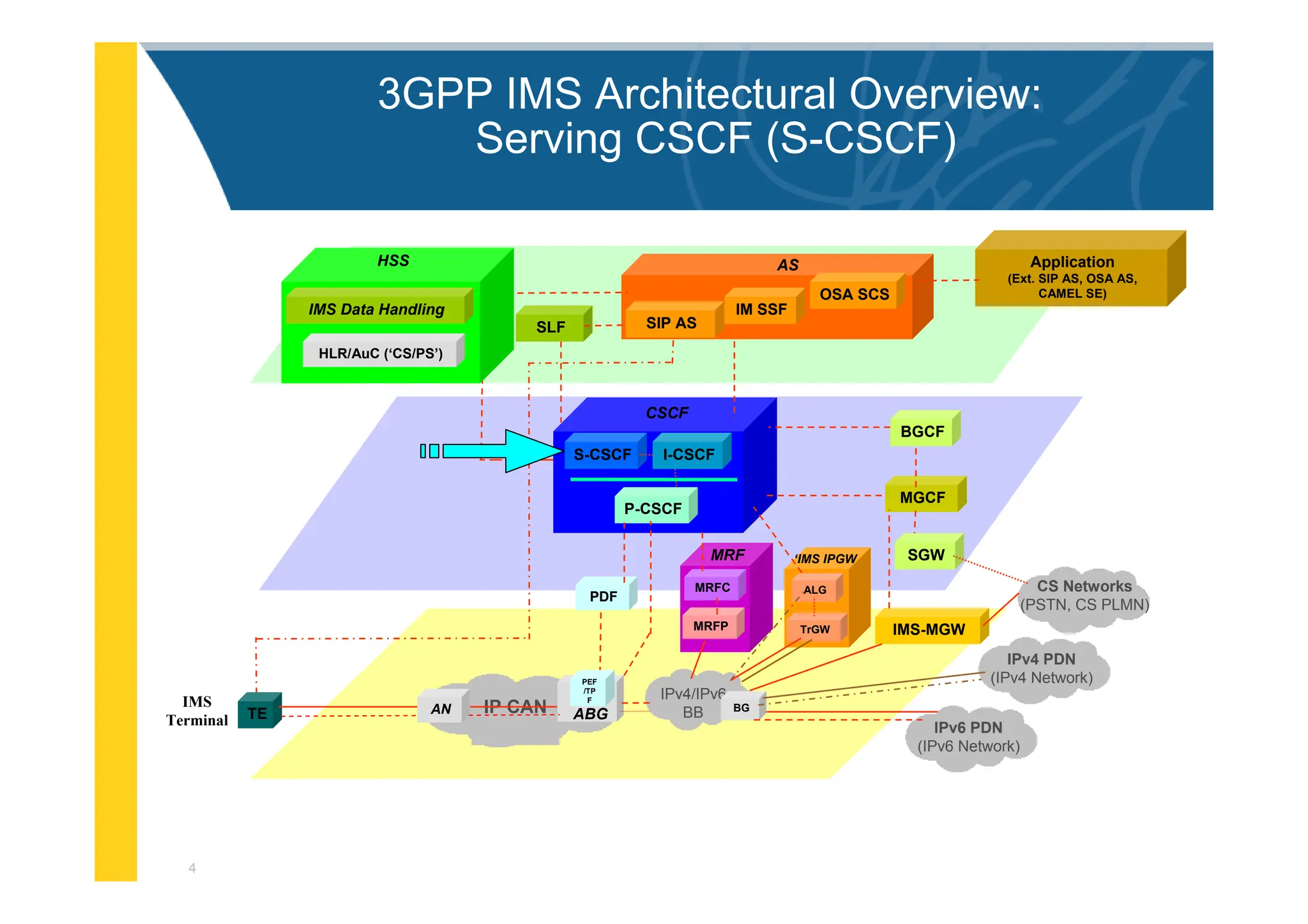
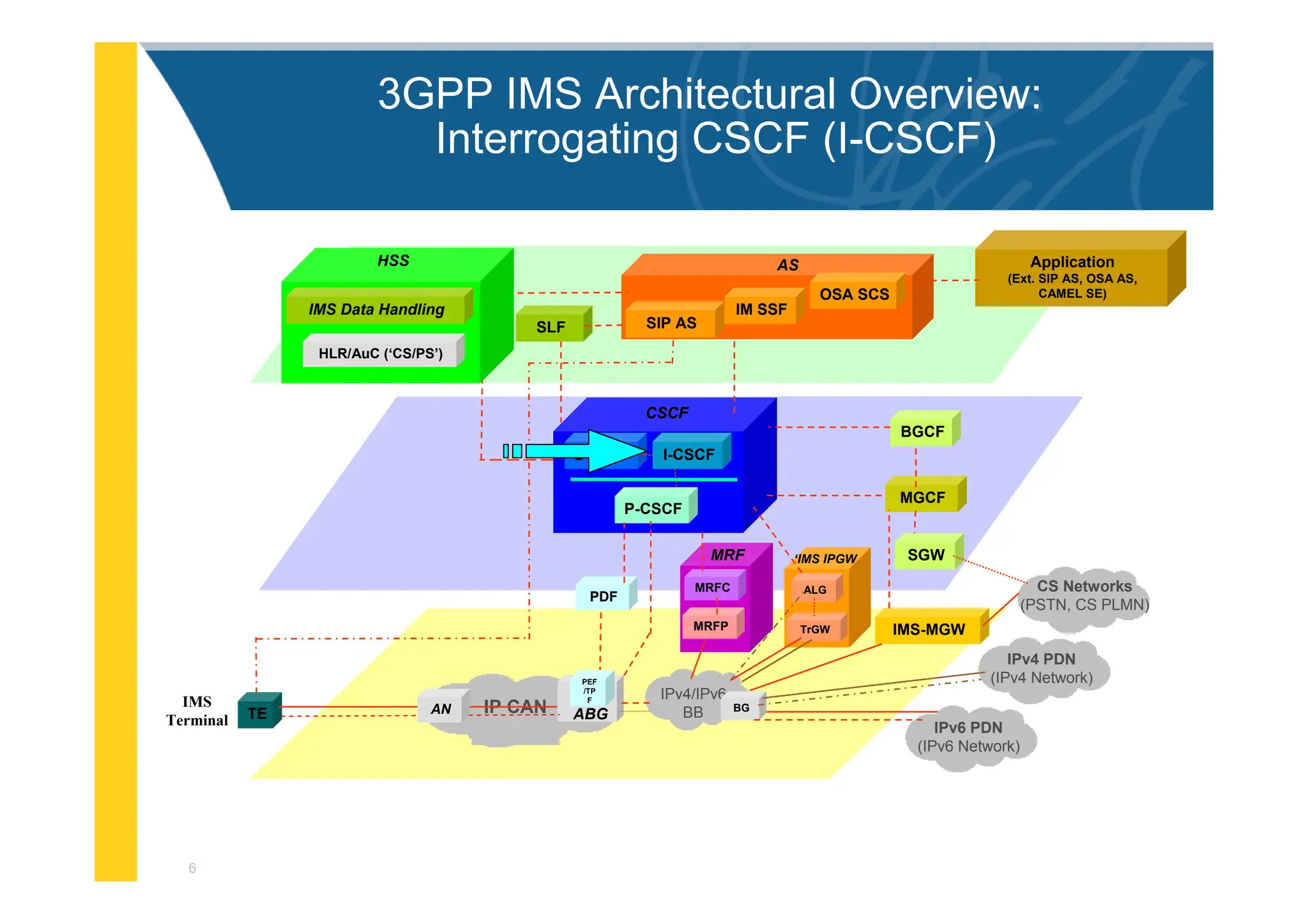
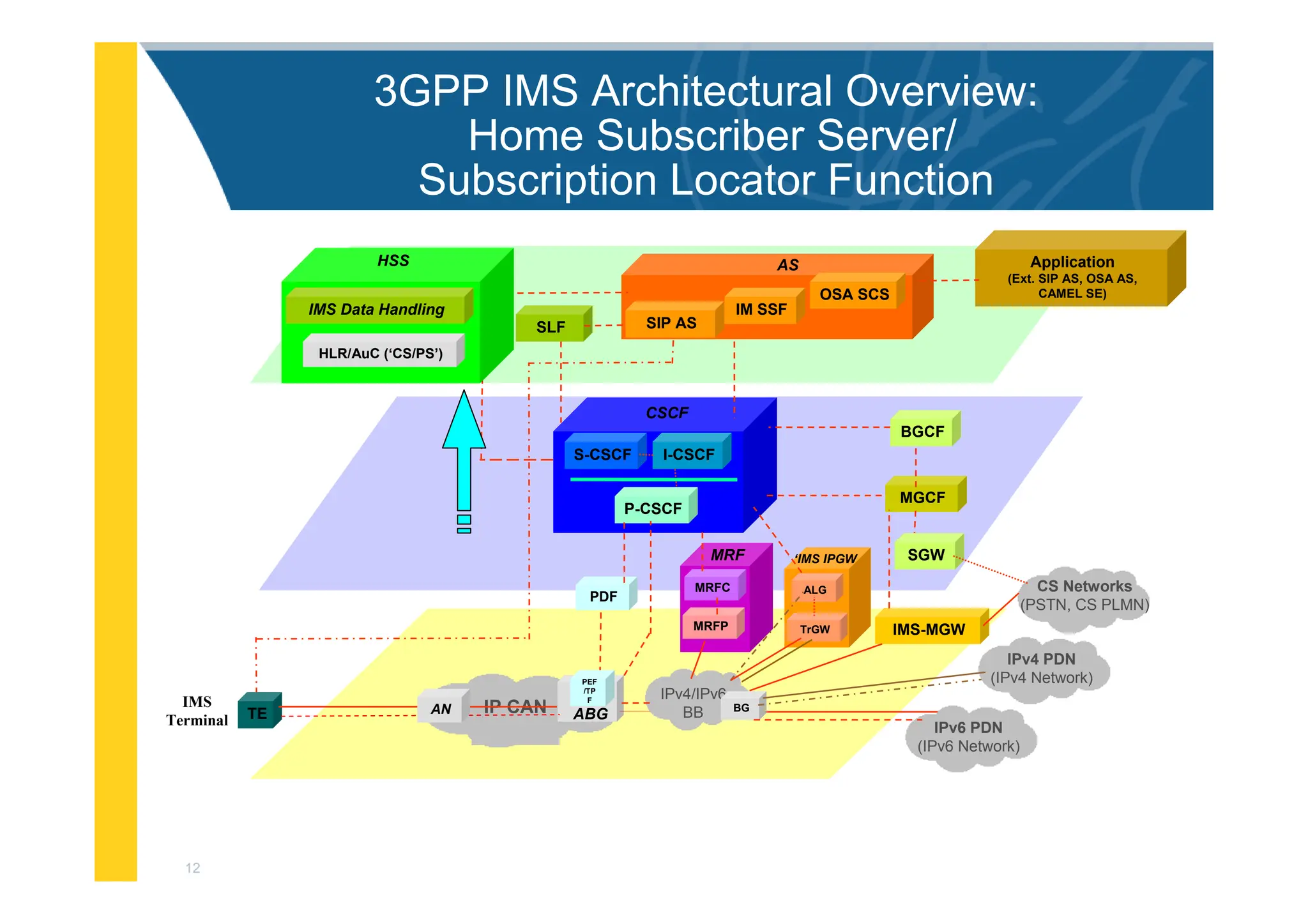
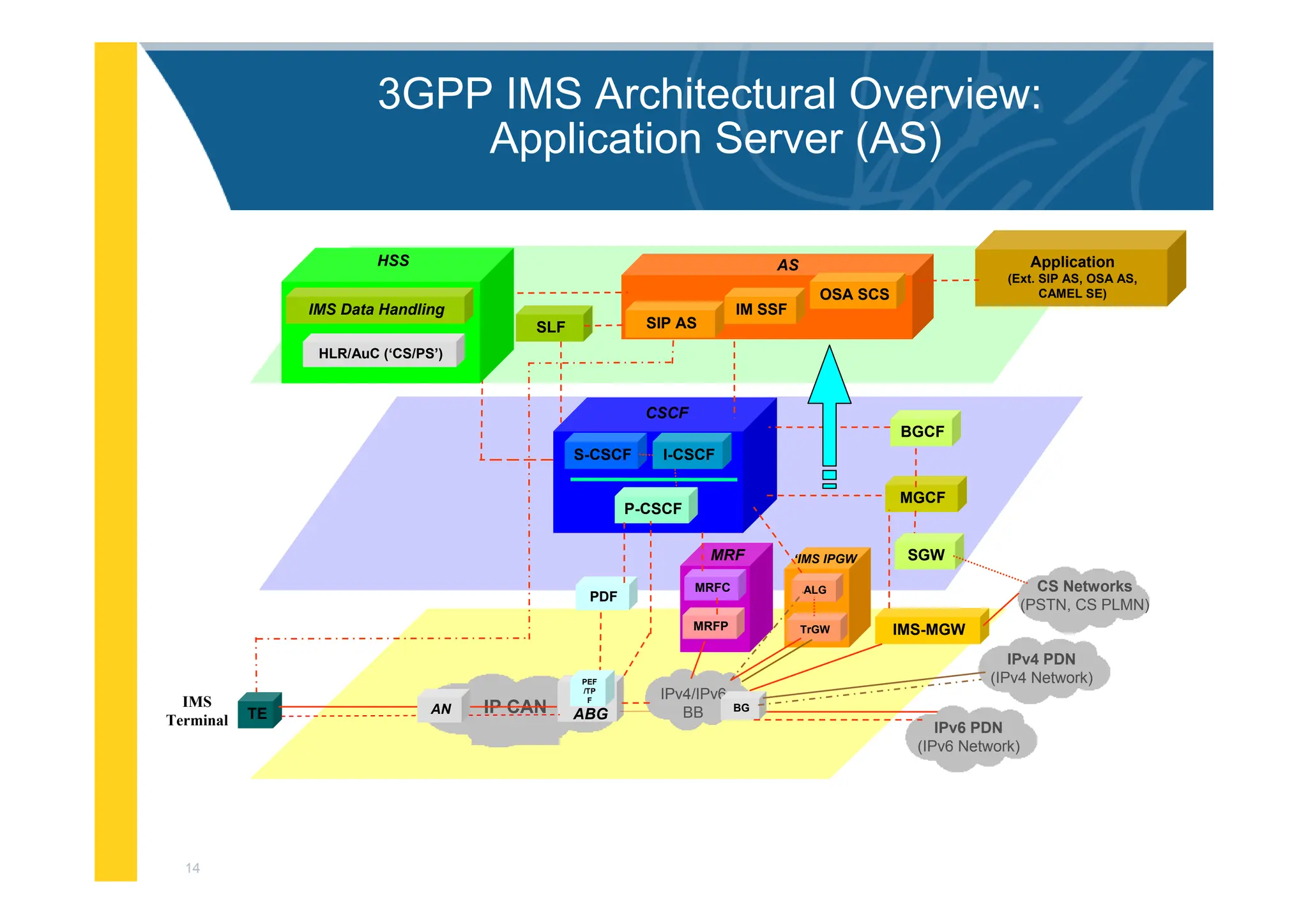
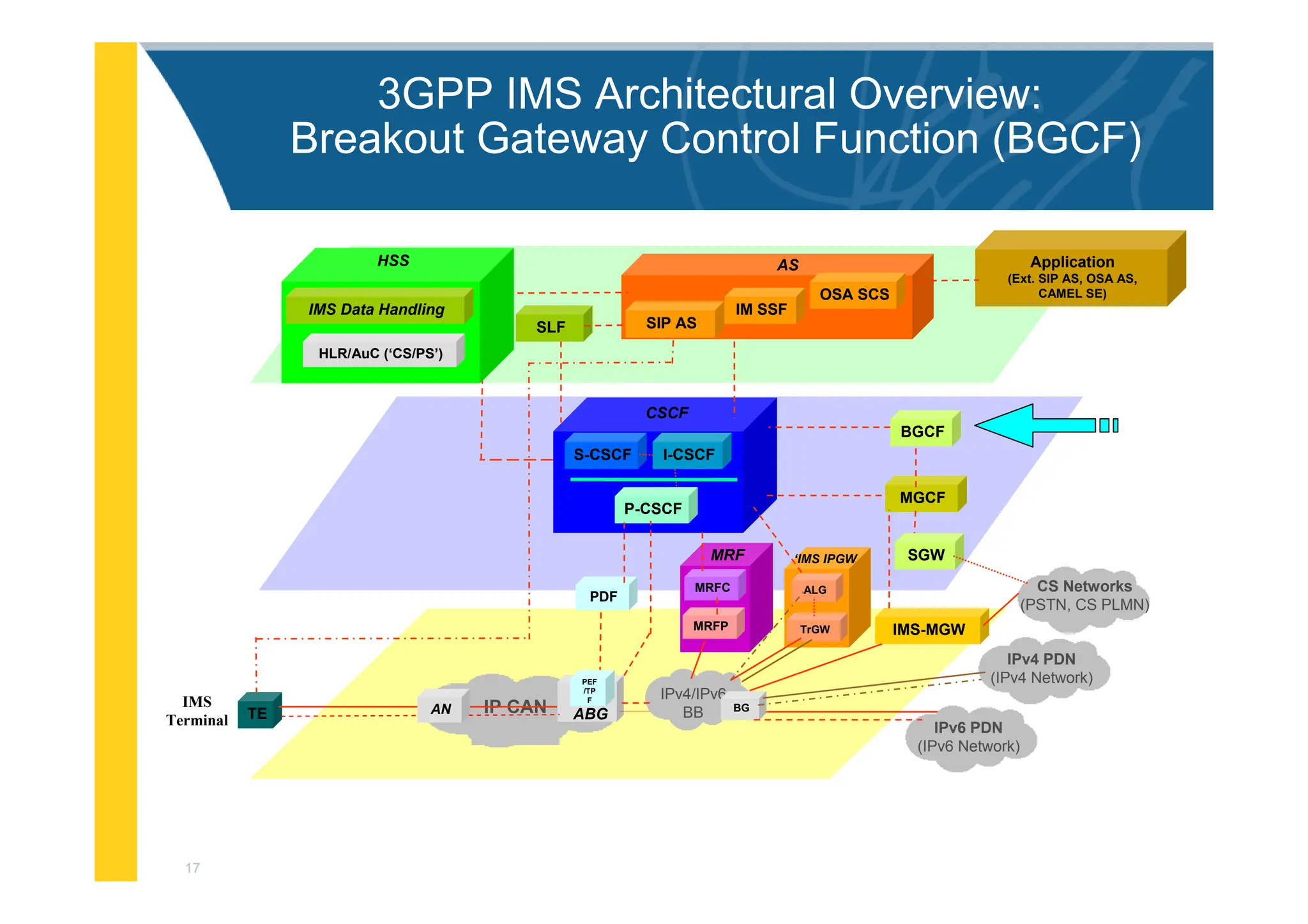
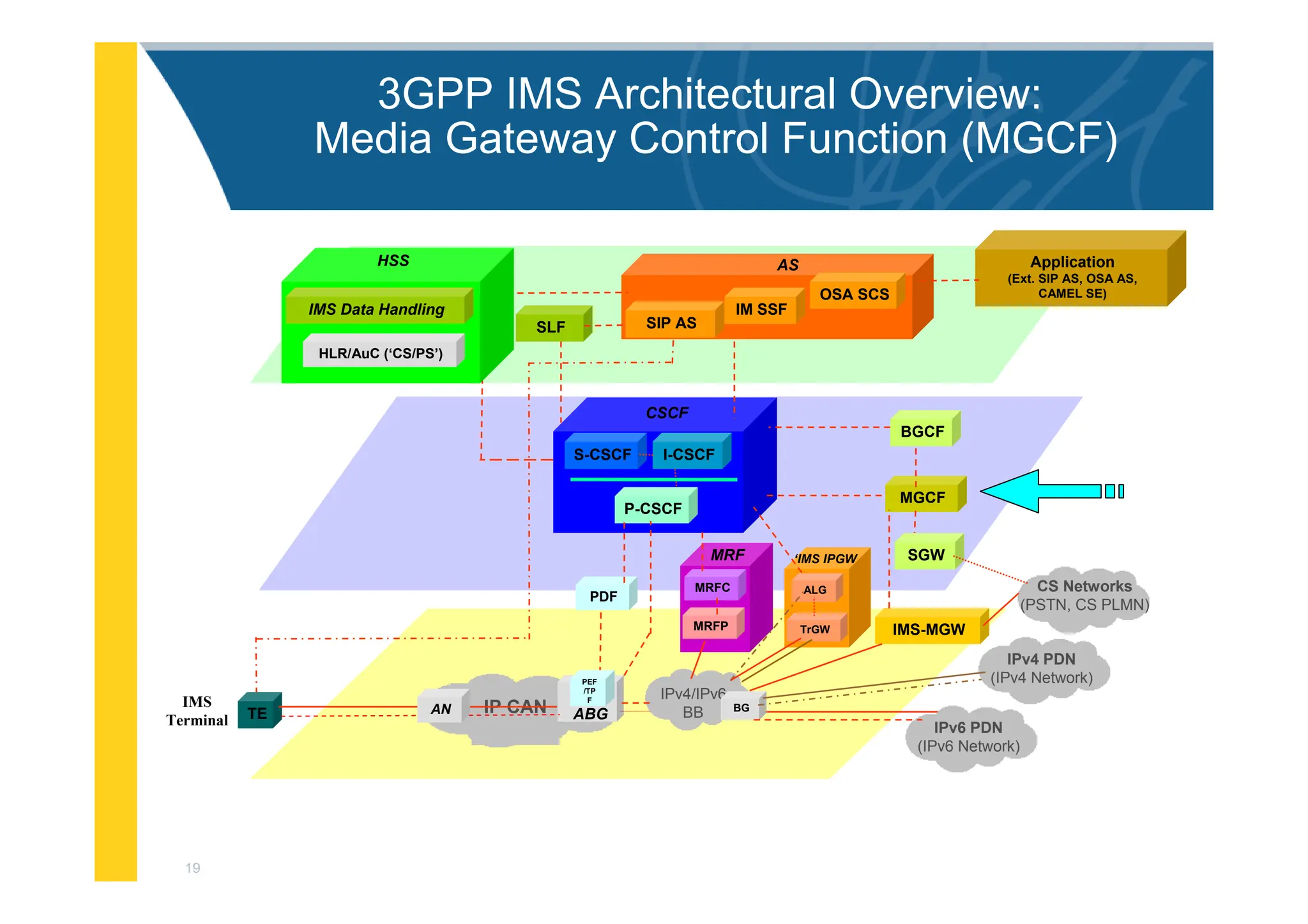
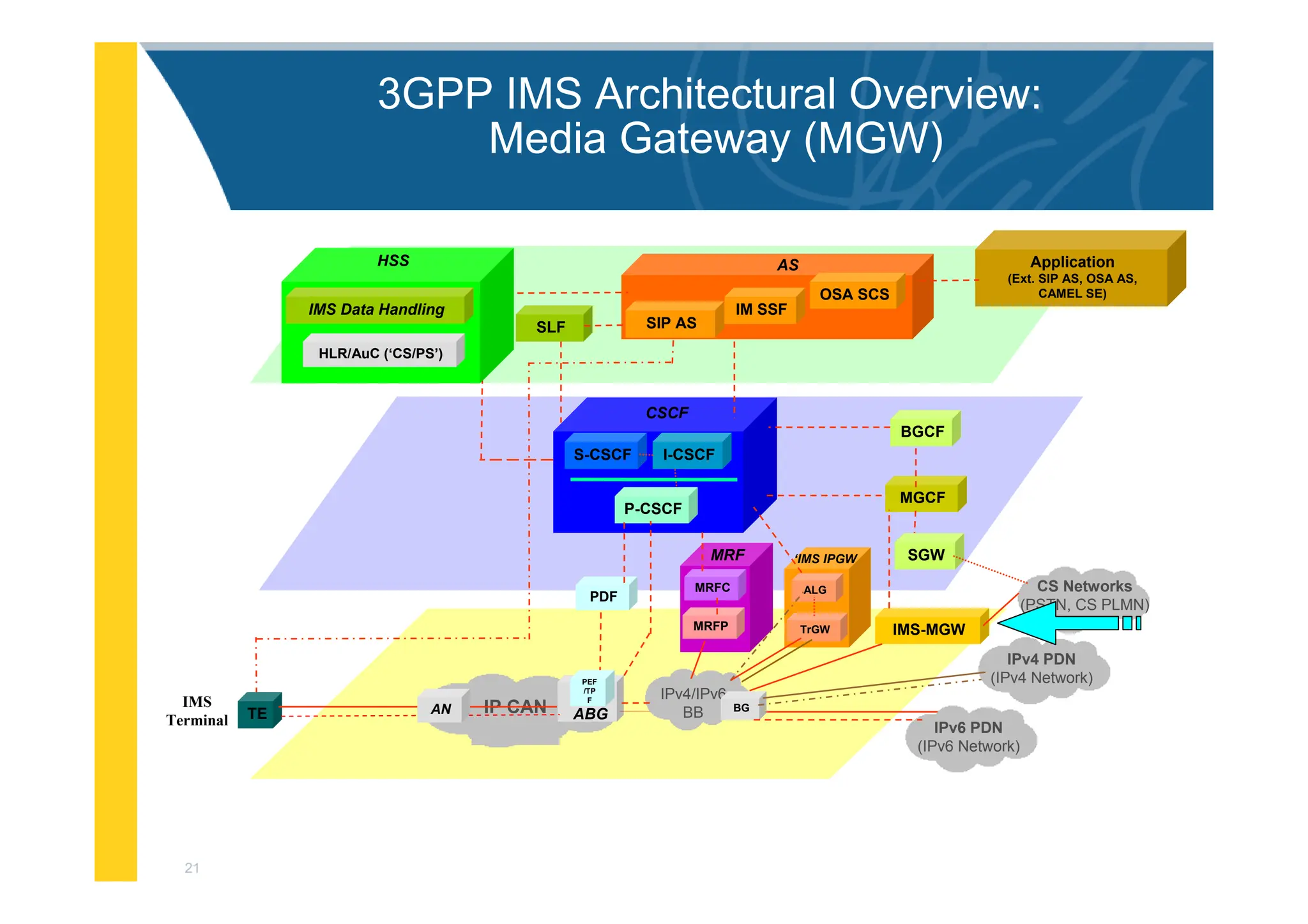
