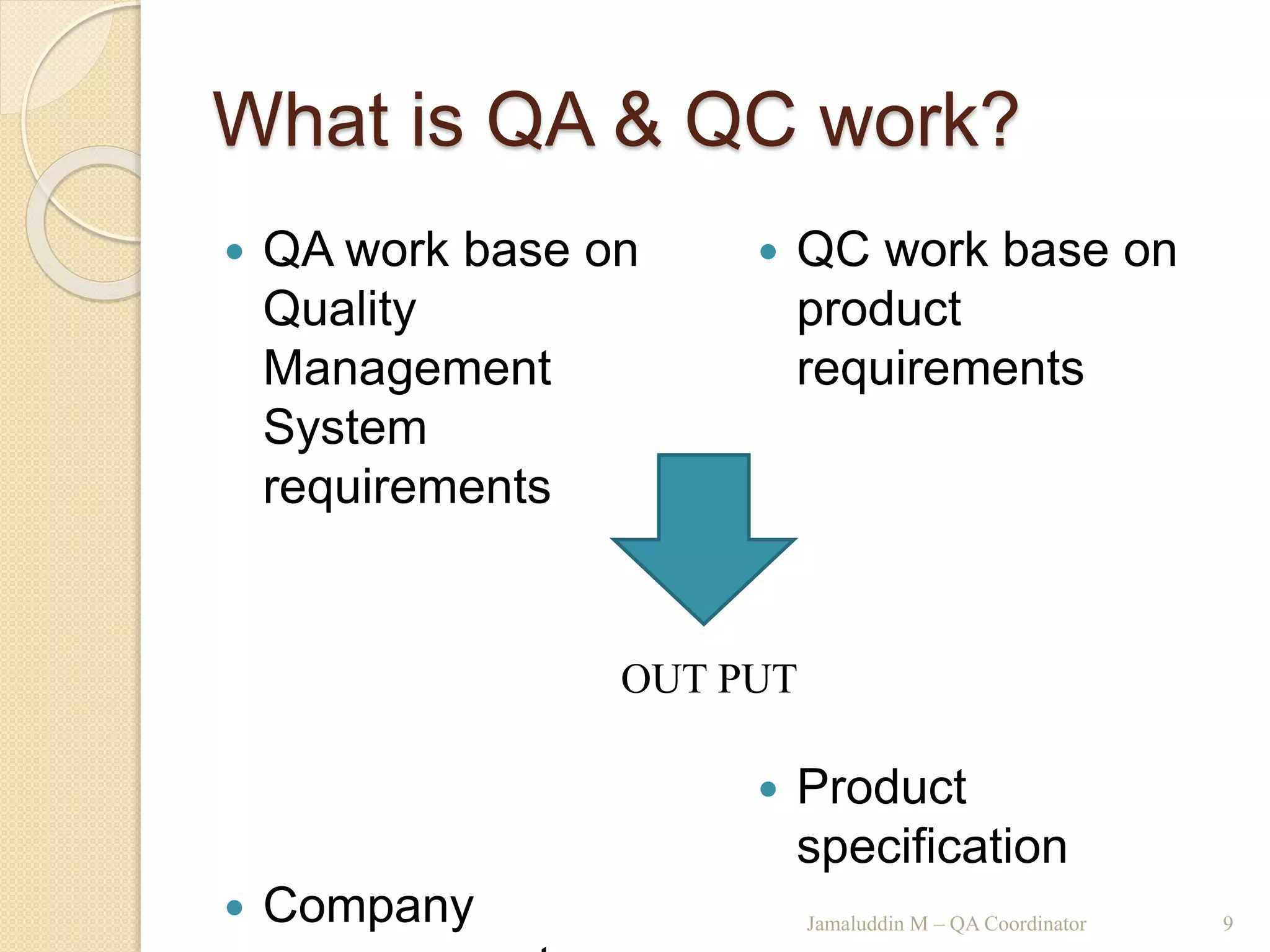
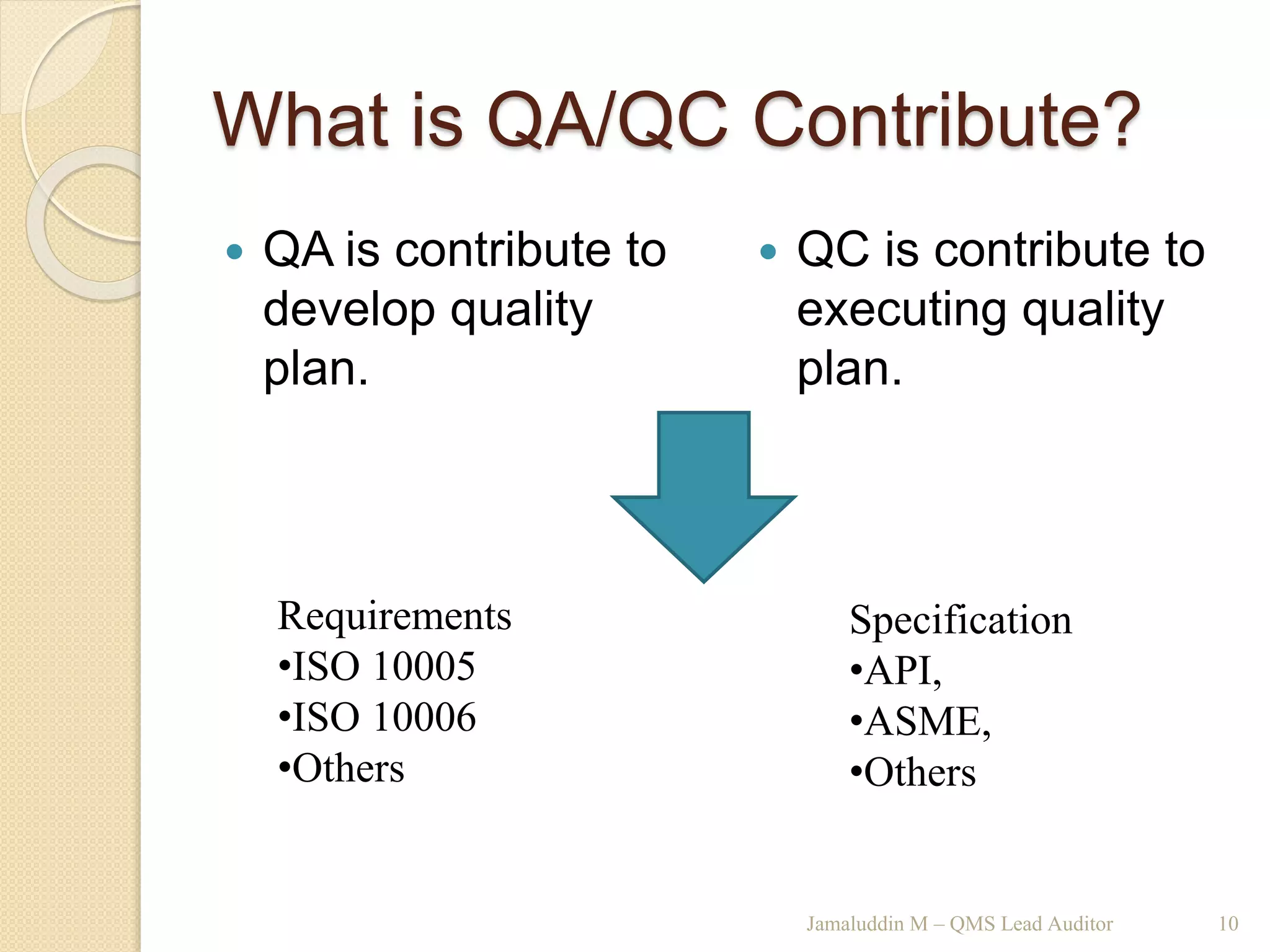
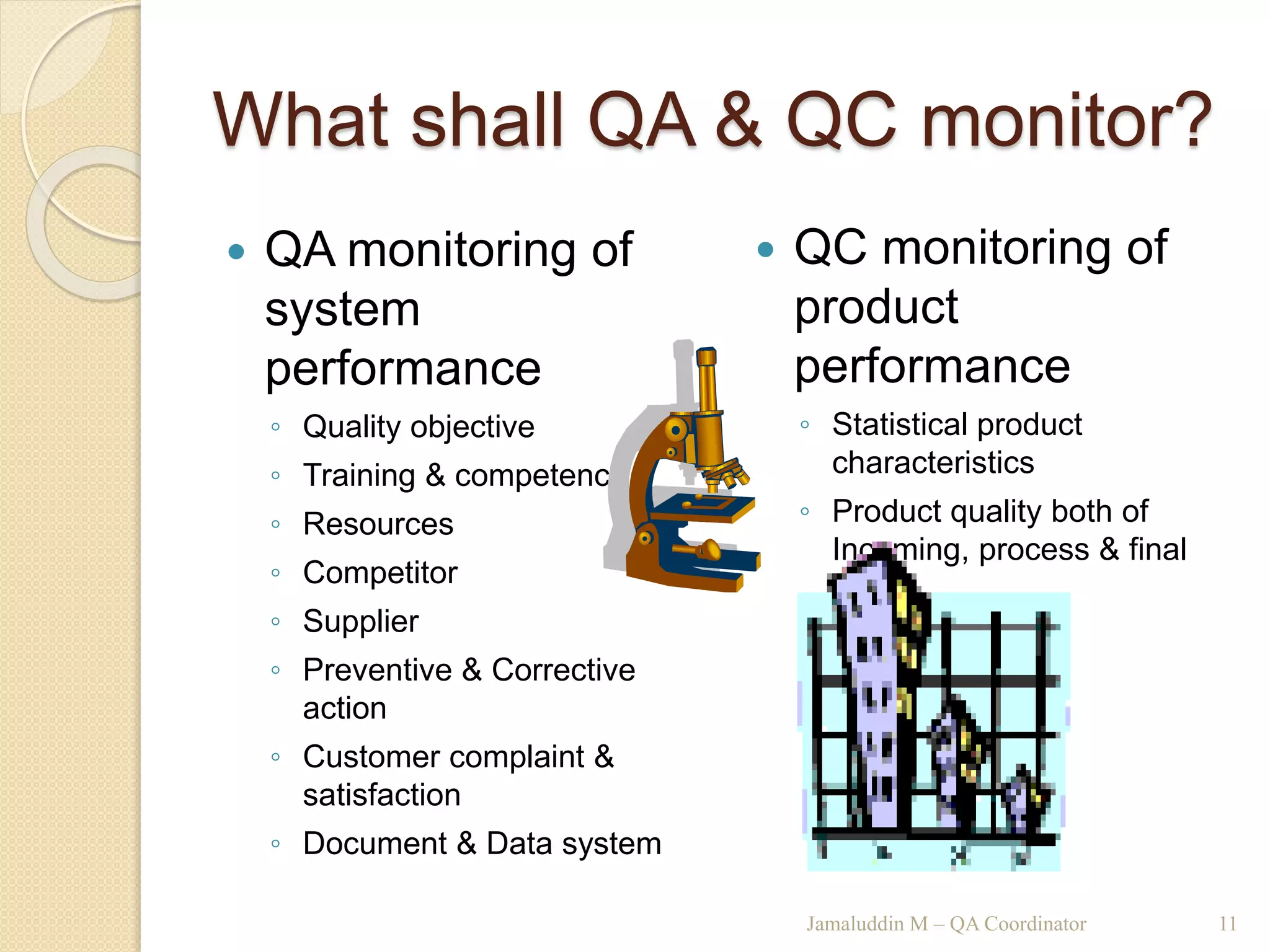