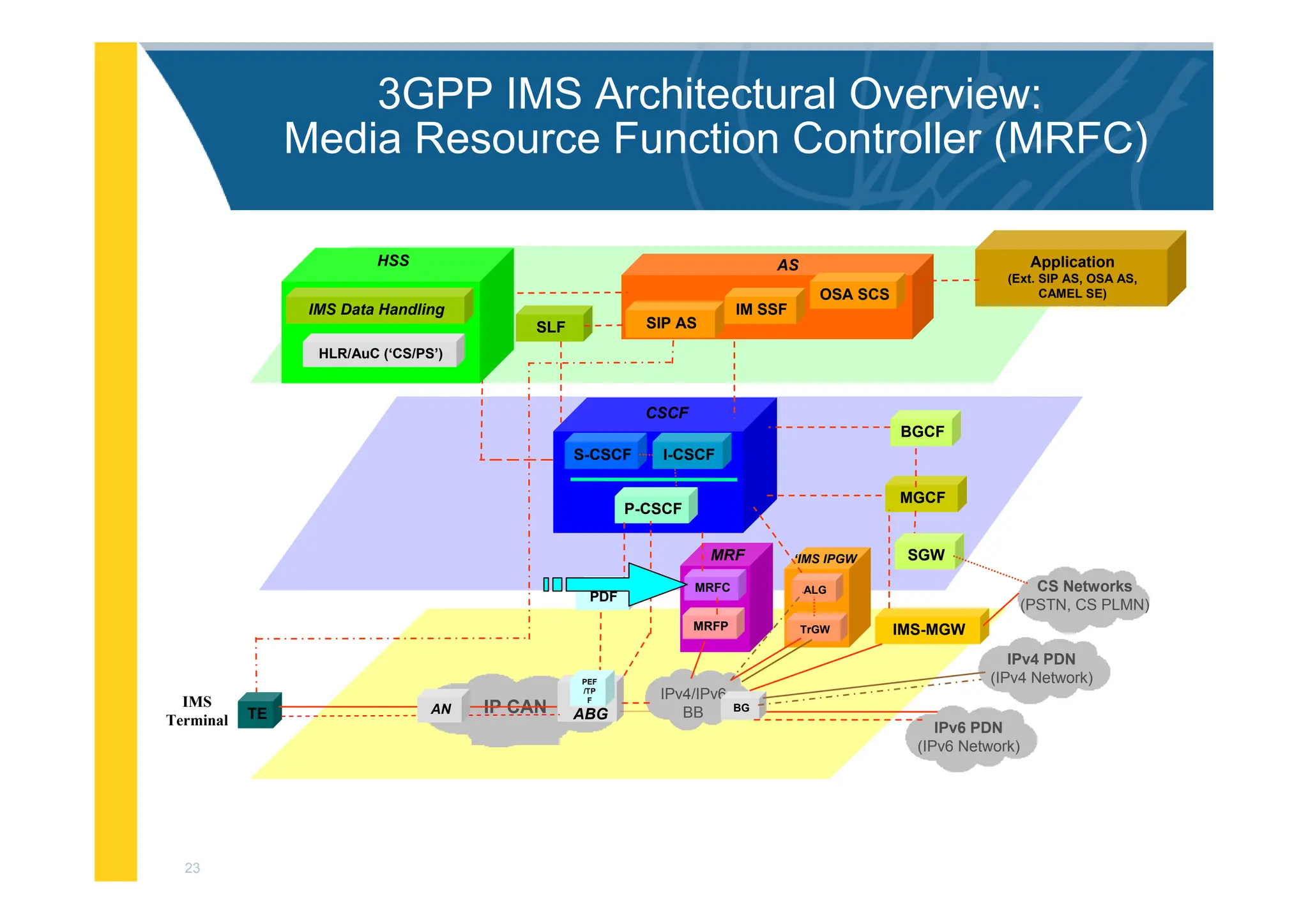
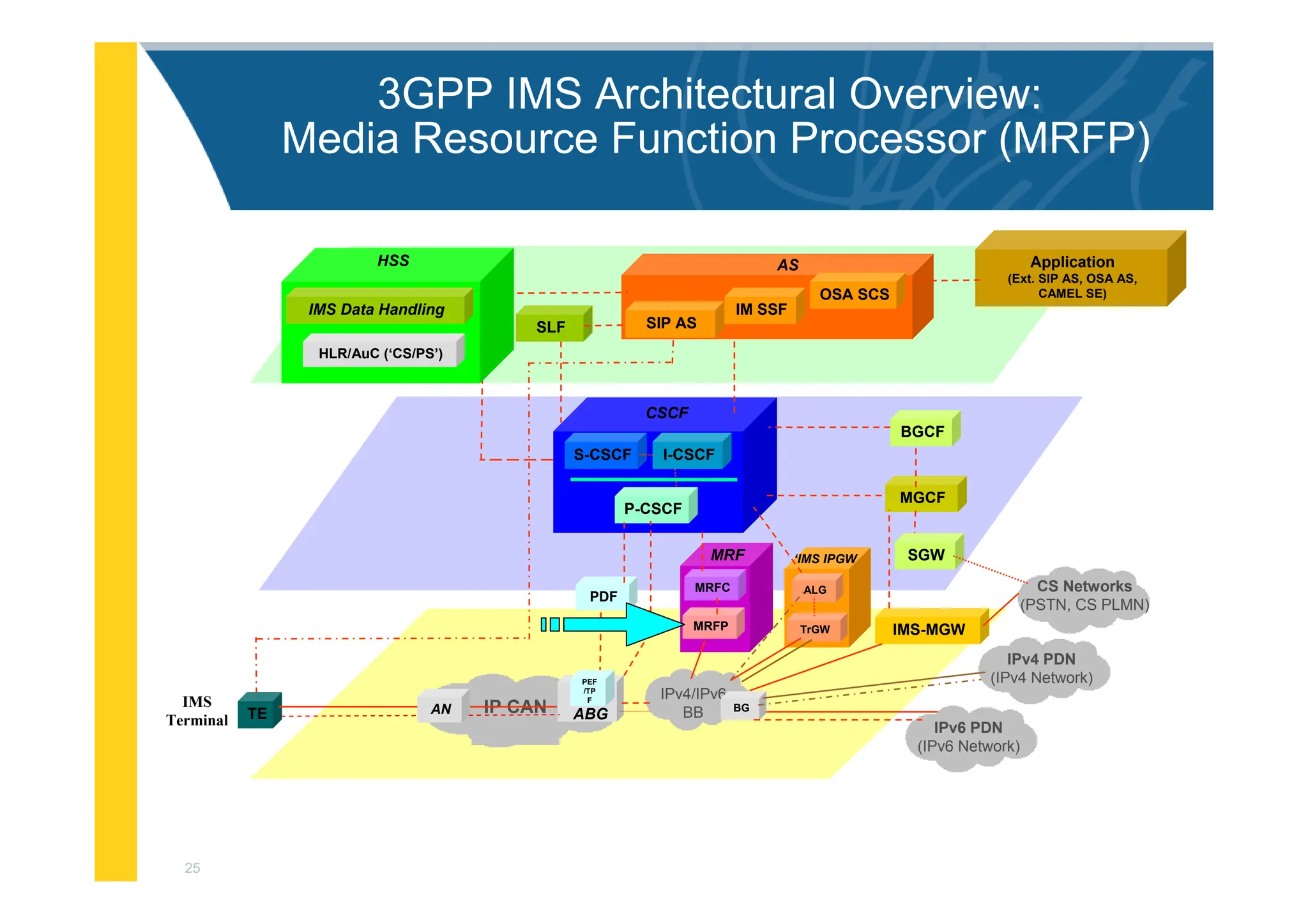
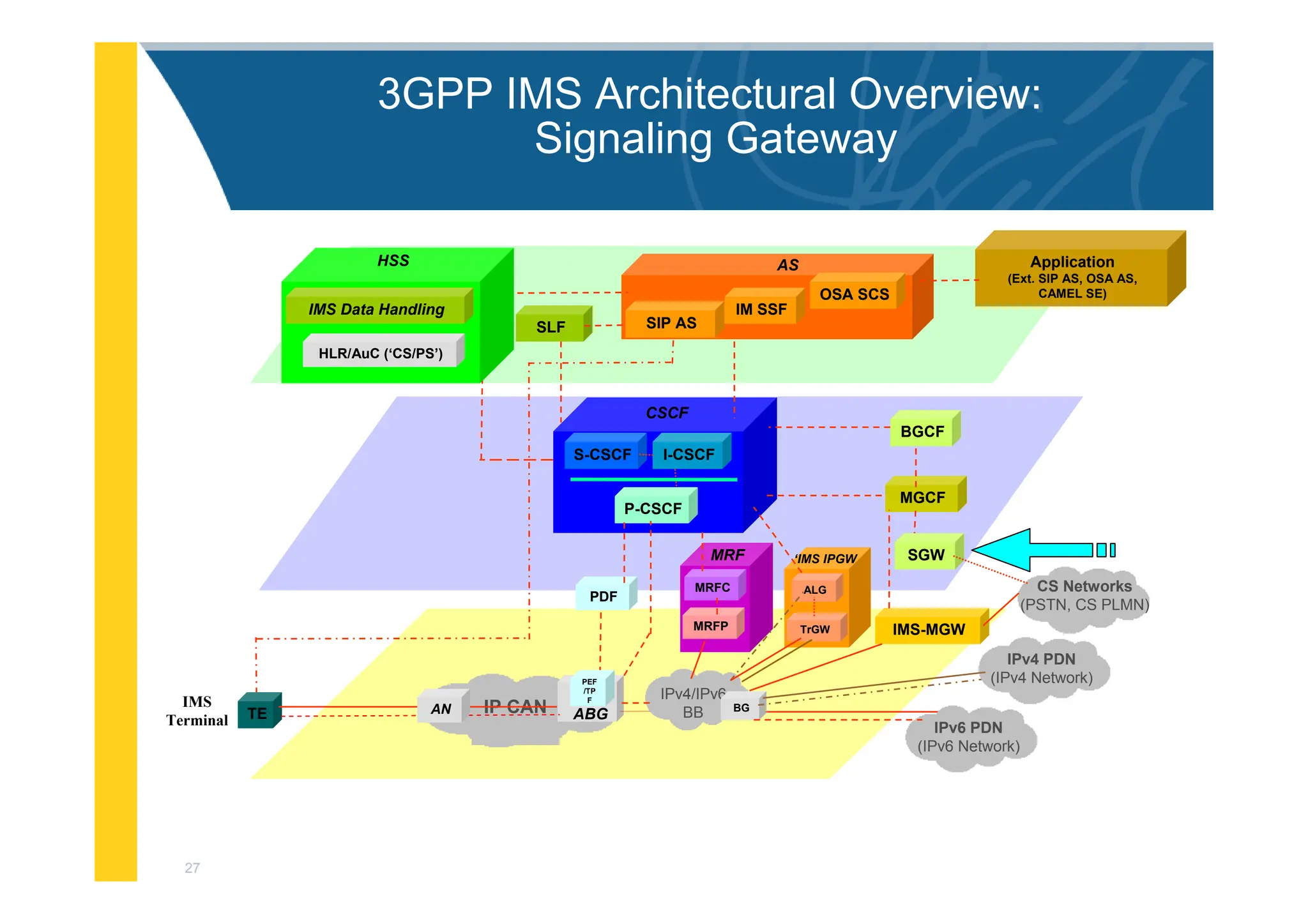
![3
3GPP IMS Architectural Overview
IMS-MGW
IPv6 PDN
(IPv6 Network)
MGCF
PDF
I-CSCF
S-CSCF
BGCF
Application
(Ext. SIP AS, OSA AS,
CAMEL SE)
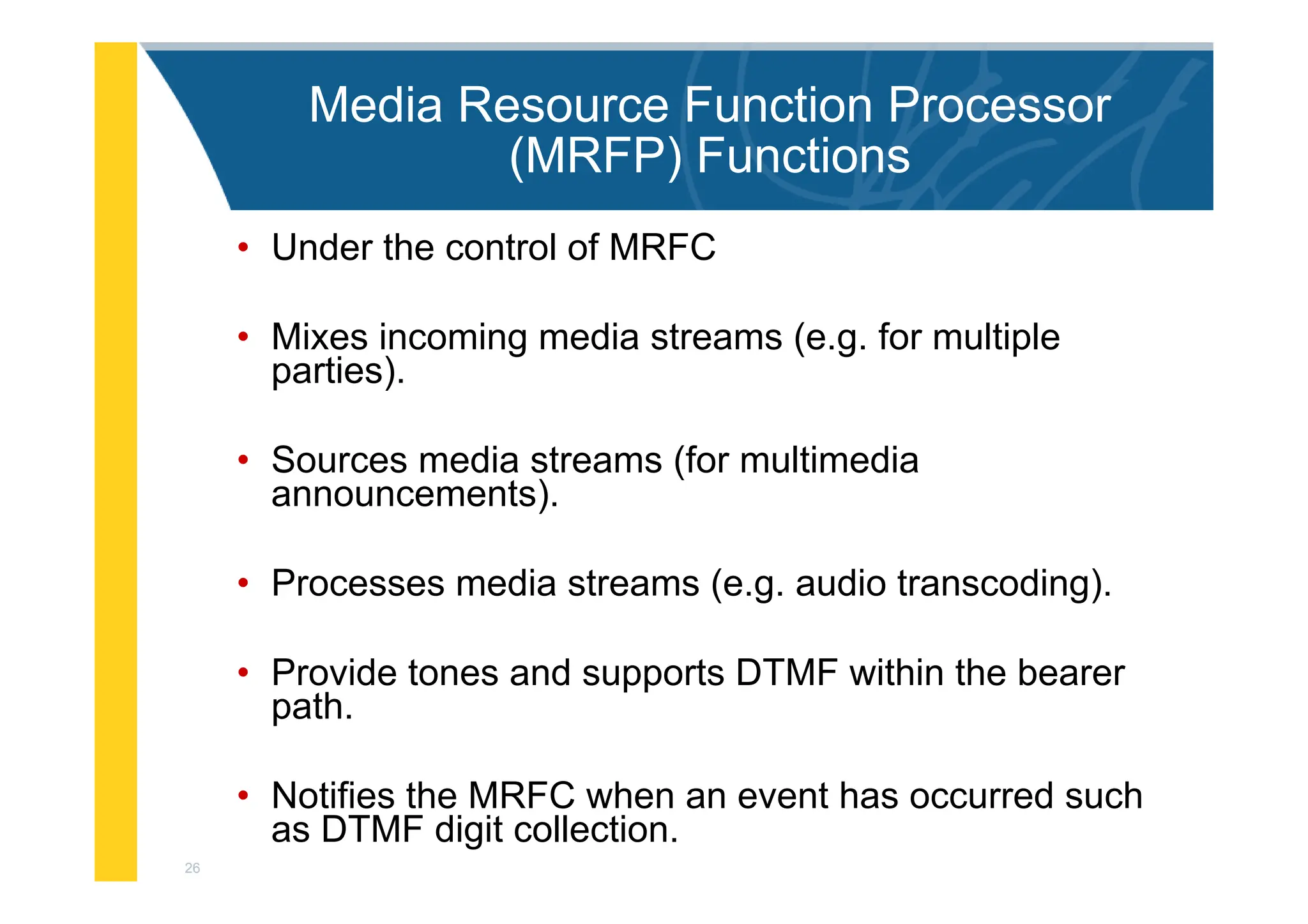
MRFC
MRFP
MRF
IPv4/IPv6
BB
CS Networks
(PSTN, CS PLMN)
CSCF
P-CSCF
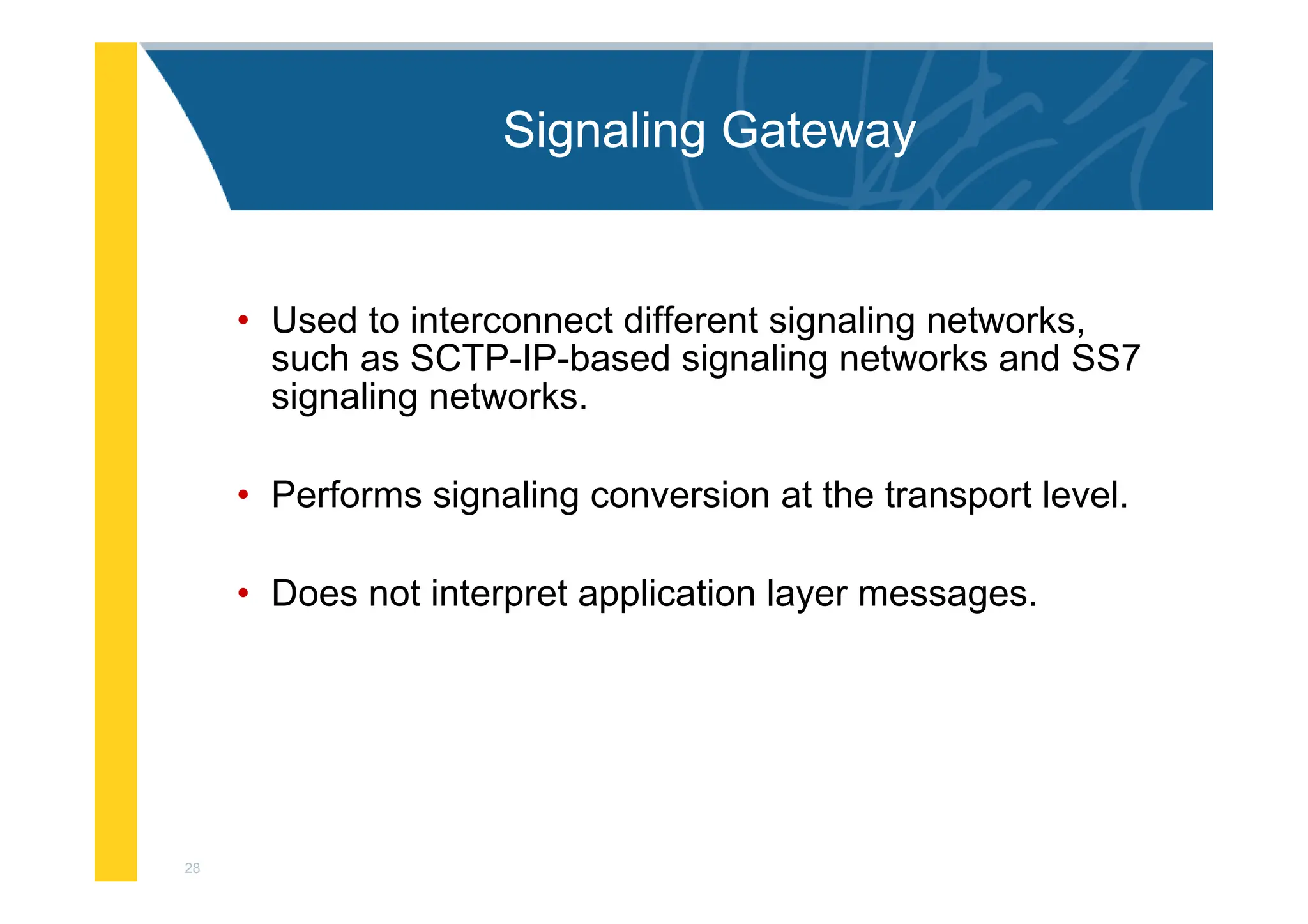
SGW
OSA SCS
IM SSF
SIP AS
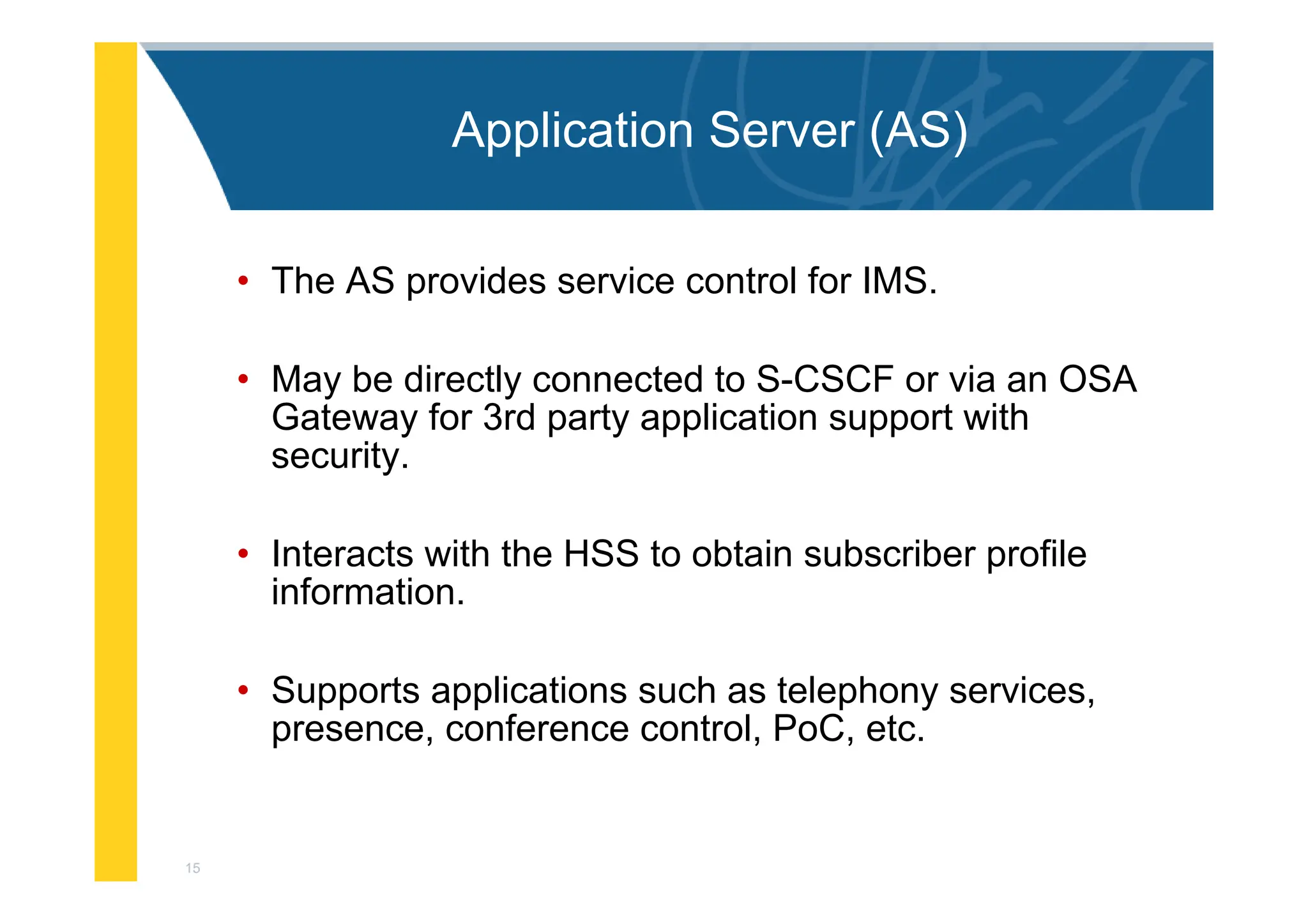
AS
BG
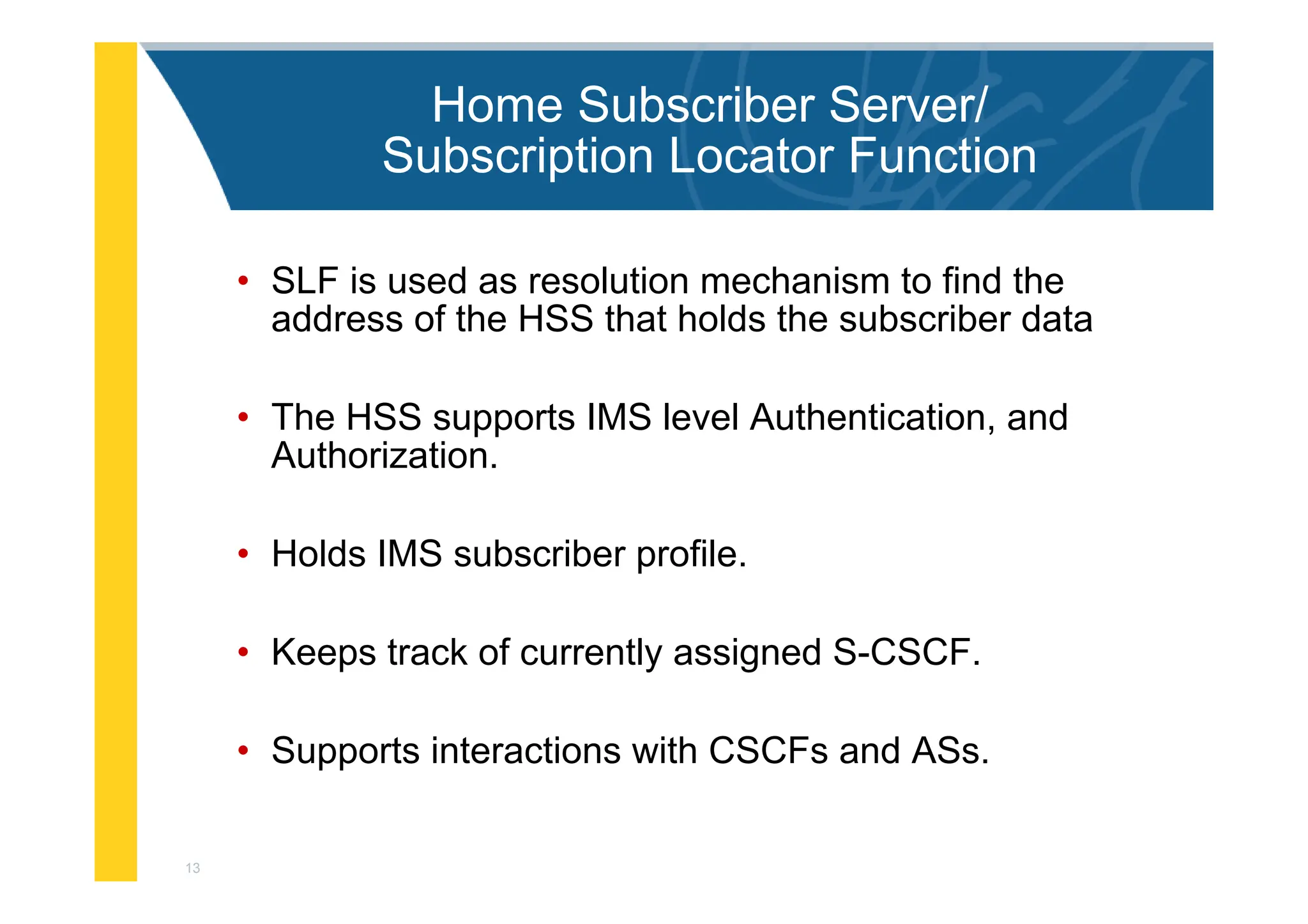
SLF
ALG
TrGW
‘IMS IPGW
IPv4 PDN
(IPv4 Network)
IP CAN ABG