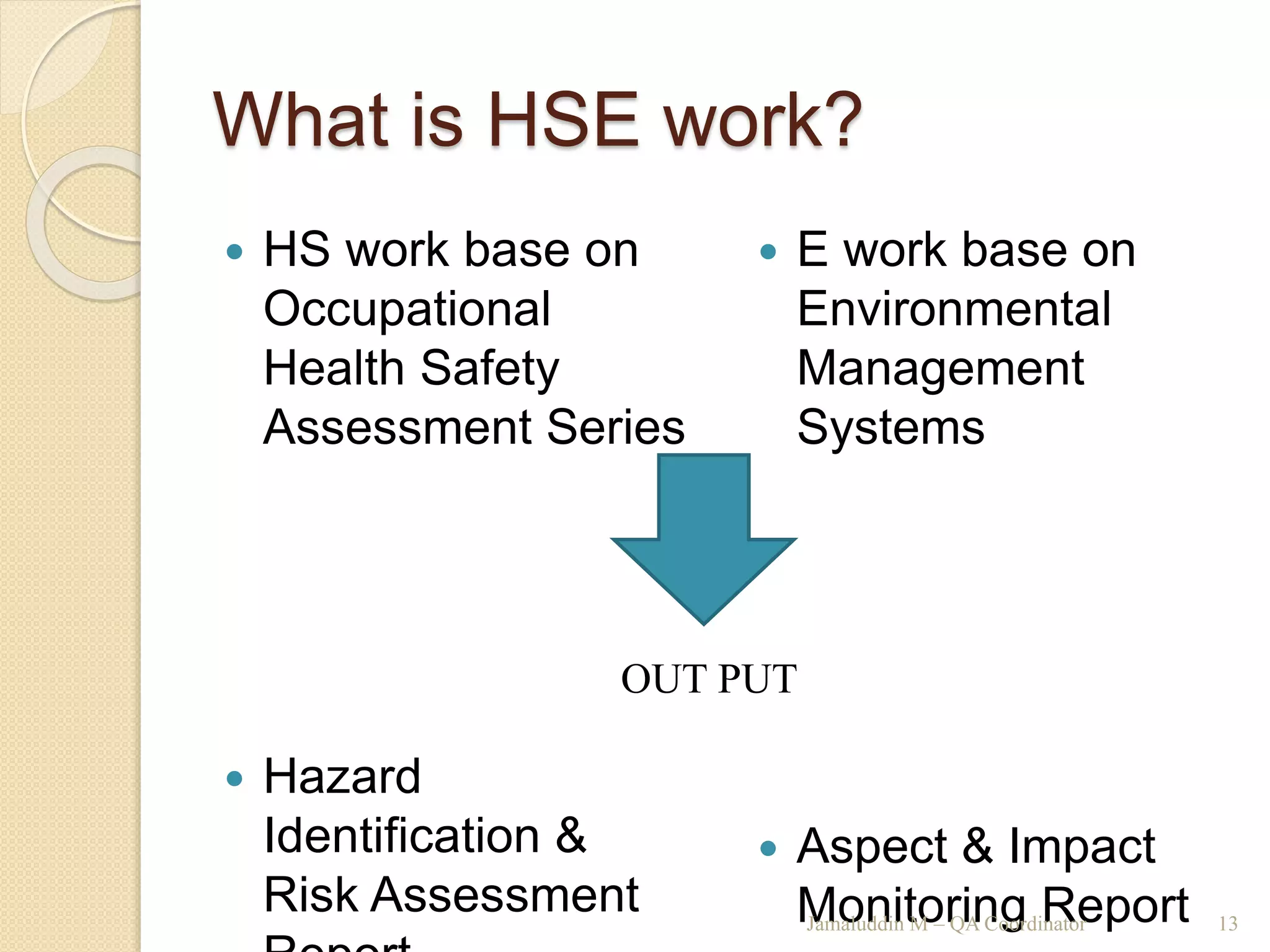
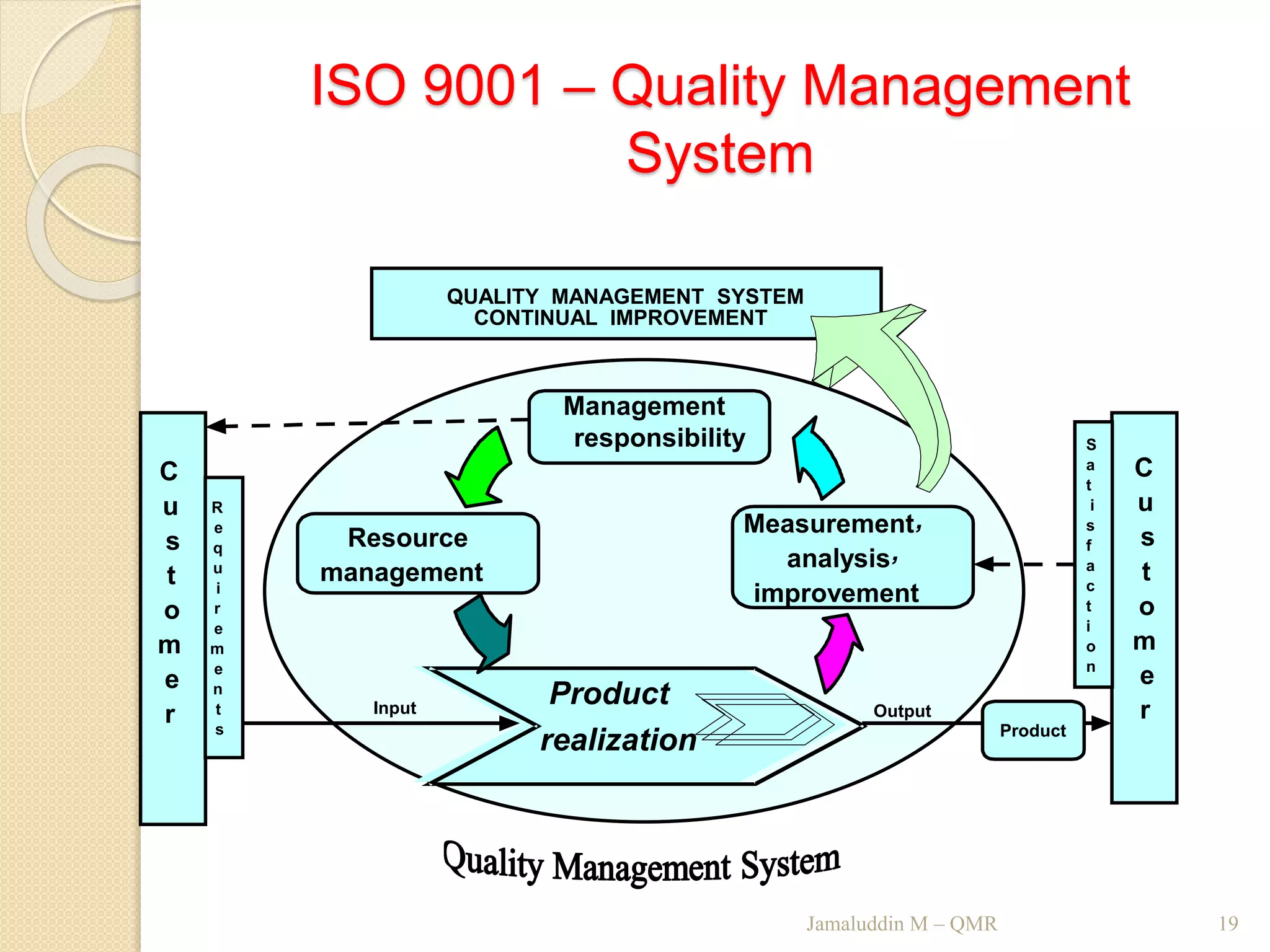
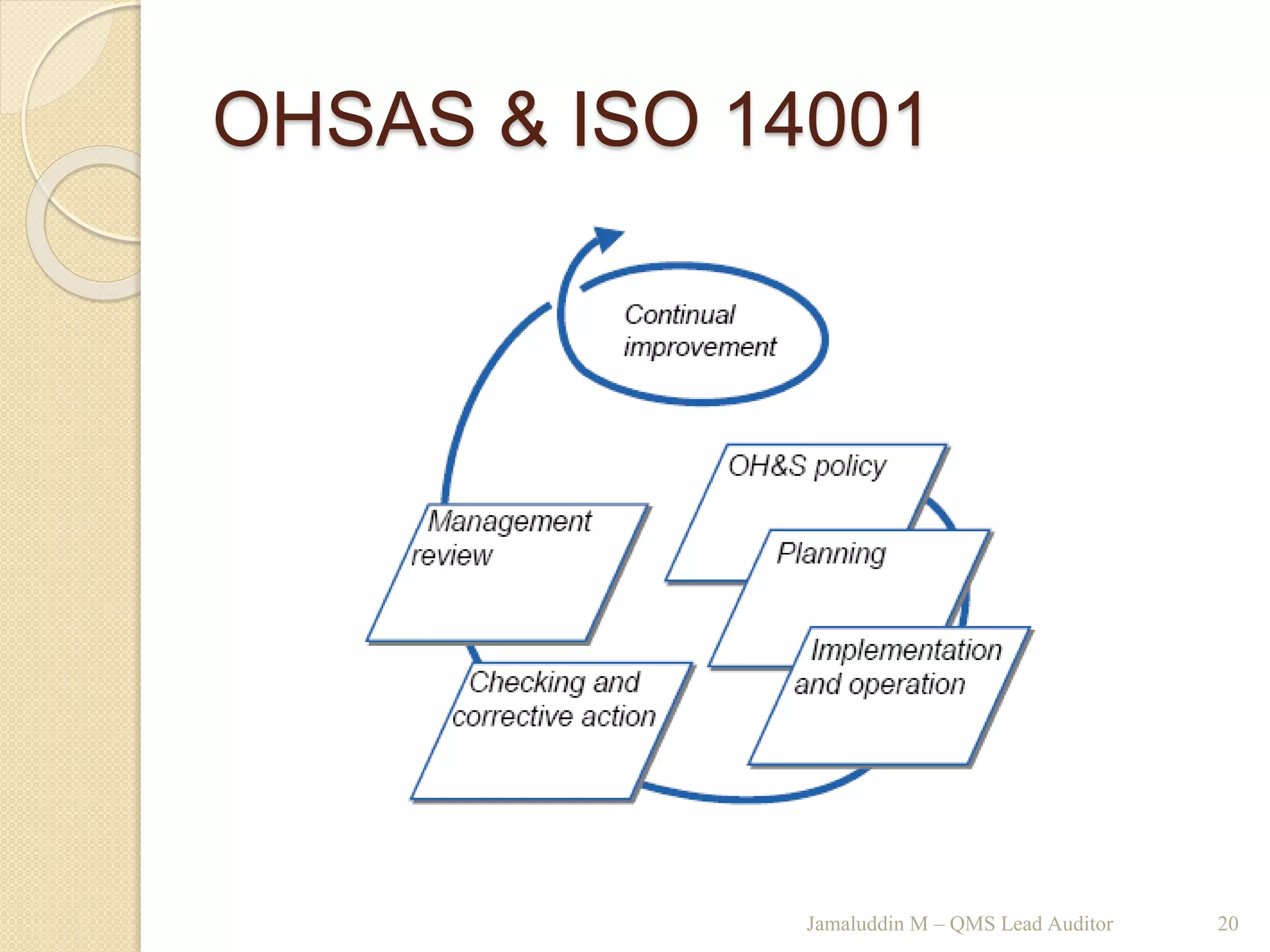
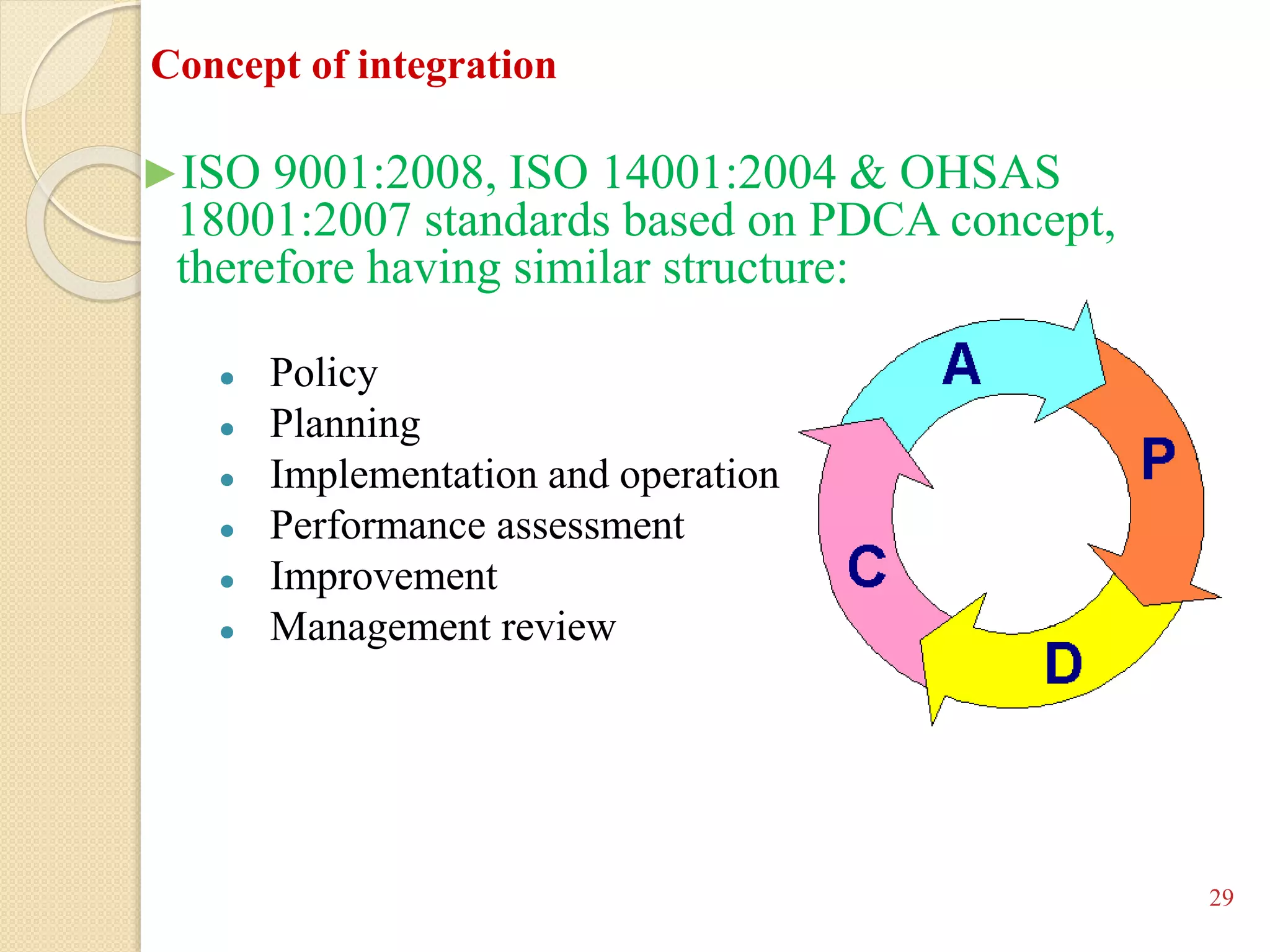
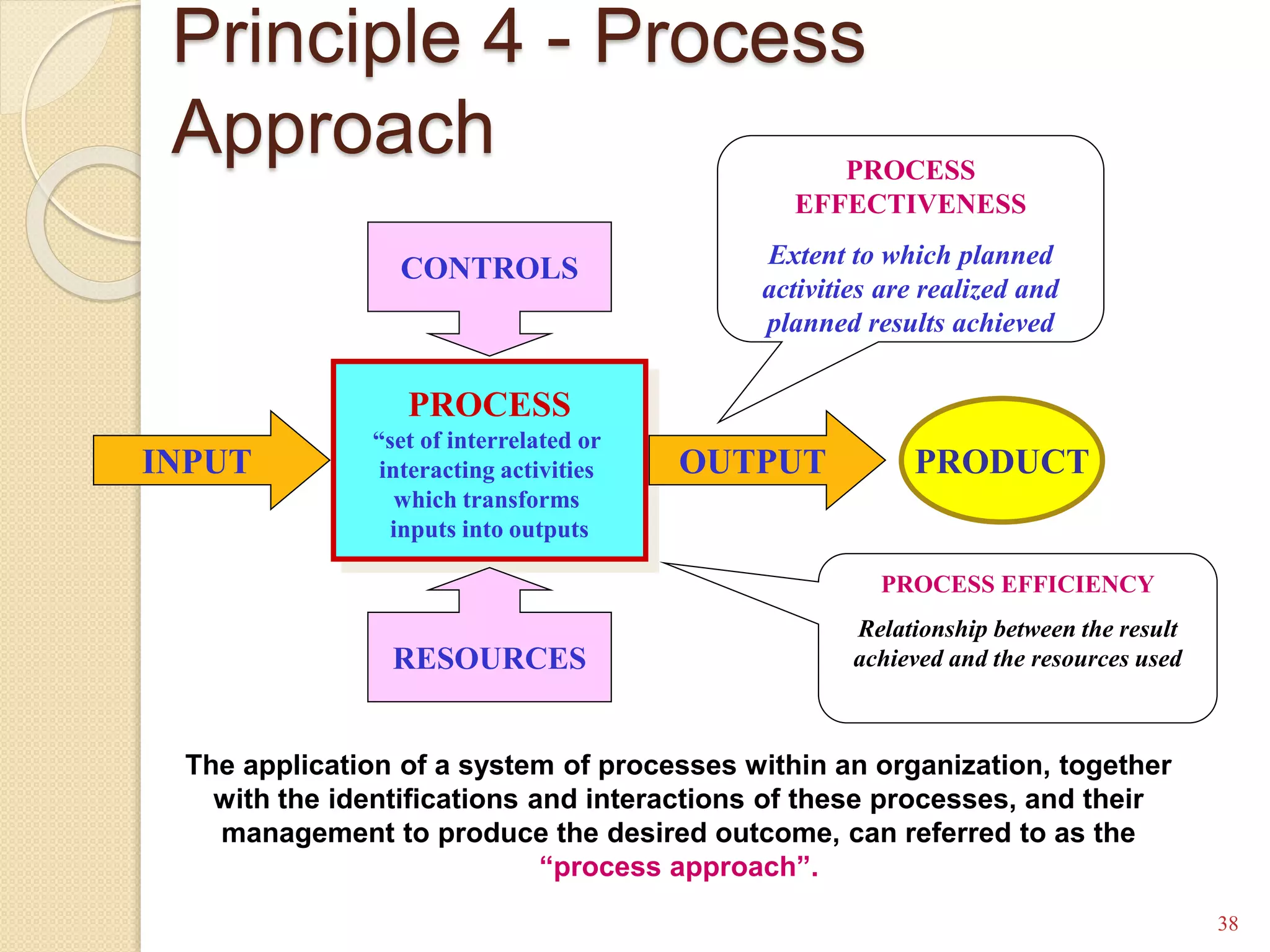
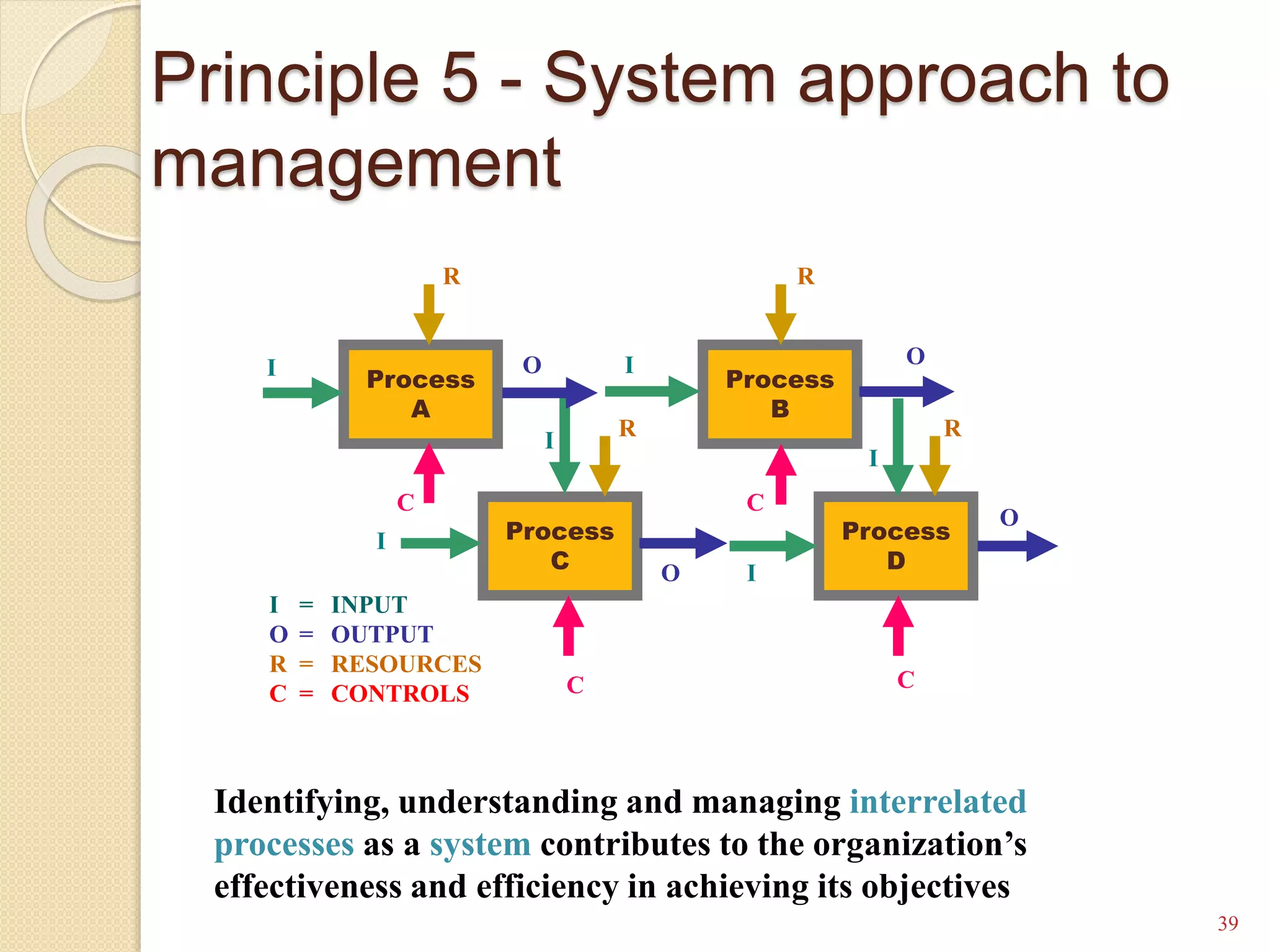
This training document outlines an agenda for a QHSE (Quality Health Safety & Environmental) Awareness Training presented by Jamaluddin Ma’ruf. The one-day training covers topics such as QHSE goals and effects, quality assurance and control, hazard identification, and integrated management systems. It discusses process models for ISO 9001, OHSAS, and ISO 14001 standards. Eight principles of management are also reviewed, including customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, and continual improvement. The training aims to help audiences understand basic concepts of integrated management systems.