TE AN
IMS
Terminal
PEF
/TP
F
HLR/AuC (‘CS/PS’)
HSS
IMS Data Handling
From [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-3-2048.jpg)


![30
2-phase registration
UE IMS
GPRS
1. Bearer Level Registration: e.g.GPRS Attach
(2. Establishing signaling link e.g. PDP Context Activation)
3. CSCF Discovery
4. Application (IMS) Level Registration
From [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-30-2048.jpg)
![31
SIP Registration of a Mobile Node
From [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-31-2048.jpg)
![32
Simple SIP Call: Caller Side (1)
From [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-32-2048.jpg)
![33
Simple SIP Call: Caller Side (2)
From [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-33-2048.jpg)
![34
References
• [1] “The IMS”
M Poikselka et al. , 2004, John Wiley, ISBN 0-470-87113-X
• [2] “Policy and Regulatory Requirements for Future Mobile
Networks”
F. Courau & M. Olsson, June 22nd 2005,
Alcatel-Ericsson Presentation
• [3] “SIP and Mobility: IP Multimedia Subsystem in 3G Release 5”
Jorg Ott, 11 November 2002, Presentation at Bremen
• [4] “IMS –IP Multimedia Subsystem”
Oct 2004, Ericsson Whitepaper
• [5] “The IP Multimedia Subsystem”
2006, Twister Consulting whitepaper](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdfslide-240510033934-66fd4229/75/pdfslide-net_architectural-overview-of-ip-multimedia-subsystem-3-3gpp-ims-architectural-overview-pdf-34-2048.jpg)
